Which Point On The Number Line Represents
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
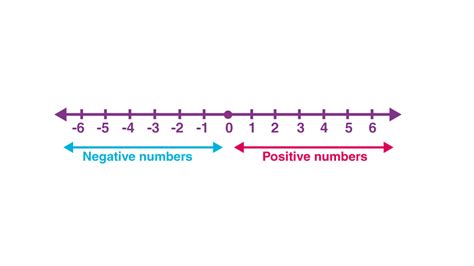
Table of Contents
Which Point on the Number Line Represents? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to represent numbers on a number line is fundamental to grasping various mathematical concepts. This guide delves deep into the topic, explaining different number types, their representation, and tackling various problems related to locating points on a number line. We'll cover integers, fractions, decimals, and even negative numbers, providing a solid foundation for further mathematical explorations.
What is a Number Line?
A number line is a visual representation of numbers on a straight line. It extends infinitely in both directions, typically marked with equally spaced intervals. Zero (0) is the central point, with positive numbers extending to the right and negative numbers extending to the left. This simple tool allows us to visualize the relative position and magnitude of numbers, making comparisons and calculations easier to understand.
Key Features of a Number Line:
- Zero (0): The central point, separating positive and negative numbers.
- Positive Numbers: Located to the right of zero.
- Negative Numbers: Located to the left of zero.
- Equal Intervals: The distance between consecutive numbers is consistent.
- Arrows: Arrows at both ends indicate that the number line extends infinitely.
Representing Different Number Types on the Number Line:
Let's examine how different number types are represented on the number line:
1. Integers:
Integers are whole numbers, including zero, positive numbers, and their negative counterparts. They are easily plotted on the number line as they correspond directly to the marked intervals.
Example:
Representing the integers -3, 0, and 5 on the number line:
-3 would be three units to the left of zero. 0 would be at the center. 5 would be five units to the right of zero.
2. Fractions:
Fractions represent parts of a whole. Representing fractions requires dividing the intervals between integers into smaller, equal parts. The denominator of the fraction determines the number of parts, and the numerator indicates how many parts to count.
Example:
Representing the fraction 3/4 on the number line:
Divide the interval between 0 and 1 into four equal parts. Count three of these parts to the right of zero. This point represents 3/4. Similarly, -1/2 would be located halfway between 0 and -1.
3. Decimals:
Decimals are another way to represent parts of a whole. They are easily plotted on a number line by considering their fractional equivalents. For instance, 0.5 is equivalent to 1/2.
Example:
Representing 0.75 and -0.25 on the number line:
0.75 is equivalent to 3/4 (as shown in the previous example). -0.25 is equivalent to -1/4, so it would be located one-quarter of the way between 0 and -1, to the left of zero.
4. Mixed Numbers:
Mixed numbers combine whole numbers and fractions (e.g., 2 1/2). Representing them involves identifying the whole number part and then adding the fractional part.
Example:
Representing 2 1/2 on the number line:
Locate the integer 2. Then, divide the interval between 2 and 3 into two equal parts and count one part to the right of 2.
Solving Problems Involving Points on a Number Line:
Let's tackle some examples to solidify our understanding:
Problem 1: Which point on the number line represents the number 7?
Solution: Locate the number 7, which is seven units to the right of zero on the number line.
Problem 2: Which point represents the fraction 2/3?
Solution: Divide the interval between 0 and 1 into three equal parts. Count two of these parts to the right of zero. This point represents 2/3.
Problem 3: What number is represented by the point located halfway between -2 and 0?
Solution: The midpoint between -2 and 0 is -1.
Problem 4: A number line is marked with intervals of 0.5. Which point represents 2.5?
Solution: Since the intervals are 0.5, count five intervals to the right of zero (5 * 0.5 = 2.5). This point represents 2.5.
Problem 5: Comparing Numbers on the Number Line:
Which is greater, -3 or -5?
Solution: On a number line, numbers increase as we move to the right. Since -3 is to the right of -5, -3 is greater than -5.
Problem 6: Absolute Value on a Number Line:
What is the absolute value of -4?
Solution: The absolute value represents the distance from zero. The distance between -4 and 0 is 4 units. Therefore, |-4| = 4.
Advanced Concepts and Applications:
Beyond basic representation, number lines are instrumental in understanding:
-
Inequalities: Number lines help visualize inequalities (e.g., x > 2, x ≤ -1). The solution set is represented by the region of the number line satisfying the inequality.
-
Coordinate Geometry: The number line is the foundation for coordinate systems (like Cartesian coordinates) which allow us to represent points in two or more dimensions.
-
Solving Equations: Number lines can provide a visual approach to solving simple equations. For example, if x + 3 = 5, we can visualize finding the value of x by moving 3 units to the left from 5 on the number line.
Practical Applications in Real Life:
Number lines are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have numerous practical applications:
-
Temperature Measurement: Thermometers essentially function as vertical number lines, representing temperature above and below zero.
-
Measurement Scales: Rulers and measuring tapes use number lines to measure length and distance.
-
Timelines: Historians and project managers use number lines (timelines) to visualize events and their chronological order.
-
Financial Tracking: Number lines can be used to represent financial gains and losses over time.
Conclusion:
The number line is a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing numbers and their relationships. Mastering its use is crucial for success in mathematics and its diverse applications in the real world. By understanding how to represent various number types on the number line and applying this knowledge to problem-solving, you build a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Practice regularly with different types of problems, and you'll find it increasingly intuitive and beneficial to your mathematical journey. Remember to focus on the core concepts – zero as the central point, the direction of positive and negative numbers, and the consistent intervals – and you'll confidently navigate the world of numbers represented on a number line.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 36 Inches
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is The Major Product Of The Following Reaction
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 50
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 50 Cm
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 48 Inches
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Point On The Number Line Represents . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
