How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Regular Hexagon Have
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
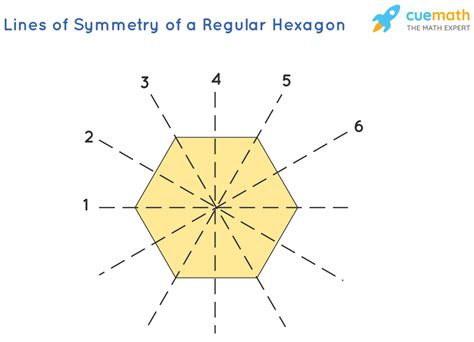
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Regular Hexagon Have? A Comprehensive Exploration
Symmetry, a fundamental concept in geometry and art, refers to a balanced and proportionate arrangement of elements within a shape or figure. Understanding symmetry helps us appreciate the underlying order in seemingly complex structures, from snowflakes to the human body. This article delves deep into the fascinating world of symmetry, focusing specifically on the regular hexagon and its lines of symmetry. We'll explore the definition of a regular hexagon, different types of symmetry, and ultimately answer the central question: how many lines of symmetry does a regular hexagon possess?
Understanding Regular Hexagons
Before we delve into the lines of symmetry, let's solidify our understanding of a regular hexagon. A hexagon is a polygon with six sides. The term "regular" signifies that all its sides are of equal length, and all its interior angles are equal (each measuring 120 degrees). This creates a perfectly balanced and symmetrical shape. Think of a honeycomb – each cell is a perfect example of a regular hexagon. This consistent structure is crucial when discussing symmetry.
Key Properties of a Regular Hexagon
Several key properties define a regular hexagon, making it unique among polygons:
- Equal Sides: All six sides have the same length.
- Equal Angles: All six interior angles are equal (120 degrees each).
- Rotational Symmetry: It exhibits rotational symmetry of order 6, meaning it can be rotated 60 degrees (360/6) about its center and still appear identical.
- Central Point: It has a clearly defined center point equidistant from all vertices and sides.
Types of Symmetry
Symmetry comes in different forms. Understanding these types is crucial for counting the lines of symmetry in any shape, including our regular hexagon. The main types of symmetry are:
- Line Symmetry (Reflectional Symmetry): A shape possesses line symmetry if it can be folded along a line (the line of symmetry) so that the two halves perfectly overlap. This line of symmetry acts as a mirror, reflecting one half onto the other.
- Rotational Symmetry: A shape has rotational symmetry if it can be rotated around a central point by a specific angle and still look identical. The number of times it looks identical during a 360-degree rotation determines the order of rotational symmetry.
Finding the Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Hexagon
Now, let's address the main question: how many lines of symmetry does a regular hexagon have? To find out, we need to systematically consider both line symmetry (reflectional symmetry) and rotational symmetry.
Line Symmetry in a Regular Hexagon
Imagine folding a regular hexagon. The most obvious lines of symmetry are those that connect opposite vertices (corners). A regular hexagon has three such lines, each passing through two opposite vertices and the center of the hexagon.
But there are more! Consider lines that bisect (cut in half) opposite sides. These lines also act as lines of symmetry, as folding the hexagon along them results in perfectly overlapping halves. There are three such lines, each connecting the midpoints of two opposite sides.
Therefore, combining both types of lines of symmetry, a regular hexagon has a total of six lines of symmetry.
Visualizing the Six Lines of Symmetry
To visualize this clearly, imagine your regular hexagon. Draw lines connecting:
- Opposite vertices: Three lines are drawn connecting opposite corners.
- Midpoints of opposite sides: Three more lines connect the midpoints of opposite edges.
These six lines represent all the lines of symmetry present in a regular hexagon. No other line will divide the hexagon into two identical halves.
Exploring Symmetry Beyond Regular Hexagons
The concept of symmetry extends far beyond regular hexagons. Understanding the lines of symmetry in other shapes can be equally fascinating and insightful. Let's briefly touch upon some examples:
- Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle (all sides equal) has three lines of symmetry, each passing through a vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
- Square: A square possesses four lines of symmetry: two lines connecting opposite vertices and two lines connecting the midpoints of opposite sides.
- Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon has five lines of symmetry, each connecting a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
- Circle: A circle has an infinite number of lines of symmetry, as any diameter acts as a line of symmetry.
Applications of Symmetry
Understanding symmetry has far-reaching implications across numerous fields:
- Mathematics: Symmetry plays a pivotal role in various mathematical concepts, from group theory to fractal geometry.
- Physics: Symmetry principles are fundamental to many physical laws and theories, impacting fields like particle physics and crystallography.
- Chemistry: Molecular symmetry is crucial in understanding the properties and behavior of molecules.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers utilize symmetry to create visually appealing and balanced compositions. Many architectural marvels and works of art incorporate symmetrical designs.
- Nature: Symmetry is abundant in nature, evident in snowflakes, flowers, and even the human body. Understanding this natural symmetry helps us appreciate the intricate order in the world around us.
Conclusion: The Significance of Symmetry in a Regular Hexagon
The regular hexagon, with its six lines of symmetry, stands as a beautiful example of geometrical balance and harmony. Its symmetrical properties are not merely aesthetic; they have profound implications in various scientific and artistic disciplines. By understanding the lines of symmetry within this simple shape, we gain a deeper appreciation of the broader concepts of symmetry and its importance in our world. The methodical approach of identifying lines of symmetry – connecting opposite vertices and midpoints of opposite sides – provides a clear and efficient method for any regular polygon. The six lines of symmetry in a regular hexagon encapsulate its inherent balance and structural integrity, demonstrating the power and elegance of symmetry in geometry. The exploration of symmetry, from simple shapes to complex structures, continues to fascinate and inspire, revealing the intricate beauty of order within apparent complexity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Highest Common Factor Of 28 And 42
Mar 09, 2025
-
The Matrix Of Blood Is Called
Mar 09, 2025
-
The Rate Of Change In Velocity Is Called
Mar 09, 2025
-
Do Plant Cells Have A Mitochondria
Mar 09, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 And 11
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Regular Hexagon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
