Most Abundant Metal In The Earth Crust
Juapaving
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
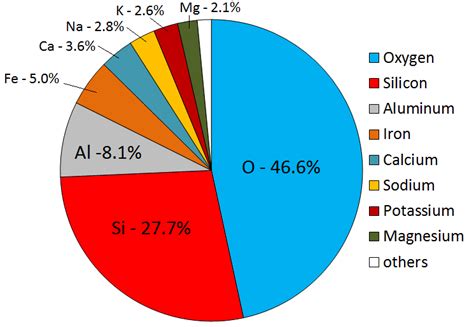
Table of Contents
The Most Abundant Metal in the Earth's Crust: Aluminum's Reign
Aluminum, a lightweight, silvery-white metal, reigns supreme as the most abundant metal in the Earth's crust. While often overlooked in everyday conversations about metals, its prevalence is staggering, shaping the landscapes we see and playing a crucial role in modern technology. Understanding aluminum's dominance, its properties, and its applications is key to appreciating the geological composition of our planet and its impact on human civilization.
The Abundance of Aluminum: A Geological Perspective
Aluminum isn't found freely in nature; instead, it exists primarily as a component of various minerals, most notably feldspars and clays. These minerals are incredibly widespread throughout the Earth's crust, making aluminum the third most abundant element overall (after oxygen and silicon), and by far the most abundant metal. Its abundance is estimated to be around 8.13% of the Earth's crust by weight. This significantly surpasses the abundance of other common metals like iron (5%), calcium (3.6%), sodium (2.8%), potassium (2.6%), and magnesium (2.1%).
Understanding Mineral Composition: The Key to Aluminum's Dominance
Aluminum's abundance isn't simply due to its presence in a few minerals; it's the vast quantity of aluminum-bearing minerals that truly underscores its dominance. Feldspars, for example, are crucial components of igneous rocks like granite and basalt, which form the bedrock of continents and ocean floors. Clays, formed from the weathering of these rocks, also contain significant amounts of aluminum. These processes of rock formation and weathering contribute to aluminum's pervasive distribution across various geological formations.
Geographic Distribution: Aluminum's Global Reach
Aluminum's widespread distribution isn't uniform across the globe. The concentration of aluminum-rich minerals varies depending on geological factors like tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, and sedimentary processes. However, its presence is globally significant, found in a diverse range of locations and geological formations worldwide.
Aluminum's Properties: A Versatile Metal
Aluminum's impressive abundance is complemented by its unique properties, making it a highly versatile and desirable metal for a vast array of applications.
Lightweight Yet Strong: A Winning Combination
One of aluminum's most attractive features is its low density. It's significantly lighter than most other common metals, including iron and steel, without compromising significantly on strength. This lightweight strength makes it ideal for various applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in aerospace engineering and automotive manufacturing.
Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Durability and Longevity
Aluminum is incredibly resistant to corrosion due to the formation of a protective aluminum oxide layer on its surface. This passivation layer shields the underlying metal from further oxidation, ensuring durability and longevity, even in harsh environments. This is a key reason why aluminum is frequently used in outdoor applications, such as building facades, window frames, and automotive body parts.
High Electrical Conductivity: Powering Modern Infrastructure
Aluminum is a remarkably good conductor of electricity, second only to copper in this regard. Its lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for electrical transmission lines and wiring, particularly for long-distance power distribution.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity: Efficient Heat Transfer
Aluminum's high thermal conductivity makes it an ideal material for heat sinks, cooking utensils, and other applications where efficient heat transfer is vital. Its ability to quickly and effectively dissipate heat contributes to improved performance and efficiency in various devices and systems.
Malleability and Ductility: Ease of Shaping and Manufacturing
Aluminum is both malleable (easily shaped) and ductile (easily drawn into wires), making it highly adaptable for various manufacturing processes. These properties enable the creation of intricate shapes and structures, contributing to its widespread use in diverse industries.
