Function Of The Base Of A Microscope
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
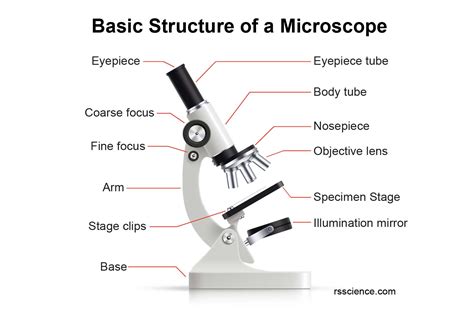
Table of Contents
The Unsung Hero: Understanding the Function of a Microscope's Base
The microscope, a cornerstone of scientific discovery, allows us to explore the intricate details of the world invisible to the naked eye. While the lenses and stage understandably garner the most attention, the often-overlooked base plays a critical, multifaceted role in ensuring the microscope's stability, functionality, and overall performance. This article delves deep into the function of the microscope base, exploring its design, materials, variations, and its crucial contribution to accurate and reliable microscopy.
The Base: Foundation of Stability and Support
The base of a microscope, simply put, is its foundation. It provides the structural support for all other components, including the stage, arm, body tube, and the optical system. Without a sturdy base, the microscope would be unstable, prone to vibrations, and incapable of providing clear, focused images. The stability offered by the base is paramount for high-magnification observations where even the slightest movement can blur the image or render it unusable.
Material Matters: Durability and Weight Distribution
The material of the microscope base is carefully chosen to optimize stability, weight distribution, and durability. Common materials include:
-
Metal Alloys: Metals like cast iron, aluminum alloys, and steel are frequently used. These materials offer high strength-to-weight ratios, ensuring the base is both robust and not excessively heavy. The weight itself contributes to stability, resisting vibrations and external disturbances.
-
Plastics (in lower-end models): While less common in high-end research microscopes, some budget-friendly models utilize high-impact plastics. These plastics are designed to be durable and lightweight, although they may not offer the same level of stability and vibration dampening as metal bases.
The base's design often incorporates features that enhance stability. A wide, flat base provides a large surface area for better contact with the working surface, minimizing wobble. Internal bracing and reinforcement further enhance rigidity.
Beyond Stability: Integrated Features of the Base
Many microscope bases incorporate additional features that extend beyond basic support:
1. Illumination Source Housing: The Power Behind the Image
The base often houses the illumination source, typically an LED or halogen lamp. This integrated design simplifies the optical pathway and contributes to the microscope's overall compactness. The base provides physical protection for the bulb and its associated electronics, preventing accidental damage and ensuring a longer lifespan for the illumination system. The positioning of the illumination system within the base, particularly its proximity to the condenser, is critical in optimizing light delivery for optimal image quality.
2. Power Switch and Controls: Easy Access and Control
The base frequently integrates the microscope's power switch and intensity controls. This convenient placement allows for easy access and adjustment of the illumination intensity without reaching for separate controls, improving the user experience. This centralized control approach keeps the microscope’s functionality streamlined and user-friendly.
3. Coarse and Fine Focus Knobs (in some designs):
Certain microscope designs incorporate the coarse and fine focus knobs directly into the base. This integration reduces clutter on the microscope's arm and makes the adjustment mechanisms more readily accessible. This design choice enhances ergonomic comfort during extended periods of microscopy.
4. Stage Adjustment Knobs (in some inverted models):
In some inverted microscope designs, the stage adjustment knobs might be integrated into the base. This strategic placement aligns with the orientation of the inverted microscope, making it intuitive for the user to manipulate the stage for sample positioning.
Variations in Base Design Across Microscope Types
The design of the microscope base varies depending on the type of microscope:
-
Upright Microscopes: Upright microscopes typically feature a sturdy, broad base to provide maximum stability, given the vertical orientation of the optical system. The base is often weighted to further enhance its stability.
-
Inverted Microscopes: Inverted microscopes, with their upside-down optical design, might have a smaller base because the weight is distributed differently. However, stability remains critical and the base design is still carefully engineered for secure operation.
-
Stereomicroscopes (Dissecting Microscopes): Stereomicroscopes, used for observing larger specimens, often have bases designed to accommodate larger samples and potentially integrated lighting systems. These bases may incorporate features for tilting or adjusting the angle of the microscope for optimal viewing.
-
Specialized Microscopes: Highly specialized microscopes, such as those used in industrial settings or for specific research applications, may feature customized base designs to meet the needs of the application. These may include vibration-dampening mechanisms or specialized attachments for precise positioning.
The Base's Contribution to Image Quality
While not directly involved in image formation, the base indirectly contributes significantly to image quality:
-
Stability: A stable base minimizes vibrations, preventing image blurring, particularly at high magnification. This is crucial for capturing sharp, detailed images.
-
Consistent Illumination: A well-designed base, securely housing the illumination system, ensures consistent and even light distribution across the sample. This is essential for achieving optimal contrast and resolving fine details.
-
Ergonomics: A thoughtfully designed base, with readily accessible controls and a comfortable working height, improves the user experience and reduces fatigue during long microscopy sessions. This in turn enhances the accuracy and consistency of observations.
Maintenance and Care of the Microscope Base
Proper maintenance of the microscope base is essential for preserving its functionality and the microscope's overall performance:
-
Cleaning: Regularly clean the base with a soft, damp cloth to remove dust and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners that could damage the surface finish.
-
Handling: Always handle the microscope carefully, avoiding dropping or bumping it, which could cause damage to the base or other components. Lift the microscope by the arm, never by the base or stage.
-
Storage: When not in use, store the microscope in a clean, dry, and dust-free environment. This helps protect the base and other components from damage and corrosion.
Conclusion: A Foundation of Excellence
The microscope base, often overlooked, is a critical component that underpins the entire system's functionality. Its role extends beyond simple support, contributing to stability, illumination, ease of use, and ultimately, the quality of the images produced. Understanding the base's function, its design variations, and its importance in microscopy allows for better appreciation of this unsung hero of scientific exploration. By ensuring proper maintenance and handling, we can prolong its lifespan and guarantee the continued success of our microscopic investigations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple For 4 And 7
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is The Roman Numeral For 30
Mar 04, 2025
-
Which Point On The Number Line Represents
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 7
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Many Chambers Does A Frog Heart Have
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Function Of The Base Of A Microscope . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
