How Long Does It Take Mars To Orbit The Sun
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
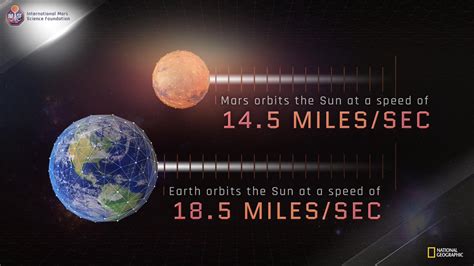
Table of Contents
How Long Does It Take Mars to Orbit the Sun? A Deep Dive into Martian Orbital Mechanics
Mars, the fourth planet from our Sun, holds a captivating allure for scientists and space enthusiasts alike. Its reddish hue, intriguing geological features, and the tantalizing possibility of past or present life have fueled countless missions and years of research. Understanding Mars’s orbit around the Sun is fundamental to planning these missions and deciphering the planet's climatic history and potential for habitability. So, how long does it actually take Mars to complete one orbit? The answer isn't as simple as a single number, and delving into the complexities of its orbital mechanics reveals fascinating insights into the Martian system.
Understanding Orbital Periods: Beyond a Simple Number
While a quick search might provide a simplified answer – approximately 687 Earth days – the reality is more nuanced. The time it takes Mars to orbit the Sun, its orbital period, isn't a fixed value like a ticking clock. Several factors contribute to the slight variations:
-
Elliptical Orbit: Unlike Earth's relatively circular orbit, Mars follows an elliptical path around the Sun. This means its distance from the Sun constantly changes throughout its orbit. When Mars is closer to the Sun (at perihelion), its orbital speed increases, and when it's farther (at aphelion), its speed decreases. This variation in speed directly impacts the time it takes to complete an orbit.
-
Gravitational Influences: The gravitational pull of other planets, particularly Jupiter, can subtly perturb Mars's orbit over time, causing minor fluctuations in its orbital period. These perturbations are small but measurable, adding complexity to precise calculations.
-
Orbital Precession: The orientation of Mars's orbit isn't fixed; it slowly rotates over time, a phenomenon known as orbital precession. This precession, caused by the gravitational influences of other planets, adds another layer of complexity when determining the precise orbital period. The precession causes the timing of seasons and perihelion/aphelion to slowly shift over many years.
The Average Orbital Period: 687 Earth Days
Despite these variations, astronomers use an average value to represent Mars's orbital period: approximately 687 Earth days. This figure represents the mean time it takes Mars to complete one revolution around the Sun, averaging out the variations caused by its elliptical orbit and gravitational perturbations. It's a crucial figure for mission planning and understanding the Martian year.
Comparing Martian and Earth Years: A Significant Difference
The significant difference between a Martian year (687 Earth days) and an Earth year (365.25 days) has profound implications for space missions. Missions to Mars must account for this difference in planning launch windows and communication timelines. A spacecraft launched to Mars will need to travel for several months to reach its destination, and the longer orbital period means that communication delays will be significantly longer than for missions to nearby planets.
Delving Deeper: The Eccentricity of Mars' Orbit
The eccentricity of an orbit describes how elongated it is. A perfectly circular orbit has an eccentricity of 0, while a highly elongated orbit approaches 1. Mars's orbit has a relatively high eccentricity of approximately 0.0934. This significant eccentricity explains why the variations in Mars's orbital speed and distance from the Sun are more pronounced than those experienced by Earth.
Perihelion and Aphelion: Closest and Furthest Points
At perihelion, Mars is closest to the Sun, approximately 206.6 million kilometers (128.4 million miles) away. At aphelion, its furthest point from the Sun, it's around 249.2 million kilometers (154.8 million miles) away. This substantial difference in distance significantly influences Mars's surface temperature and atmospheric conditions throughout the year. The variation in solar energy received at the surface strongly influences Martian weather patterns and the possibility of liquid water existing on the surface.
The Impact of Mars' Orbital Mechanics on its Climate and Habitability
The eccentricity of Mars's orbit plays a crucial role in shaping its climate. The significant variation in solar radiation received throughout the year leads to large temperature swings and influences the distribution of water ice on the planet's surface. Understanding these orbital variations is crucial for modeling the Martian climate and assessing its potential for past or present life. The cyclical nature of these variations, influenced by both the eccentricity and the precession of the orbit, creates long-term climate cycles that could have greatly impacted the potential for liquid water and habitability over Martian geological history.
Calculating Martian Orbital Parameters: Advanced Techniques
Precisely calculating Mars's orbital parameters requires sophisticated techniques that go beyond simple averaging. Astronomers use Kepler's laws of planetary motion as a foundation, but also incorporate perturbations from other planets and sophisticated numerical integration methods to create highly accurate orbital models. These models consider the gravitational interactions between all planets in our solar system to predict Mars's position and velocity at any given time with high precision.
Kepler's Laws and Martian Orbit
Johannes Kepler's laws of planetary motion provide a fundamental framework for understanding planetary orbits. His first law states that the orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. His second law describes the relationship between a planet's speed and its distance from the Sun; the planet moves faster when closer to the Sun and slower when farther away. His third law relates the orbital period of a planet to the semi-major axis of its orbit. While these laws provide a solid starting point, the complexities of the solar system necessitate more advanced computational techniques for accurate predictions.
The Importance of Accurate Orbital Data for Space Missions
Precise knowledge of Mars's orbital parameters is crucial for the success of space missions. Mission planners use highly accurate orbital models to determine optimal launch windows, trajectory calculations, and communication strategies. Slight errors in the calculation could lead to missed opportunities, increased fuel consumption, and even mission failure. The longer travel times and greater distance involved in Martian missions emphasize the critical need for accurate orbital prediction.
Beyond the Orbital Period: Martian Seasons and their Length
The elliptical nature of Mars's orbit, combined with the tilt of its axis (similar to Earth's), results in distinct seasons. However, due to the longer orbital period and eccentricity, Martian seasons are of unequal lengths. The northern hemisphere's summer is shorter and warmer than its winter, while the southern hemisphere experiences a longer, colder winter and a shorter, warmer summer. This asymmetry in seasonal lengths further emphasizes the impact of orbital mechanics on the Martian climate.
Future Research and Exploration: Unraveling Martian Mysteries
Ongoing research and future missions to Mars aim to further refine our understanding of its orbital mechanics and its impact on the planet's evolution and potential for habitability. Advanced observational techniques, coupled with sophisticated computer modeling, will continue to improve the accuracy of orbital predictions and deepen our knowledge of this fascinating planet. The ongoing search for evidence of past or present life on Mars is closely tied to understanding the planet's climatic history, which is directly influenced by its orbital dynamics.
Conclusion: A Complex Dance Around the Sun
The question "How long does it take Mars to orbit the Sun?" might seem straightforward, but the answer reveals a rich tapestry of orbital mechanics. The approximately 687 Earth-day orbital period is an average, concealing the complexities of an elliptical orbit, gravitational perturbations, and orbital precession. Understanding these complexities is vital not only for a deeper appreciation of the Martian system but also for the success of future space exploration endeavors. Mars's orbital dynamics continue to be a source of scientific fascination, driving ongoing research and fueling our quest to unlock the secrets of this captivating red planet.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Pair Of Angles Is Supplementary
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Color Do Acids Turn Litmus Paper
Mar 15, 2025
-
Youngest Mountain Range In The World
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is Most Abundant Metal In Earths Crust
Mar 15, 2025
-
Chromosomes Line Up Along The Equator
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Long Does It Take Mars To Orbit The Sun . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
