How Do You Multiply Using Partial Products
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
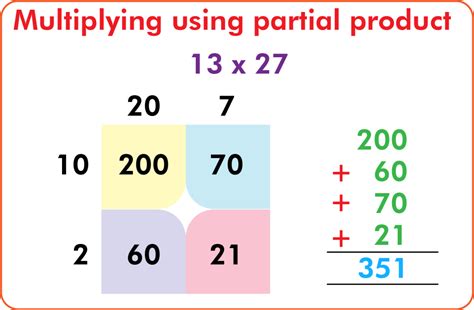
Table of Contents
How Do You Multiply Using Partial Products? A Comprehensive Guide
Multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic operation, and understanding different methods can significantly improve your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities. While the standard algorithm is widely taught, the partial products method offers a valuable alternative, particularly for understanding the underlying logic of multiplication. This detailed guide explores the partial products method, explaining its steps, benefits, and applications.
Understanding the Partial Products Method
The partial products method, also known as the distributive property of multiplication, breaks down a multiplication problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Instead of multiplying numbers directly, it involves multiplying each digit of one number by each digit of the other number separately and then adding the resulting partial products together. This approach makes multiplication more intuitive and transparent, particularly for larger numbers.
The Foundation: The Distributive Property
The core principle behind the partial products method is the distributive property of multiplication over addition. This property states that multiplying a number by a sum is the same as multiplying the number by each addend individually and then adding the products. For example:
a * (b + c) = (a * b) + (a * c)
This principle is the key to understanding how the partial products method works. By breaking down numbers into their place values (ones, tens, hundreds, etc.), we can apply the distributive property repeatedly to simplify the multiplication process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Multiplying Using Partial Products
Let's illustrate the partial products method with an example: Multiply 35 x 12.
1. Expand the Numbers Based on Place Value:
First, break down each number based on its place value. This means expressing each number as a sum of its digits multiplied by their respective powers of 10.
- 35 = (30 + 5)
- 12 = (10 + 2)
2. Apply the Distributive Property:
Now, apply the distributive property. We'll multiply each part of the first number by each part of the second number:
- (30 + 5) x (10 + 2) = (30 x 10) + (30 x 2) + (5 x 10) + (5 x 2)
3. Calculate the Partial Products:
Next, calculate each individual multiplication:
- 30 x 10 = 300
- 30 x 2 = 60
- 5 x 10 = 50
- 5 x 2 = 10
4. Add the Partial Products:
Finally, add up all the partial products to obtain the final answer:
- 300 + 60 + 50 + 10 = 420
Therefore, 35 x 12 = 420.
Visualizing Partial Products: The Area Model
The area model offers a visual representation of the partial products method. Imagine a rectangle with dimensions corresponding to the two numbers you're multiplying. Divide the rectangle into smaller rectangles based on the place values of the numbers. The area of each smaller rectangle represents a partial product. Adding the areas of all the smaller rectangles gives you the total product.
For our example (35 x 12):
Imagine a rectangle with length 35 and width 12. We can break this down into four smaller rectangles:
- A rectangle with dimensions 30 x 10 (area = 300)
- A rectangle with dimensions 30 x 2 (area = 60)
- A rectangle with dimensions 5 x 10 (area = 50)
- A rectangle with dimensions 5 x 2 (area = 10)
The sum of these areas (300 + 60 + 50 + 10) is 420, which is the final product.
Advantages of Using the Partial Products Method
The partial products method offers several advantages over the standard algorithm:
-
Improved Understanding: It clarifies the underlying logic of multiplication, making it easier to grasp the concept and its application. It emphasizes the distributive property, a fundamental concept in algebra.
-
Error Reduction: By breaking down the problem into smaller steps, the partial products method reduces the chances of making calculation errors. Each partial product can be checked independently, minimizing mistakes.
-
Flexibility and Adaptability: It can be easily applied to multiplying numbers of any size, making it a versatile method. It is not limited by the number of digits.
-
Foundation for Advanced Math: It provides a solid foundation for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts such as polynomial multiplication and algebraic manipulations.
-
Enhanced Estimation Skills: The method encourages estimation as you calculate the partial products, aiding in developing better number sense.
Working with Larger Numbers: A More Complex Example
Let's apply the partial products method to a more complex multiplication: 234 x 156.
1. Expand the Numbers:
- 234 = 200 + 30 + 4
- 156 = 100 + 50 + 6
2. Apply the Distributive Property and Calculate Partial Products:
-
(200 + 30 + 4) x (100 + 50 + 6) =
- (200 x 100) + (200 x 50) + (200 x 6) +
- (30 x 100) + (30 x 50) + (30 x 6) +
- (4 x 100) + (4 x 50) + (4 x 6)
-
Calculating each partial product:
- 20000
- 10000
- 1200
- 3000
- 1500
- 180
- 400
- 200
- 24
3. Add the Partial Products:
- 20000 + 10000 + 1200 + 3000 + 1500 + 180 + 400 + 200 + 24 = 36504
Therefore, 234 x 156 = 36504. This example demonstrates how the method remains effective even with larger numbers. The organized approach helps avoid confusion.
Connecting Partial Products to the Standard Algorithm
While the partial products method provides a clear understanding of the underlying principles, it's useful to connect it to the standard algorithm. The standard algorithm is essentially a condensed version of the partial products method, where some steps are combined for efficiency. Understanding this connection reinforces your understanding of both methods.
Conclusion: Mastering Multiplication through Partial Products
The partial products method offers a powerful and versatile approach to multiplication, fostering a deeper understanding of the mathematical concepts involved. Its structured approach, suitability for large numbers, and clear visualization make it an invaluable tool for students and anyone looking to improve their mathematical skills. While the standard algorithm might seem faster for routine calculations, the partial products method provides a robust foundation and invaluable insight into the fundamental principles of arithmetic. By embracing this method, you enhance your mathematical proficiency and build a stronger foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Refers To The Division Of The Nucleus
Mar 22, 2025
-
Work Is A Scalar Or Vector Quantity
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Side Does A Circle Have
Mar 22, 2025
-
Find The Least Common Multiple Lcm Of 6 And 10
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Does Instantaneous Rate Of Change Mean
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Multiply Using Partial Products . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
