How Are Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes Alike
Juapaving
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
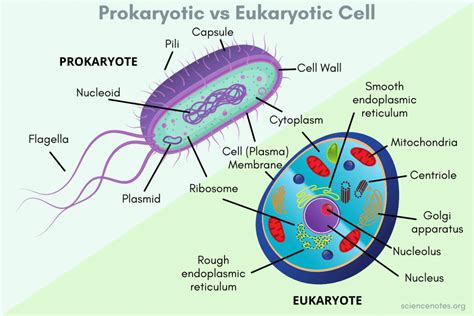
Table of Contents
How Are Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Alike? Exploring the Similarities Between These Cellular Worlds
While prokaryotes and eukaryotes represent two fundamentally different branches of life, a closer examination reveals a surprising number of similarities. Although their cellular structures differ dramatically, these two cell types share core processes vital for survival and reproduction. Understanding these shared features is crucial for grasping the overarching principles of cellular biology and the evolutionary history of life on Earth. This article delves deep into the remarkable similarities between these seemingly disparate cellular worlds.
Fundamental Similarities: The Building Blocks of Life
At their core, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share several fundamental similarities that highlight the underlying unity of life:
1. Genetic Material: The Blueprint of Life
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes utilize deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as their genetic material. This molecule, a double helix structure, carries the instructions for building and maintaining the organism. While the organization and packaging of DNA differ significantly (eukaryotic DNA is housed within a nucleus, while prokaryotic DNA resides in the cytoplasm), the fundamental language of DNA—the genetic code—remains remarkably consistent across all domains of life. This universality underscores the common ancestry of all living things.
2. Ribosomes: Protein Factories
Both cell types possess ribosomes, the molecular machines responsible for protein synthesis. Ribosomes translate the genetic information encoded in mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) into polypeptide chains, which fold into functional proteins. While the size and structure of ribosomes differ slightly between prokaryotes and eukaryotes (prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S, while eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S), their fundamental function remains identical. This similarity highlights the importance of protein synthesis as a central process for all life forms.
3. Basic Metabolic Pathways: Energy Production and Utilization
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes both employ similar basic metabolic pathways to generate energy and utilize nutrients. Glycolysis, for example, a fundamental process for breaking down glucose to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's energy currency, is present in both cell types. Furthermore, both utilize similar mechanisms for transporting molecules across their cell membranes, including active and passive transport systems. This shared metabolic machinery reflects the fundamental requirement for all living organisms to acquire and utilize energy.
4. Cell Membrane: The Gatekeeper
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are enclosed by a plasma membrane, a selectively permeable barrier that regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. This membrane, composed primarily of a phospholipid bilayer, maintains the cell's internal environment distinct from its surroundings. The basic structure and function of this membrane are conserved across all life forms, reflecting its essential role in maintaining cellular integrity and homeostasis.
5. Cytoplasm: The Cellular Matrix
Both cell types contain cytoplasm, the gel-like substance filling the cell interior. This cytoplasm houses the cell's organelles and provides a medium for biochemical reactions. Although the organization and complexity of the cytoplasm differ significantly (eukaryotic cytoplasm is far more structured due to the presence of membrane-bound organelles), the fundamental role of the cytoplasm as a site for cellular processes remains the same.
Deeper Similarities: Exploring Shared Mechanisms
Beyond the basic building blocks, a closer examination reveals more subtle but equally important similarities:
1. DNA Replication: Copying the Genetic Code
The process of DNA replication, the copying of the genetic material, shares remarkable similarities in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Both cell types employ DNA polymerases, enzymes that catalyze the addition of nucleotides to the growing DNA strand. While the specific enzymes and associated proteins differ slightly, the fundamental mechanism—semi-conservative replication, where each new DNA molecule consists of one original and one newly synthesized strand—remains consistent.
2. Transcription and Translation: From DNA to Protein
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes utilize the processes of transcription (the synthesis of RNA from DNA) and translation (the synthesis of protein from RNA) to express their genetic information. While the details of these processes differ (eukaryotic transcription and translation are spatially and temporally separated, whereas in prokaryotes they are often coupled), the underlying principles remain the same. Both cell types employ RNA polymerase for transcription and ribosomes for translation, highlighting the conserved nature of gene expression.
3. Cell Signaling: Communication and Coordination
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes utilize cell signaling mechanisms to communicate with their environment and coordinate cellular processes. These signaling pathways involve the reception of extracellular signals, signal transduction across the cell membrane, and ultimately, a cellular response. While the complexity of these signaling pathways differs significantly (eukaryotes possess much more intricate signaling networks), the fundamental principles of signal reception, transduction, and response are conserved across both cell types.
4. Cell Division: Reproduction and Growth
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes undergo cell division to reproduce and grow. Prokaryotes utilize binary fission, a simpler form of cell division, while eukaryotes use mitosis or meiosis, more complex processes involving multiple stages. Despite these differences, both processes involve the accurate replication and segregation of the genetic material, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information to daughter cells.
5. Evolutionary Conservation: A Shared Ancestry
The numerous similarities between prokaryotes and eukaryotes provide compelling evidence for their shared evolutionary ancestry. The conservation of fundamental cellular processes, such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, and basic metabolic pathways, suggests that these processes were present in the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) of all life on Earth. The subsequent evolution of eukaryotes involved the acquisition of more complex cellular features, but the fundamental building blocks and processes remained conserved.
Differences Highlighting the Similarities: A Comparative Perspective
While the similarities are striking, it is crucial to acknowledge the significant differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. These differences, however, serve to highlight the ingenuity of life's evolutionary adaptations and the remarkable versatility of fundamental cellular processes. The presence of membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes, the complexity of their genetic material organization, and the development of intricate cellular signaling pathways all represent evolutionary innovations built upon a foundation of shared cellular mechanisms.
The detailed comparison between the two cell types helps us appreciate the conserved mechanisms adapted and modified to produce the diversity of life we see today. This is a testament to the efficiency of fundamental cellular processes.
By understanding both the similarities and differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate complexity and remarkable unity of life on Earth. The shared features highlight the fundamental principles of cellular biology, while the differences showcase the amazing diversity and adaptability of life's evolutionary trajectory. Further research into these areas continues to reveal fascinating insights into the evolution and function of cells, providing a richer understanding of the fundamental processes that underpin all life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Herd Of Kangaroos Called
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Write A Check For 11550
Apr 04, 2025
-
Cbse Class 6th Maths Book Pdf
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In Carbon
Apr 04, 2025
-
3 632 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Are Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes Alike . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
