What Is The Prime Factorization Of 225
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 5 min read
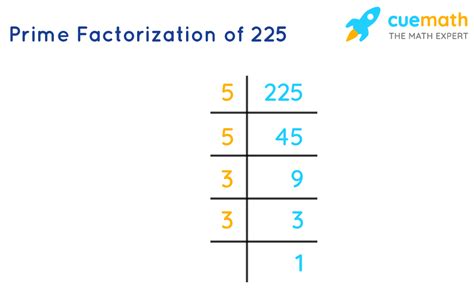
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 225? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 225?", opens the door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, a cornerstone of mathematics. This article will not only answer that question definitively but will also delve into the concepts of prime numbers, factorization, and the significance of prime factorization in various mathematical fields. We'll explore different methods to find the prime factorization, discuss its applications, and address some common misconceptions.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the prime factorization of 225, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it cannot be expressed as a product of two smaller whole numbers. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The sequence of prime numbers is infinite, a fact that has captivated mathematicians for centuries. The fundamental theorem of arithmetic rests on the unique nature of prime numbers.
The Sieve of Eratosthenes: A Method for Finding Primes
One effective method for identifying prime numbers is the Sieve of Eratosthenes. This ancient algorithm systematically eliminates multiples of each prime number, leaving only the prime numbers remaining. While not directly used for factorization, it's a crucial tool for generating a list of primes that can be used in the factorization process.
What is Factorization?
Factorization, in its simplest form, is the process of breaking down a number into smaller numbers that when multiplied together, equal the original number. These smaller numbers are called factors. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because 1 x 12 = 12, 2 x 6 = 12, and 3 x 4 = 12.
Prime Factorization: The Unique Representation
Prime factorization is a special type of factorization where a number is expressed as a product of only prime numbers. This representation is unique for every number (except for the order of the factors). This uniqueness is essential in various mathematical applications. The prime factorization of a number is often written using exponents to indicate repeated prime factors. For instance, 12 can be written as 2² x 3 (2 squared times 3).
Finding the Prime Factorization of 225
Now, let's address the central question: What is the prime factorization of 225? We can use several methods to determine this.
Method 1: Repeated Division by Prime Numbers
The most straightforward method is to repeatedly divide 225 by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly. Let's demonstrate this:
- Divide by 3: 225 ÷ 3 = 75
- Divide by 3 again: 75 ÷ 3 = 25
- Divide by 5: 25 ÷ 5 = 5
- Divide by 5 again: 5 ÷ 5 = 1
We've reached 1, indicating that we've found all the prime factors. Therefore, the prime factorization of 225 is 3 x 3 x 5 x 5, which can be written more concisely as 3² x 5².
Method 2: Factor Tree
Another visual approach is using a factor tree. Start with 225 and branch it out into two factors. Continue branching until all the factors are prime numbers.
225
/ \
3 75
/ \
3 25
/ \
5 5
As you can see from the factor tree, the prime factors are 3, 3, 5, and 5, leading us to the same conclusion: the prime factorization of 225 is 3² x 5².
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has profound implications across various mathematical fields and even in computer science:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization is crucial for efficiently calculating the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
-
Simplifying Fractions: Prime factorization helps simplify fractions to their lowest terms by canceling out common factors in the numerator and denominator.
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers play a fundamental role in modern cryptography, particularly in RSA encryption, a widely used algorithm for secure online communication. The security of RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Prime factorization is vital in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory that deals with remainders after division. This has applications in various fields, including cryptography and computer science.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization is a key concept in abstract algebra, particularly in the study of rings and fields. Prime ideals, which are related to prime numbers, are fundamental concepts in this field.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several common misconceptions surround prime numbers and factorization:
-
1 is a prime number: This is incorrect. By definition, a prime number must have only two distinct divisors, 1 and itself. 1 only has one divisor (itself), so it is neither prime nor composite.
-
Prime factorization is only useful for small numbers: While it's easier to visualize with small numbers, prime factorization is essential for extremely large numbers in applications like cryptography.
-
There's only one way to find prime factorization: While the repeated division method is efficient, other methods like the factor tree provide alternative visual approaches. The choice of method depends on personal preference and the size of the number being factored.
-
Finding the prime factorization of large numbers is easy: Factoring extremely large numbers into their prime factors is computationally very challenging, forming the basis of many cryptographic systems.
Conclusion: The Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple act of finding the prime factorization of 225, as we have demonstrated, is far more significant than it initially appears. Understanding prime factorization unlocks a deeper understanding of number theory and its applications across various fields. From simplifying fractions to securing online communications, the concept of prime numbers and their unique factorization holds immense value in the world of mathematics and beyond. The prime factorization of 225, 3² x 5², serves as a gateway to exploring this fascinating world of numbers and their properties. By understanding the fundamental concepts explained here, you can confidently tackle more complex factorization problems and appreciate the elegance and power of prime numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Items Are In A Gross
May 09, 2025
-
13 10 As A Mixed Number
May 09, 2025
-
Most Abundant Cartilage In The Body
May 09, 2025
-
2 Cubic Feet Equal How Many Quarts
May 09, 2025
-
Verbs That Start With A Y
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 225 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.