What Do Elements In The Same Column Have In Common
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
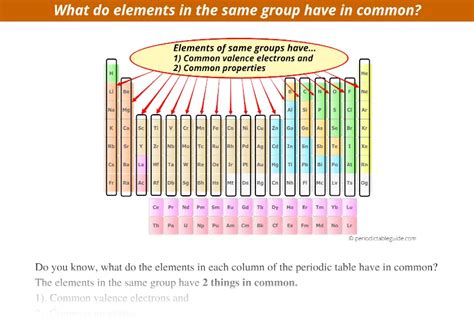
Table of Contents
What Do Elements in the Same Column Have in Common? Understanding Periodic Table Groupings
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, organizes elements based on their atomic structure and properties. A fundamental concept in understanding this organization is recognizing the similarities between elements found within the same column, also known as a group or family. This article delves deep into the shared characteristics of elements in the same column, exploring the underlying reasons for these similarities and their implications in various chemical and physical phenomena.
The Significance of Electron Configuration
The key to understanding why elements in the same column share similar properties lies in their electron configuration. Specifically, it's the number of electrons in their outermost shell, called the valence shell, that dictates their reactivity and bonding behavior. Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. This fundamental similarity is the driving force behind their shared chemical properties.
Valence Electrons: The Key Players
Valence electrons are the electrons located in the highest energy level of an atom. These electrons are the ones most readily involved in chemical bonding. They are responsible for the formation of chemical bonds, determining an element's reactivity, and influencing its overall behavior in chemical reactions.
For example: Elements in Group 1 (alkali metals) all have one valence electron. Elements in Group 18 (noble gases) all have a full valence shell (except helium, which has only two electrons, but a full valence shell), making them exceptionally unreactive.
Exploring the Main Groups: A Detailed Look
Let's explore the similarities within some of the major groups of the periodic table. We'll examine their general properties, common reactions, and real-world applications.
Group 1: Alkali Metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr)
- Shared Property: All alkali metals have one valence electron. This single valence electron is easily lost, resulting in the formation of +1 ions.
- Reactivity: They are highly reactive, readily reacting with water to produce hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. Their reactivity increases as you go down the group.
- Physical Properties: They are soft, silvery-white metals with low melting points and densities.
- Applications: Sodium (Na) is crucial in our bodies, potassium (K) is essential for plant growth, and lithium (Li) is used in batteries.
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra)
- Shared Property: These metals possess two valence electrons. They tend to lose these two electrons to form +2 ions.
- Reactivity: They are reactive but less so than alkali metals. They react with water, but the reaction is slower and less vigorous.
- Physical Properties: They are harder, denser, and have higher melting points than alkali metals.
- Applications: Magnesium (Mg) is used in alloys and in medicine, calcium (Ca) is vital for bones and teeth, and strontium (Sr) is used in fireworks.
Group 17: Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At)
- Shared Property: Halogens have seven valence electrons. They are one electron short of a full valence shell, making them highly reactive.
- Reactivity: They readily gain one electron to form -1 ions, forming halide ions (F⁻, Cl⁻, Br⁻, I⁻). Reactivity decreases down the group.
- Physical Properties: Their physical states vary: fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid.
- Applications: Chlorine (Cl) is used in water purification, fluorine (F) is used in toothpaste, and iodine (I) is essential for thyroid function.
Group 18: Noble Gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn)
- Shared Property: Noble gases have a complete valence shell (except helium). This full valence shell makes them extremely stable and unreactive.
- Reactivity: They are largely inert and rarely form compounds. However, under certain conditions, heavier noble gases can form compounds.
- Physical Properties: They are all gases at room temperature.
- Applications: Helium (He) is used in balloons and MRI machines, neon (Ne) is used in lighting, and argon (Ar) is used in welding.
Transition Metals: A Different Story
Transition metals, located in the middle of the periodic table, exhibit a more complex pattern of similarities. While they don't share the same number of valence electrons like the main group elements, they share certain characteristics:
- Variable Oxidation States: Transition metals can exist in multiple oxidation states, meaning they can lose varying numbers of electrons to form ions with different charges. This leads to a greater diversity of compounds.
- Formation of Colored Compounds: Many transition metal compounds are brightly colored due to the electronic transitions within their d orbitals.
- Catalytic Activity: Many transition metals and their compounds act as catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions.
- Magnetic Properties: Some transition metals exhibit magnetic properties, such as ferromagnetism (like iron).
Beyond the Columns: Understanding Trends Across the Periodic Table
While columns highlight similarities, understanding trends across the periodic table (periods) is equally important. These trends include:
- Atomic Radius: Atomic radius generally increases down a group and decreases across a period.
- Electronegativity: Electronegativity, the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond, generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Ionization Energy: Ionization energy, the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Applications and Real-World Implications
The properties of elements within the same group have profound implications across various fields:
- Medicine: Many elements are essential for human health. For instance, sodium, potassium, calcium, and iodine play vital roles in bodily functions. Understanding the properties of these elements is crucial in developing medications and treatments.
- Materials Science: The properties of elements determine the characteristics of materials. The choice of elements in alloys and other materials depends heavily on their group properties. For example, the strength and lightness of magnesium alloys make them suitable for aerospace applications.
- Energy: The reactivity of alkali metals and the inertness of noble gases are exploited in various energy technologies. Lithium-ion batteries utilize the reactivity of lithium, while argon is used in incandescent light bulbs.
- Environmental Science: Understanding the reactivity of elements is essential for managing environmental issues like water purification and air pollution.
Conclusion: The Periodic Table – A Powerful Tool
The periodic table is more than just a list of elements; it's a powerful tool that organizes elements based on their fundamental properties. The similarities shared by elements in the same column – a direct result of their identical valence electron configurations – are the foundation for understanding their chemical behavior, reactivity, and vast array of applications. By understanding these relationships, we can unlock a deeper appreciation of the chemical world and its influence on our lives. The careful study of these groupings and the trends across the periodic table remains crucial for advances in various scientific and technological fields. Further research into the nuances of electronic configurations and their impact on chemical behavior continues to expand our knowledge and capabilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Real Life Example Of A Scalene Triangle
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Do You Convert A Ratio Into A Percent
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Fahrenheit Is 32 Degrees Celsius
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Sides Is A Heptagon
Mar 18, 2025
-
Who Was The Father Of The Renaissance
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Do Elements In The Same Column Have In Common . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
