Examples Of Elements In Everyday Life
Juapaving
Apr 03, 2025 · 7 min read
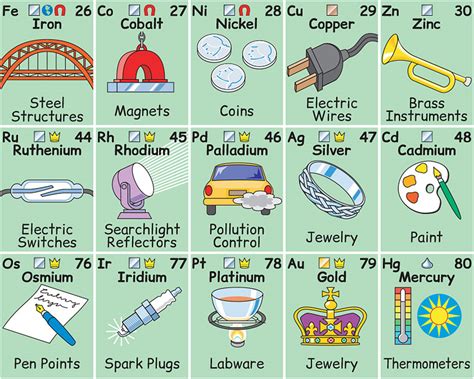
Table of Contents
Examples of Elements in Everyday Life: A Comprehensive Guide
We are surrounded by elements, the fundamental building blocks of matter, in our everyday lives. While we may not always realize it, these elements are essential components of everything from the air we breathe to the food we eat and the technology we use. Understanding these elements and their properties provides a deeper appreciation for the world around us. This article will delve into various examples of elements found in everyday life, exploring their properties and applications.
The Common Elements: Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen
Four elements – oxygen (O), carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and nitrogen (N) – are particularly prevalent and crucial for life on Earth. Let's explore their ubiquitous presence:
Oxygen (O): The Breath of Life
Oxygen constitutes approximately 21% of Earth's atmosphere. Its most critical role is in respiration, the process by which living organisms convert glucose into energy. We inhale oxygen, and it's vital for cellular respiration, allowing our bodies to function. Beyond respiration, oxygen is also a key component in combustion, the process of burning, which is used in many everyday applications, from cooking to powering vehicles. Oxygen is also a crucial element in many industrial processes, including the production of steel and other metals. Think of its presence in welding and cutting torches!
Carbon (C): The Backbone of Life and Beyond
Carbon is the fundamental element of organic chemistry, forming the backbone of all living organisms. It is incredibly versatile, forming strong bonds with other carbon atoms and numerous other elements. This allows carbon to create a vast array of complex molecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids – all essential for life. Beyond biological systems, carbon is found in countless other materials, including graphite (in pencils), diamonds, and coal. The versatile nature of carbon also makes it a key player in the manufacturing of various materials, such as plastics and synthetic fibers.
Hydrogen (H): The Lightest Element with Huge Impact
Hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe. While it's not often seen in its pure form in daily life, hydrogen is a crucial component of many important compounds. Water (H₂O), for instance, is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Hydrogen is also a key element in numerous fuels, including natural gas and propane. The development of hydrogen fuel cells offers a promising avenue for cleaner energy in the future. Hydrogen's lightness and reactivity make it a valuable element in various industrial processes.
Nitrogen (N): Essential for Growth and Beyond
Nitrogen makes up about 78% of Earth's atmosphere. While we can't breathe nitrogen directly, it's a vital component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil through a process called nitrogen fixation, a critical part of the nitrogen cycle. This cycle makes nitrogen available to plants, and consequently, the animals that consume them. Nitrogen is also used extensively in the production of fertilizers, ensuring crop growth and feeding the global population. Beyond agriculture, nitrogen finds its use in the production of various chemicals, including explosives and pharmaceuticals.
The Metals: Iron, Aluminum, and More
Metals are essential components of many everyday objects and technologies. Let’s examine some key examples:
Iron (Fe): Strength and Durability
Iron is a strong, relatively abundant, and readily available metal, making it an indispensable part of many everyday items and infrastructure. Steel, an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, is exceptionally strong and durable, used extensively in construction, vehicles, and countless other applications. Iron is also a crucial element in our bodies, forming part of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in our blood. The importance of iron in our diet highlights its essential role in maintaining good health.
Aluminum (Al): Lightweight and Versatile
Aluminum is a lightweight yet remarkably strong metal with excellent corrosion resistance. Its widespread use is evident in everything from beverage cans to aircraft parts. Aluminum's lightweight nature makes it ideal for transportation, while its corrosion resistance ensures long-lasting products. Its use is also expanding in the construction industry, providing lighter and more durable building materials. The recyclability of aluminum makes it an environmentally friendly choice.
