Examples For Push And Pull Forces
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
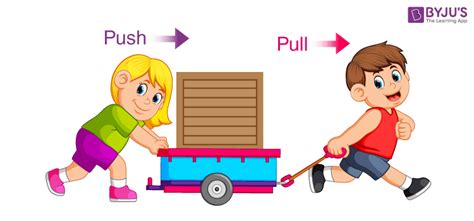
Table of Contents
Examples of Push and Pull Forces: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding push and pull forces is fundamental to grasping the principles of physics and how objects interact with each other. These forces, though seemingly simple, govern everything from the movement of planets to the everyday actions we perform. This comprehensive guide delves into numerous examples of push and pull forces, categorizing them to enhance understanding and demonstrating their significance in various contexts.
What are Push and Pull Forces?
Before exploring specific examples, let's define the core concepts. A force is simply an interaction that, when unopposed, will change the motion of an object. This change can be a change in speed, direction, or both. Forces are vector quantities, meaning they have both magnitude (strength) and direction.
A push force is a force applied to an object to move it away from the force's source. Think of pushing a shopping cart, opening a door, or hitting a baseball. The force is directed away from your body.
A pull force is a force applied to an object to move it towards the force's source. Examples include pulling a wagon, opening a drawer, or reeling in a fishing line. The force is directed towards your body.
It's crucial to remember that these are not mutually exclusive categories. Many actions involve a combination of push and pull forces.
Examples of Push Forces: A Diverse Spectrum
Let's delve into a multitude of examples, categorized for clarity:
Everyday Push Forces:
- Opening a door: Applying a force away from the door's hinges to open it.
- Pushing a shopping cart: Exerting force to move the cart across the store.
- Kicking a soccer ball: A powerful push force imparts momentum to the ball.
- Pushing a lawnmower: Applying force to move the mower across the lawn.
- Moving a piece of furniture: Requires significant push force to overcome inertia and friction.
- Writing on a whiteboard: The chalk or marker applies a push force to leave a mark.
- Typing on a keyboard: Pushing down on the keys generates the input.
- Playing a musical instrument (e.g., piano, organ): Pushing down on the keys to produce sound.
- Starting a car (manual transmission): Pushing the clutch pedal in and pushing the gear stick.
- Operating a pump: Pushing a lever or handle to pump water or air.
Examples in Sports and Recreation:
- Serving a tennis ball: A powerful push generates the initial velocity of the ball.
- Shooting a basketball: A forceful push launches the ball towards the hoop.
- Hitting a golf ball: A controlled push using a golf club.
- Pushing a sled: Generating force to propel the sled across snow or ice.
- Wrestling: Pushing and shoving opponents to gain advantage.
- Boxing: Punching is a direct application of push force.
Examples in Nature:
- Volcanic eruptions: Massive push force expels molten rock, ash, and gases.
- Earthquakes: The movement of tectonic plates generates enormous push forces that cause ground shaking.
- Glacial movement: The immense weight of glaciers generates a slow, continuous push force that reshapes the landscape.
- Wind pushing trees: Wind exerts a push force on trees, causing them to bend or sway.
- Water erosion: The relentless push of water can wear away rock and soil over time.
- Landslides: Gravity and the weight of the material cause a powerful downward push.
Examples in Machines and Technology:
- A piston in an engine: The explosion of fuel pushes the piston down, converting chemical energy into mechanical energy.
- A rocket launching: The expulsion of hot gases exerts a powerful push force, propelling the rocket upwards.
- A hydraulic press: Uses liquid pressure to generate a strong push force.
- A jet engine: Hot gases expelled from the engine exert a powerful push force, propelling the aircraft forward.
- A bulldozer pushing earth: The machine utilizes a strong push force to move large amounts of earth.
- A printing press: Applies pressure (push force) to transfer ink to paper.
Examples of Pull Forces: A Variety of Applications
Now let's explore a range of examples of pull forces:
Everyday Pull Forces:
- Pulling a drawer open: Applying a force to draw the drawer towards you.
- Pulling a wagon: Exerting a force to move the wagon towards you.
- Pulling a suitcase: Applying force to move your luggage.
- Zipping a zipper: Pulling the slider to close the zipper.
- Unrolling a scroll: Pulling the scroll to reveal its contents.
- Pulling weeds: Removing weeds from the ground by pulling them upwards.
- Opening a curtain: Pulling the curtain cords to open or close them.
- Lifting an object with a rope: Applying upward force to lift the object.
- Using a vacuum cleaner: The suction is essentially a pull force drawing dust and debris into the machine.
- Pulling a bowstring: The action of pulling the bowstring stores potential energy.
Examples in Sports and Recreation:
- Archery: Pulling back the bowstring to launch an arrow.
- Rowing: Pulling the oars through the water to propel the boat.
- Fishing: Pulling the fishing rod to reel in a fish.
- Rock climbing: Pulling oneself upwards using hands and feet.
- Weightlifting: Pulling weights upwards against gravity.
- Kayaking or Canoeing: Pulling the paddle through the water to move forward.
Examples in Nature:
- Gravity: The pull of gravity draws objects towards the Earth's center.
- Magnets: Magnets exert a pull force on ferrous materials.
- The moon's gravitational pull on the tides: The moon's gravity pulls on the Earth's oceans, causing tides.
- Roots of plants pulling nutrients: Plant roots exert a pull force to absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
- Animals pulling food: Animals use their mouths or claws to pull food toward themselves.
- Tendrils of plants pulling on support: Tendrils use pull forces to cling to structures for support.
Examples in Machines and Technology:
- A crane lifting a load: The crane's mechanism exerts a pull force to lift heavy objects.
- A tow truck pulling a car: Exerts a pull force to move a disabled vehicle.
- A winch pulling a cable: Used for various applications requiring pulling force, such as lifting or lowering heavy objects.
- An elevator pulling a car upwards: Uses cables and a motor to generate the necessary pull force.
- A magnetic crane: Uses powerful magnets to pull ferrous materials, such as scrap metal.
- Data cables pulling data: Although not a physical pull, the data transmission uses the concept of pulling data from one point to another.
The Interplay of Push and Pull Forces
It's crucial to understand that many real-world situations involve a complex interplay of both push and pull forces. Consider these examples:
- Walking: While it might seem like simply a push-off from the ground, walking involves a complex interplay of push and pull forces from various muscles in the legs and body, working together to propel you forward.
- Driving a car: The car engine's pistons push, the wheels push against the road, and the brakes pull to slow down.
- Flying an airplane: The engines push the plane forward, while air resistance pulls against it. Lift is a more complex upwards push.
- Swimming: Pushing water backward propels the swimmer forward.
Conclusion: Understanding Forces in Our World
This comprehensive guide illustrates the diverse range of push and pull forces present in our everyday lives, across various scientific fields and in technology. By understanding the fundamental principles of push and pull forces, we gain a deeper appreciation of how the world around us works. From the smallest interactions to the largest cosmic events, these fundamental forces govern movement and interaction at every scale. Further exploration into Newton's Laws of Motion will enhance your understanding of how forces cause changes in motion and the concept of balanced and unbalanced forces.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Minerals Are Considered To Be Essential
Mar 18, 2025
-
Natural Boundary Between France And Itsly
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Side Does A Octagon Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Kingdom Does Euglena Belong To
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lcm Of 5 4 And 2
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Examples For Push And Pull Forces . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
