Formula Of Perimeter Of Regular Polygon
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 4 min read
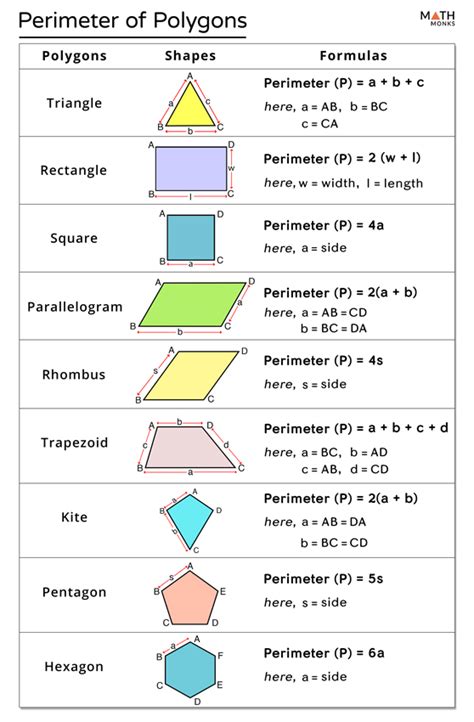
Table of Contents
- Formula Of Perimeter Of Regular Polygon
- Table of Contents
- The Formula for the Perimeter of a Regular Polygon: A Comprehensive Guide
- What is a Regular Polygon?
- The Perimeter Formula: Simplicity and Elegance
- Understanding the Formula's Components
- Example Calculations: Putting the Formula into Practice
- Beyond the Basic Formula: Exploring Related Concepts
- Apothem and Area: Interconnected Concepts
- Relationship with Radius and Central Angle
- Applications in Real-World Scenarios
- Advanced Concepts and Considerations
- Circumradius and Inradius
- Derivation of Area Formula from Perimeter
- Dealing with Irregular Polygons
- Conclusion: Mastering the Perimeter of Regular Polygons
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Formula for the Perimeter of a Regular Polygon: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the perimeter of a regular polygon is fundamental in geometry and has wide-ranging applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will delve into the formula, its derivation, applications, and related concepts, ensuring a thorough understanding for students and professionals alike.
What is a Regular Polygon?
Before diving into the perimeter formula, let's define our subject: a regular polygon. A regular polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure with straight sides of equal length and equal angles. This uniformity is key to understanding its perimeter calculation. Examples include:
- Equilateral Triangle: A three-sided regular polygon.
- Square: A four-sided regular polygon.
- Regular Pentagon: A five-sided regular polygon.
- Regular Hexagon: A six-sided regular polygon.
- Regular Octagon: An eight-sided regular polygon.
And so on, extending to polygons with any number of sides. The key is the regularity – equal sides and equal angles. Irregular polygons, on the other hand, lack this uniformity.
The Perimeter Formula: Simplicity and Elegance
The formula for the perimeter of a regular polygon is remarkably straightforward:
Perimeter = n * s
Where:
- n represents the number of sides in the polygon.
- s represents the length of one side.
This simplicity stems directly from the polygon's regularity. Since all sides are equal in length, we can simply multiply the length of a single side by the total number of sides to obtain the total perimeter.
Understanding the Formula's Components
Let's break down the components of the formula to further solidify understanding:
-
'n' - The Number of Sides: This is a whole number representing how many sides the polygon possesses. It's crucial to correctly identify this value before applying the formula.
-
's' - The Side Length: This represents the length of a single side of the polygon. Ensure consistent units (e.g., centimeters, meters, inches) are used throughout the calculation to avoid errors.
Example Calculations: Putting the Formula into Practice
Let's illustrate the formula with a few examples:
Example 1: A Regular Hexagon
Imagine a regular hexagon with a side length (s) of 5 cm. To calculate the perimeter:
Perimeter = n * s = 6 * 5 cm = 30 cm
Example 2: A Regular Pentagon
Consider a regular pentagon with a side length (s) of 8 inches. The perimeter is:
Perimeter = n * s = 5 * 8 inches = 40 inches
Example 3: A Square (A Special Case)
A square is a special case of a regular polygon (a quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles). If a square has a side length of 12 meters, its perimeter is:
Perimeter = n * s = 4 * 12 meters = 48 meters
Beyond the Basic Formula: Exploring Related Concepts
While the basic perimeter formula is simple, understanding related concepts enhances its applicability and broadens geometrical knowledge.
Apothem and Area: Interconnected Concepts
The apothem of a regular polygon is the distance from the center of the polygon to the midpoint of any side. The apothem is crucial in calculating the area of a regular polygon. The area (A) is given by:
A = (1/2) * n * s * a
Where 'a' represents the apothem. This formula demonstrates the interconnectedness of different geometrical properties.
Relationship with Radius and Central Angle
The radius of a regular polygon is the distance from the center to any vertex. The central angle, formed by two consecutive radii, is given by:
Central Angle = 360° / n
This relationship highlights the inherent symmetry within regular polygons.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The formula for the perimeter of a regular polygon finds practical application in various fields:
- Engineering: Calculating the length of materials needed for constructing regular polygonal structures.
- Architecture: Designing buildings with regular polygonal features.
- Cartography: Measuring distances on maps involving regular polygonal shapes.
- Computer Graphics: Creating regular polygonal shapes in computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Game Development: Designing game levels and environments involving regular polygons.
Advanced Concepts and Considerations
For more advanced applications, a deeper understanding is required.
Circumradius and Inradius
The circumradius is the radius of the circumscribed circle (the circle that passes through all vertices of the polygon). The inradius is the radius of the inscribed circle (the circle that is tangent to all sides of the polygon). These radii are related to the side length and apothem.
Derivation of Area Formula from Perimeter
The area formula, A = (1/2) * n * s * a, can be derived using trigonometry and the concept of dividing the regular polygon into congruent triangles. This demonstrates the mathematical underpinnings of the formula.
Dealing with Irregular Polygons
While the simple formula only applies to regular polygons, finding the perimeter of an irregular polygon involves summing the lengths of all its sides individually. This calculation is more involved and requires knowing the length of each side.
Conclusion: Mastering the Perimeter of Regular Polygons
The formula for the perimeter of a regular polygon, Perimeter = n * s, is a fundamental concept in geometry. Its simplicity belies its power and versatility across various disciplines. Understanding this formula, coupled with related concepts like apothem, radius, and area calculations, provides a robust foundation for tackling more complex geometrical problems. By applying the concepts explained in this guide, students and professionals can confidently solve problems involving regular polygons and appreciate the beauty and practicality of geometrical principles. Remember to always double-check your work and ensure consistent units for accurate results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
List Of All Perfect Square Numbers
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Smallest Fruit In The World
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Do Elements In The Same Column Have In Common
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is More Important Heart Or Brain
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Has The Most Biomass
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Formula Of Perimeter Of Regular Polygon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
