How Much Sides Does A Heptagon Have
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
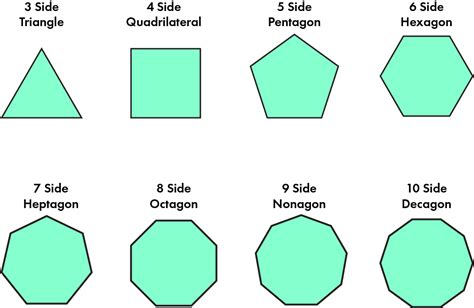
Table of Contents
How Many Sides Does a Heptagon Have? A Deep Dive into Heptagonal Geometry
The question, "How many sides does a heptagon have?" might seem trivially simple at first glance. The answer, of course, is seven. However, delving deeper into the properties of a heptagon reveals a fascinating world of geometry, mathematics, and even applications in various fields. This comprehensive article explores the heptagon in detail, going beyond the simple answer to uncover its unique characteristics and significance.
Understanding Polygons: A Foundation for Heptagons
Before we delve into the specifics of heptagons, let's establish a foundational understanding of polygons. A polygon is a two-dimensional closed shape formed by connecting a number of straight line segments. These segments are called the sides of the polygon, and the points where the sides meet are called vertices or corners. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they possess. Some common examples include:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon: 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
- Nonagon: 9 sides
- Decagon: 10 sides
And so on... The number of sides directly determines the polygon's name and many of its geometric properties.
The Heptagon: A Seven-Sided Polygon
Now, let's focus our attention on the heptagon, a polygon with precisely seven sides and seven angles. Its name is derived from the Greek words "hepta" (meaning seven) and "gonia" (meaning angle). Heptagons can be regular or irregular.
Regular Heptagons: Symmetry and Precision
A regular heptagon is a heptagon where all seven sides are equal in length, and all seven angles are equal in measure. This creates a highly symmetrical shape with rotational symmetry of order 7. This means that the heptagon can be rotated 7 times by 360°/7 (approximately 51.43°) and still look identical. The angles in a regular heptagon each measure (5 × 180°)/7 ≈ 128.57°.
Constructing a Regular Heptagon: Constructing a perfect regular heptagon using only a compass and straightedge is impossible. This is because the angle 360°/7 is not constructible using these tools. However, approximate constructions are possible, employing methods that reach a high degree of accuracy. These methods often involve iterative processes or approximations using trigonometric functions.
Irregular Heptagons: Variations in Sides and Angles
Irregular heptagons, on the other hand, have sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. There is a vast array of possible irregular heptagons, each with its unique characteristics. The lack of symmetry makes analyzing their properties more complex than with regular heptagons.
Mathematical Properties of Heptagons
The mathematical properties of heptagons, particularly regular heptagons, are rich and fascinating. Some key properties include:
- Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of any heptagon is (7-2) × 180° = 900°. In a regular heptagon, each interior angle is 900°/7 ≈ 128.57°.
- Exterior Angles: The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, including a heptagon, is always 360°. In a regular heptagon, each exterior angle measures 360°/7 ≈ 51.43°.
- Area Calculation: The area of a regular heptagon can be calculated using various formulas, often involving the length of its side and the apothem (the distance from the center to the midpoint of a side). Complex formulas are required for irregular heptagons, involving the coordinates of their vertices.
- Diagonals: A heptagon has a number of diagonals connecting non-adjacent vertices. The formula to calculate the number of diagonals in any polygon with n sides is n(n-3)/2. For a heptagon (n=7), this gives 14 diagonals.
Heptagons in the Real World: Applications and Examples
While less common than triangles, squares, or hexagons, heptagons appear in various contexts in the real world, though often in slightly imperfect forms. Examples include:
- Architecture and Design: Although not as prevalent as other polygons, some buildings and structures incorporate heptagonal elements in their design, often for aesthetic purposes or to achieve specific spatial arrangements.
- Nature: While not as frequent as other shapes in natural phenomena, certain crystal structures or naturally occurring formations can exhibit approximate heptagonal symmetry.
- Tessellations: Heptagons cannot tessellate on their own to cover a plane without gaps or overlaps, unlike triangles, squares, or hexagons. However, combinations of heptagons with other polygons can create interesting tessellations.
- Games and Puzzles: Heptagons can appear in various games and puzzles, sometimes as part of more complex geometric designs or as individual puzzle pieces.
The Mathematical Intricacies of Heptagonal Constructions
The impossibility of constructing a perfect regular heptagon using only a compass and straightedge stems from the fact that the angle 360°/7 is not a constructible angle. Constructible angles are those whose cosine or sine can be expressed using only square roots and rational numbers. This limitation has significant implications in geometry and related fields. The search for methods to approximate heptagonal constructions has led to the development of sophisticated geometric techniques and algorithms.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
The study of heptagons opens doors to more complex mathematical concepts:
- Trigonometry and Heptagonal Functions: Specialized trigonometric functions can be defined for heptagons, relating to their angles and side lengths. These functions play a role in more advanced geometric calculations involving heptagons.
- Group Theory and Symmetry: The symmetries of regular heptagons are explored using group theory, providing a powerful mathematical framework to understand their rotational and reflective symmetries.
- Computational Geometry: Algorithms in computational geometry are used for efficient calculation of areas, intersections, and other properties of both regular and irregular heptagons.
Conclusion: The Significance of the Seven-Sided Shape
While the simple answer to "How many sides does a heptagon have?" is seven, this article has demonstrated the far-reaching significance of this seemingly straightforward polygon. From its underlying mathematical properties to its surprising appearances in the real world, the heptagon offers a fascinating glimpse into the beauty and complexity of geometry. Its inherent constructibility challenges have spurred mathematical advancements, and its diverse applications demonstrate the versatility of this often overlooked seven-sided shape. Further exploration into heptagonal geometry promises to uncover even more intriguing aspects of this unique polygon.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 6 7 As A Percent
Mar 25, 2025
-
How To Prove Two Triangles Are Similar
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Muscles Is Voluntary
Mar 25, 2025
-
How To Find The Experimental Probability
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Grooved Wheel With A Rope Running Along The Groove
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Much Sides Does A Heptagon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
