Equation For The Combustion Of Propane
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
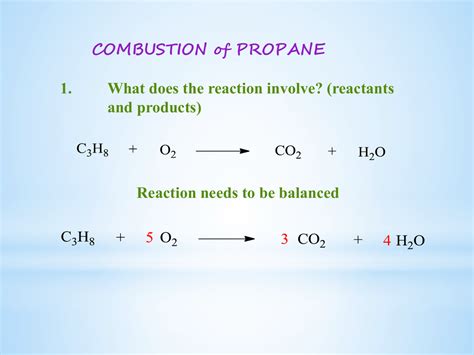
Table of Contents
The Complete Guide to the Propane Combustion Equation: Understanding the Chemistry and Applications
Propane, a ubiquitous fuel source powering everything from barbeques to industrial heating systems, undergoes a fascinating chemical reaction when it burns – combustion. Understanding the equation for propane combustion is crucial for various applications, from ensuring efficient energy utilization to mitigating environmental impact. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this reaction, exploring its balanced equation, different types of combustion, factors influencing the reaction, and its significance in various industries.
The Balanced Equation for Complete Combustion of Propane
The combustion of propane involves its reaction with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat. A balanced chemical equation accurately represents the proportions of reactants and products involved. For complete combustion of propane (C₃H₈), the balanced equation is:
C₃H₈ + 5O₂ → 3CO₂ + 4H₂O + Heat
This equation signifies that one molecule of propane reacts with five molecules of oxygen to produce three molecules of carbon dioxide, four molecules of water, and releases a significant amount of heat. The heat released is the driving force behind propane's utility as a fuel. The balanced equation ensures that the number of atoms of each element remains the same on both sides of the equation, adhering to the fundamental principle of conservation of mass.
Understanding the Different Types of Propane Combustion
While the complete combustion equation provides a simplified picture, propane combustion can occur under varying conditions, resulting in different types of combustion:
1. Complete Combustion:
This is the ideal scenario represented by the balanced equation above. It requires sufficient oxygen to completely oxidize all the carbon and hydrogen atoms in propane. The products are primarily carbon dioxide and water, maximizing heat production and minimizing pollutants.
2. Incomplete Combustion:
Incomplete combustion occurs when there is insufficient oxygen available for the complete oxidation of propane. This results in the formation of carbon monoxide (CO), a highly toxic gas, and soot (carbon particles) in addition to carbon dioxide and water. The equation for incomplete combustion can vary depending on the oxygen availability, but a general representation would be:
C₃H₈ + xO₂ → yCO₂ + zCO + wH₂O + Carbon (Soot) + Heat
Where 'x', 'y', 'z', and 'w' represent variable stoichiometric coefficients depending on the oxygen supply. Incomplete combustion is less efficient, producing less heat and emitting harmful pollutants.
3. Oxidative Combustion:
This type of combustion involves the use of an oxidant stronger than oxygen, such as nitrous oxide (N₂O). Oxidative combustion can lead to higher temperatures and potentially different products. The exact equation will depend on the specific oxidant used.
Factors Influencing Propane Combustion
Several factors significantly influence the efficiency and type of propane combustion:
1. Oxygen Supply:
The most crucial factor is the availability of oxygen. Sufficient oxygen ensures complete combustion, maximizing energy output and minimizing pollutant formation. Insufficient oxygen leads to incomplete combustion, generating harmful byproducts.
2. Temperature:
The initial temperature of the propane and the surrounding environment affects the reaction rate. Higher temperatures generally accelerate the combustion process.
3. Pressure:
Pressure also plays a role. Higher pressures can increase the reaction rate and potentially alter the equilibrium between complete and incomplete combustion.
4. Mixing of Propane and Oxygen:
Proper mixing of propane and oxygen is essential for efficient combustion. Inhomogeneous mixing can lead to localized areas with insufficient oxygen, resulting in incomplete combustion.
5. Presence of Catalysts:
Catalysts can influence the reaction rate and potentially alter the reaction pathway, affecting the products formed.
Applications of Propane Combustion
Propane's combustion finds widespread applications across various sectors:
1. Residential Heating:
Propane is a popular fuel for home heating systems, offering efficient and reliable heat generation. The combustion process warms air or water, which is then circulated throughout the house.
2. Industrial Heating:
Various industrial processes utilize propane combustion for heating applications, including metalworking, manufacturing, and drying. The high heat output of propane makes it suitable for high-temperature applications.
3. Cooking:
Propane-powered stoves and grills are commonly used for cooking, providing a controllable and efficient heat source. The clean burning nature of propane (during complete combustion) makes it preferable in many culinary settings.
4. Transportation:
While less common than gasoline or diesel, propane is utilized as a fuel for vehicles, offering a cleaner-burning alternative. Propane autogas is gaining popularity as environmental concerns become increasingly important.
5. Power Generation:
Propane combustion can generate electricity in power plants, particularly in smaller-scale applications. Propane-fired generators provide a reliable backup power source during outages.
Environmental Impact of Propane Combustion
While propane is considered a relatively clean-burning fuel compared to other fossil fuels like coal or oil, its combustion still produces greenhouse gases. Complete combustion primarily yields carbon dioxide (CO₂), a significant contributor to climate change. Incomplete combustion releases carbon monoxide (CO), a toxic pollutant, and soot (particulate matter), which negatively impacts air quality and human health.
Minimizing the environmental impact requires ensuring complete combustion through proper combustion equipment design and operation, along with efficient fuel utilization. Ongoing research explores alternative fuel sources and technologies to further reduce the carbon footprint associated with propane combustion.
Conclusion: A Versatile and Powerful Reaction
The equation for the combustion of propane, seemingly simple, underpins a complex chemical reaction with profound implications. Understanding the different types of combustion, influencing factors, and applications of this reaction is essential for optimizing energy efficiency, mitigating environmental impact, and ensuring safe and responsible use of propane as a fuel source. The balanced equation serves as a foundation for further investigation into the intricacies of this vital chemical process, enabling us to utilize propane's energy potential while minimizing its detrimental effects. As we continue to explore cleaner energy solutions, a thorough comprehension of propane combustion remains critical in managing the transition towards a more sustainable future. Future research focusing on enhanced combustion technologies and alternative fuel sources will further refine our understanding and application of this fundamental chemical reaction.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not
Mar 10, 2025
-
250 Square Meters To Square Feet
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Millimeters Are In One Meter
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Milliseconds Are In A Minute
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Copper Have
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Equation For The Combustion Of Propane . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