Applications of Aluminum: A Metal for the Modern Age
The combination of abundance, desirable properties, and ease of processing has made aluminum a cornerstone of modern society. Its applications span a vast range of industries, demonstrating its versatility and importance.
Transportation: Lightweight and Durable Vehicles
The automotive and aerospace industries heavily rely on aluminum due to its lightweight yet robust nature. Aluminum alloys are used extensively in car bodies, aircraft components, and spacecraft structures, significantly reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency in vehicles.
Packaging: Protecting Goods and Preserving Freshness
Aluminum foil and cans are ubiquitous in food and beverage packaging. Aluminum's corrosion resistance and ability to form airtight seals make it ideal for preserving food freshness and preventing contamination. Its recyclability adds to its environmentally friendly profile.
Construction: Durable and Aesthetic Buildings
Aluminum's corrosion resistance and lightweight nature make it a popular choice in construction. It's used in building facades, window frames, roofing, and various structural components, offering both durability and aesthetic appeal. Aluminum's recyclability makes it a sustainable building material.
Electrical Engineering: Powering Our World
Aluminum's high electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness have led to its widespread use in electrical transmission lines and wiring. Its lightweight nature also makes it easier to install and maintain these vital infrastructure components.
Consumer Electronics: Lightweight and Efficient Devices
Aluminum's lightweight nature, strength, and heat dissipation capabilities make it an attractive material for consumer electronics such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets. Its sleek appearance also enhances the aesthetic appeal of these devices.
Other Applications: A Diverse Range of Uses
Aluminum's applications extend far beyond the examples mentioned above. It's used in the production of kitchen utensils, medical devices, sporting goods, and a wide range of other products, demonstrating its versatility and importance in modern manufacturing.
The Recycling of Aluminum: A Sustainable Practice
Aluminum is a highly recyclable material, making it an environmentally friendly choice compared to other metals. Recycling aluminum requires significantly less energy compared to producing aluminum from bauxite ore, reducing the environmental impact associated with its production. This recyclability contributes to the sustainability of aluminum's use in various industries, promoting a circular economy and reducing reliance on virgin aluminum production.
The Environmental Benefits of Aluminum Recycling
Aluminum recycling significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and water usage compared to primary aluminum production. It also helps conserve natural resources and minimizes the environmental impact associated with mining and processing bauxite ore.
The Process of Aluminum Recycling
Recycling aluminum involves collecting aluminum scrap, melting it down, and recasting it into new products. This process can be repeated multiple times without significant loss of quality, making aluminum a highly sustainable material.
The Future of Aluminum: Continued Importance and Innovation
Aluminum's importance in modern society is expected to continue, with ongoing research and development focused on improving aluminum alloys and expanding its applications. The development of new aluminum alloys with enhanced properties, such as increased strength or corrosion resistance, will further broaden its use across various industries.
Aluminum's Role in Sustainable Technologies
Aluminum's lightweight nature and recyclability make it a critical component in the development of sustainable technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure. Its use in these sectors is expected to increase significantly in the coming years.
Ongoing Research and Development
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving aluminum's properties and developing new aluminum alloys with enhanced performance characteristics. This continuous innovation ensures aluminum remains a relevant and versatile material for future applications.
In conclusion, aluminum's reign as the most abundant metal in the Earth's crust is firmly established. Its unique combination of properties, coupled with its widespread availability and ease of processing, has made it an indispensable material across numerous industries. Furthermore, aluminum's recyclability and sustainability contribute to its enduring importance in a world increasingly focused on environmental responsibility and resource conservation. Aluminum's story is not just a geological tale but a testament to the human ingenuity in harnessing the Earth's resources for progress and innovation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many 1000s In A Million
Apr 04, 2025
-
Evaporation Of Water Endothermic Or Exothermic
Apr 04, 2025
-
Difference Between Real And Natural Numbers
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Energy Conversion Occurs During Photosynthesis
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Are Fish Able To Live In A Frozen Lake
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Most Abundant Metal In The Earth Crust . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