Other Important Metals
Numerous other metals play crucial roles in our daily lives. Copper (Cu) is an excellent conductor of electricity, making it vital for electrical wiring. Gold (Au) is a highly prized metal due to its inertness and aesthetic appeal, used in jewelry and electronics. Zinc (Zn) is an essential trace element for human health, playing a crucial role in numerous enzymatic processes. These are but a few examples of the many metals that contribute to our modern world.
Non-Metals: Silicon, Sulfur, and Chlorine
Non-metals also play vital roles, often in unexpected ways:
Silicon (Si): The Heart of Modern Electronics
Silicon is a non-metal vital to the technology that defines the modern age. Silicon chips, the foundation of computers and electronic devices, rely on silicon's unique semiconducting properties. These properties allow silicon to control the flow of electricity, making it the workhorse of modern electronics. The miniaturization of electronic devices is largely attributable to advances in silicon technology.
Sulfur (S): From Matches to Medicine
Sulfur is a non-metal with diverse applications. Historically, sulfur was used in the production of gunpowder and matches. Today, it remains crucial in the manufacture of sulfuric acid, a key industrial chemical used in the production of fertilizers and various other products. Sulfur compounds also play a significant role in certain medicinal applications.
Chlorine (Cl): Water Purification and Beyond
Chlorine is a highly reactive non-metal commonly used in water purification to disinfect drinking water and swimming pools. It effectively kills harmful bacteria and other microorganisms, ensuring the safety of water supplies. Chlorine also finds applications in the production of various chemicals and industrial processes. Its reactivity needs careful management and safety precautions.
The Noble Gases: Inert and Useful
The noble gases – helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn) – are chemically inert elements, meaning they rarely react with other elements. This property makes them useful in various applications:
Helium (He): Balloons and More
Helium is the most well-known noble gas, frequently used in balloons and airships due to its lightness and non-flammability. It's also used in cryogenics, particularly in MRI machines.
Neon (Ne): Glowing Lights
Neon is famous for its use in neon signs, producing a characteristic bright red light. Other noble gases are also used in lighting, producing different colors.
Argon (Ar): Protective Atmosphere
Argon is an inert gas used to create a protective atmosphere in welding and other industrial processes, preventing oxidation and other unwanted reactions.
Elements in Everyday Materials
Many everyday materials are composed of multiple elements combined to form compounds or alloys. Let’s examine some examples:
- Steel: Primarily iron and carbon, but often contains other alloying elements like manganese, chromium, nickel, and molybdenum to enhance its properties.
- Brass: An alloy of copper and zinc, known for its golden color and ductility.
- Bronze: An alloy of copper and tin, historically significant and still used in various applications.
- Glass: Primarily silicon dioxide (SiO₂), often with additives to modify its properties.
- Cement: A complex mixture of various compounds, including calcium silicates and aluminates.
- Plastics: Polymers composed of long chains of carbon-based molecules, often incorporating other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, chlorine, and nitrogen.
Conclusion: The Elemental World Around Us
This comprehensive overview demonstrates the pervasive presence of elements in our daily lives. From the air we breathe to the technology we use, elements form the foundation of our world. Understanding the properties and applications of these elements fosters a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of the natural world and the ingenuity of human innovation. As we continue to explore the potential of these fundamental building blocks of matter, we can expect even more significant advancements in technology and materials science, shaping our future in countless ways. The study of elements is a journey into the very essence of our existence, revealing the remarkable complexity and beauty inherent in the seemingly simple.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
4 Kingdoms In The Domain Eukarya
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is In One Meter
Apr 03, 2025
-
Most Abundant Metal In The Earth Crust
Apr 03, 2025
-
Who Is Credited For Discovering Cells
Apr 03, 2025
-
Is 7 A Prime Or Composite Number
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Examples Of Elements In Everyday Life . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
