How Many Square Meter In 1 Meter
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
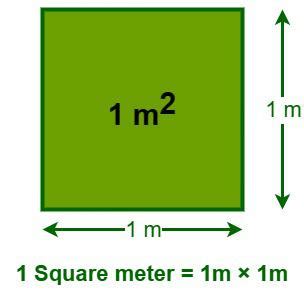
Table of Contents
How Many Square Meters in 1 Meter? Understanding Area and Linear Measurement
The question "How many square meters in 1 meter?" reveals a common misunderstanding about units of measurement. It's a question that stems from conflating linear measurement (length) with area measurement (surface). A meter measures length, while a square meter measures area. They are fundamentally different concepts. This article will delve into the distinction, explore the calculations involved, and clarify related concepts to provide a comprehensive understanding.
Understanding the Difference: Meters and Square Meters
Meters (m): This is a unit of linear measurement. It measures length or distance in a single dimension. Imagine a straight line; a meter measures the length of that line. You use meters to measure the height of a wall, the length of a table, or the distance between two points.
Square Meters (m²): This is a unit of area measurement. It measures the size of a two-dimensional surface. Imagine a square with sides of 1 meter each. The area enclosed within that square is 1 square meter. You use square meters to measure the area of a floor, a room, a field, or a piece of land.
Why the Question is Misleading
The question "How many square meters in 1 meter?" is inherently flawed. You cannot directly convert meters to square meters because they measure different things. It's like asking how many apples are in an orange – they are fundamentally different entities. You need additional information, such as width or another dimension, to calculate area from a linear measurement.
Calculating Area: The Importance of Two Dimensions
To determine the area of a surface in square meters, you need at least two linear measurements. The most common shapes are:
1. Calculating the Area of a Square or Rectangle
For squares and rectangles, the calculation is straightforward:
Area = Length × Width
If the length and width are both measured in meters, then the area is calculated in square meters. For example:
- A rectangle with a length of 4 meters and a width of 3 meters has an area of 4 m × 3 m = 12 m².
2. Calculating the Area of a Triangle
Triangles require a slightly different formula:
Area = (1/2) × Base × Height
Where the base and height are measured in meters. For instance:
- A triangle with a base of 6 meters and a height of 4 meters has an area of (1/2) × 6 m × 4 m = 12 m².
3. Calculating the Area of a Circle
Circles utilize the following formula:
Area = π × Radius²
Where the radius is measured in meters. Remember that π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- A circle with a radius of 2 meters has an area of π × (2 m)² ≈ 12.57 m².
4. Calculating the Area of Irregular Shapes
For irregular shapes, more complex methods are needed. These often involve dividing the shape into smaller, more manageable shapes (like squares, rectangles, or triangles) and calculating the area of each individual shape before summing them up to find the total area. Techniques like using graph paper to approximate the area or employing integral calculus are also applicable.
5. Dealing with Units
Always ensure consistency in your units. If you are using meters for length and width, the resulting area will be in square meters. If you are working with centimeters, the area will be in square centimeters. Remember to convert your units to maintain accuracy and avoid errors in your calculations.
Common Applications of Area Calculations in Square Meters
Understanding how to calculate area in square meters is crucial in many real-world scenarios:
1. Real Estate and Property
Real estate agents use square meters to determine the size of properties, influencing their pricing and marketability. Buyers and sellers rely on accurate area calculations to make informed decisions.
2. Construction and Architecture
Architects and contractors use square meters to estimate material requirements (e.g., flooring, paint, tiles), plan layouts, and determine project costs. Precise measurements are essential for accurate budgeting and successful project execution.
3. Interior Design and Decoration
Interior designers use square meters to determine the amount of flooring, wall coverings, or other materials needed for a room or space. This ensures they have enough supplies and minimizes waste.
4. Landscaping and Gardening
Landscapers use square meters to calculate the area of lawns, flowerbeds, or other landscape features to determine the amount of soil, fertilizer, or plants needed.
5. Agriculture and Farming
Farmers use square meters to measure the size of fields, calculate crop yields, and optimize planting density. Precise area calculations are essential for maximizing crop production and managing resources effectively.
Beyond Square Meters: Understanding Volume
While this article focuses on area (measured in square meters), it is important to understand its relation to volume, which is measured in cubic meters (m³). Volume adds a third dimension (height, depth, or thickness) to area. For instance, the volume of a rectangular prism (like a box) is calculated as:
Volume = Length × Width × Height
Understanding both area and volume is crucial for many tasks, from calculating the amount of paint needed for a room (area) to determining the capacity of a storage container (volume).
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Working with Square Meters
Several common mistakes can lead to inaccurate area calculations:
-
Confusing linear and area units: The most frequent error is mixing up meters and square meters. Remember that they measure different things.
-
Incorrect formulas: Using the wrong formula for the shape you are calculating can lead to significantly inaccurate results.
-
Unit inconsistencies: Ensure all your measurements are in the same units (e.g., all in meters) before calculating the area.
-
Rounding errors: While rounding numbers can simplify calculations, excessive rounding can accumulate errors, leading to inaccuracies.
-
Ignoring irregular shapes: Approximating complex shapes accurately using simplified calculations is crucial for obtaining reliable results.
Conclusion: Mastering Area Calculations
Understanding the difference between meters and square meters, along with the proper techniques for calculating area, is crucial for accuracy in various applications. This article clarifies the common misconception surrounding the conversion and underscores the importance of using appropriate formulas and consistent units. Mastering these concepts will improve precision in tasks involving area measurement, ranging from everyday home projects to large-scale professional endeavors. By avoiding common mistakes and employing the methods explained here, you can confidently and accurately determine the area of any space, ensuring success in your projects.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Demagnetize A Permanent Magnet
Mar 11, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 225
Mar 11, 2025
-
Magnetic Field Lines Inside A Bar Magnet
Mar 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Square Meter In 1 Meter . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
