Give An Example Of A Real Number That Is Irrational
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
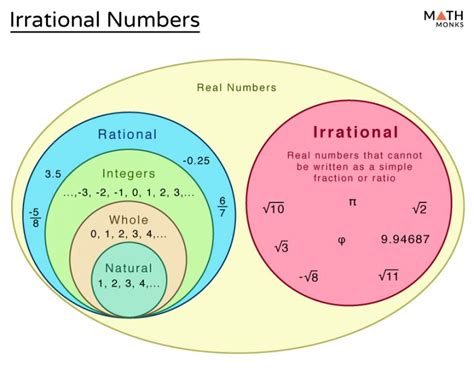
Table of Contents
- Give An Example Of A Real Number That Is Irrational
- Table of Contents
- Give an Example of a Real Number That is Irrational: Exploring the World of Pi
- What are Rational Numbers?
- Defining Irrational Numbers: The Opposite of Rational
- Pi (π): The quintessential Irrational Number
- The Historical Significance of Pi
- Pi's Ubiquity in Mathematics and Science
- Other Examples of Irrational Numbers
- Why is it Important to Understand Irrational Numbers?
- Conclusion: Pi as a Perfect Example
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Give an Example of a Real Number That is Irrational: Exploring the World of Pi
The realm of mathematics is vast and intricate, filled with numbers of various types. Understanding the distinctions between these types of numbers, like rational and irrational numbers, is crucial to grasping fundamental mathematical concepts. This article delves deep into the definition of irrational numbers and provides a compelling example: the ubiquitous and fascinating number Pi (π). We'll explore its properties, history, and significance, illustrating why it perfectly exemplifies the concept of an irrational number.
What are Rational Numbers?
Before we dive into irrational numbers, it's vital to understand their counterpart: rational numbers. A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers (whole numbers), and 'q' is not equal to zero. This simple definition encompasses a wide range of numbers, including:
- Integers: Whole numbers, both positive and negative (e.g., -3, 0, 5). These can be expressed as fractions with a denominator of 1 (e.g., -3/1, 0/1, 5/1).
- Fractions: Numbers expressed as a ratio of two integers (e.g., 1/2, 3/4, -2/5).
- Terminating Decimals: Decimals that end after a finite number of digits (e.g., 0.75, 2.5, -1.234). These can always be converted to fractions.
- Repeating Decimals: Decimals with a pattern of digits that repeats infinitely (e.g., 0.333..., 0.142857142857...). These also have fractional equivalents.
Defining Irrational Numbers: The Opposite of Rational
An irrational number, as its name suggests, is a real number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers and 'q' is not zero. This means irrational numbers cannot be written as terminating or repeating decimals. Their decimal representations continue indefinitely without ever settling into a repeating pattern.
This seemingly simple definition leads to a surprisingly rich and complex world of numbers. Many famous mathematical constants fall into this category, and understanding their irrationality is key to advancing in various mathematical fields.
Pi (π): The quintessential Irrational Number
Pi (π), arguably the most famous irrational number, is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. This constant appears repeatedly in various mathematical and scientific fields, making it one of the most important numbers in all of mathematics.
Why is Pi Irrational?
The proof of Pi's irrationality is not trivial; it involves advanced mathematical concepts and techniques. However, the core idea is that if you attempt to express Pi as a fraction, you will always find that you cannot find a fraction that precisely represents its value. The decimal representation of Pi never terminates, and it never settles into a repeating pattern. It's an infinitely non-repeating decimal.
The first few digits of Pi are 3.1415926535..., but this sequence continues infinitely without ever repeating. This infinite and non-repeating nature is the hallmark of an irrational number.
The Historical Significance of Pi
The quest to understand and approximate Pi has captivated mathematicians for millennia. Ancient civilizations, including the Babylonians and Egyptians, developed surprisingly accurate approximations of Pi for their practical needs in construction and astronomy. The symbol "π" itself was introduced much later, in the 18th century.
Over centuries, mathematicians developed increasingly sophisticated methods to calculate Pi to greater and greater precision. The pursuit of more accurate approximations of Pi not only led to advancements in computational techniques but also fueled the development of new mathematical theories and concepts.
Pi's Ubiquity in Mathematics and Science
Pi's significance extends far beyond its simple geometrical definition. It appears in a wide range of formulas and equations across diverse scientific disciplines, including:
- Geometry: Calculating the area and circumference of circles, the volume and surface area of spheres, and other circular or spherical shapes.
- Trigonometry: Pi is fundamental in understanding trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent.
- Calculus: Pi appears in numerous integral and differential equations, making it crucial in fields like physics and engineering.
- Statistics and Probability: Pi pops up in probability distributions and statistical analyses.
- Physics and Engineering: Pi is essential in describing wave phenomena, oscillations, and many other physical processes.
This widespread presence underscores Pi's profound importance and fundamental role in describing the natural world.
Other Examples of Irrational Numbers
While Pi is the most well-known example, other irrational numbers abound. Some notable examples include:
-
Euler's number (e): Approximately 2.71828, it's the base of the natural logarithm and appears frequently in calculus and exponential growth/decay problems. Like Pi, its decimal representation is infinite and non-repeating.
-
Square root of 2 (√2): This number, approximately 1.41421, represents the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle with legs of length 1. Its irrationality was proven by the ancient Greeks, and it was a pivotal discovery in mathematics.
-
The Golden Ratio (φ): Approximately 1.61803, it's a mathematical ratio that appears in various natural phenomena and artistic designs. It's also an irrational number.
Why is it Important to Understand Irrational Numbers?
Understanding irrational numbers is not just an academic pursuit; it's crucial for:
-
Advanced Mathematical Studies: Irrational numbers are fundamental to calculus, analysis, and various advanced mathematical fields. Without understanding them, progress in these areas is impossible.
-
Scientific and Engineering Applications: Many scientific and engineering formulas rely on irrational numbers like Pi and e, so understanding them is essential for accurate calculations and modeling.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms for approximating irrational numbers are crucial in computer graphics, simulations, and other computational tasks.
-
Problem Solving: Encountering irrational numbers often requires creative approaches and a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: Pi as a Perfect Example
Pi (π) serves as an excellent and readily understandable example of an irrational number. Its infinite and non-repeating decimal representation, combined with its ubiquity across mathematics and science, makes it an ideal illustration of this important mathematical concept. Understanding irrational numbers, and Pi in particular, is crucial for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of mathematics and its applications in the wider world. The fascinating history of Pi's exploration and the ongoing efforts to calculate its digits to ever-increasing precision only serve to highlight its enduring allure and significant role in mathematics and beyond. From the ancient civilizations that first approximated its value to modern-day scientists utilizing its properties, Pi's influence remains undeniable and continues to inspire mathematical exploration and discovery. Further exploration into the world of irrational numbers opens doors to a deeper appreciation of the intricacies and beauty inherent within the mathematical universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Triangle Has 2 Equal Sides
Mar 28, 2025
-
Metal Which Is Poor Conductor Of Heat
Mar 28, 2025
-
Nouns That Start With A V
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Piece Of Land Completely Surrounded By Water
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is A Group Of Angels
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Give An Example Of A Real Number That Is Irrational . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
