Earth Is Divided Into How Many Time Zones
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
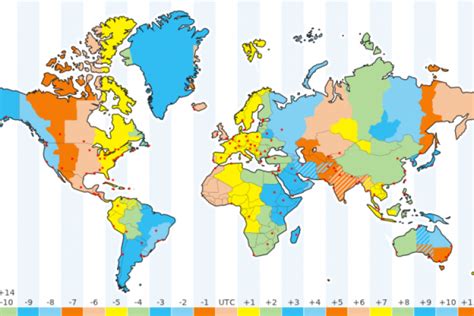
Table of Contents
Earth is Divided into How Many Time Zones? A Comprehensive Guide
The Earth, our magnificent blue marble, spins gracefully on its axis, completing one rotation every 24 hours. This rotation, coupled with the sun's position, gives rise to the concept of time zones – a crucial element in our globally interconnected world. But how many time zones actually divide our planet? The answer isn't as straightforward as you might think. Let's delve into the fascinating world of time zones, exploring their history, their complexities, and the surprisingly nuanced answer to our central question.
The Simple Answer: 24 Time Zones
The most common and readily accepted answer is 24 time zones. This is based on a simple calculation: the Earth's 360 degrees of longitude are divided by 24 hours in a day, yielding 15 degrees of longitude per time zone. This seemingly straightforward system, however, masks a far more intricate reality.
The 15-Degree Rule: A Theoretical Ideal
The 15-degree-per-time-zone rule is a convenient simplification. It provides a framework for understanding the basic principle: as the Earth rotates eastward, each 15-degree increment marks a one-hour shift in time. This is largely true, creating a consistent system for coordinating global activities and avoiding perpetual confusion. However, national borders, geographical realities, and political considerations often supersede this theoretical ideal.
The Complex Reality: More Than Just 24
While 24 time zones provide a foundational understanding, the actual number of time zones in use globally is significantly higher. This discrepancy arises due to several factors:
Irregular Time Zone Boundaries: Political and Practical Considerations
Time zone boundaries rarely align precisely with the 15-degree meridians. National and regional boundaries often override the geographical neatness of the theoretical system. Countries frequently adopt time zones that best suit their economic and social needs, leading to irregular and often seemingly illogical boundaries. For instance, a single country might span multiple time zones or a time zone might encompass parts of multiple countries. This means the map of time zones is a patchwork quilt, far from a neat grid.
Fractional Time Zones: Sub-Hour Offsets
To further complicate matters, some regions utilize fractional time zones. These areas don't follow the strict one-hour increments. Instead, they might deviate by 30 minutes or even 15 minutes. This phenomenon is prevalent in places where unique geographical conditions or economic considerations necessitate a slight adjustment to the standard time zone. Such adjustments ensure a more efficient alignment with neighboring countries or regions.
Daylight Saving Time (DST): A Seasonal Shift
The widespread implementation of Daylight Saving Time (DST) adds another layer of complexity. Many countries shift their clocks forward by an hour during warmer months to maximize daylight hours. This seasonal change means that the effective time zone can change twice a year, further blurring the lines of a fixed number. This seasonal adjustment doesn't change the core number of time zones, but it does increase the number of different times actively in use at any given moment.
Multiple Time Zones Within a Single Country: The Case of Russia
Some countries even maintain multiple time zones within their own borders. Russia, for example, has an extensive landmass spanning several longitudinal degrees. As a result, it uses eleven distinct time zones. This highlights the practical necessity of adjusting time to accommodate the vast geographical extent of certain nations.
Beyond the Numbers: The Significance of Time Zones
The intricacies of time zones go far beyond simple counting. The establishment of time zones reflects human efforts to organize, coordinate, and synchronize activities across a globally interconnected world. Understanding these complexities is crucial for several reasons:
International Commerce and Communication: Streamlining Global Interactions
The standardization of time zones, despite its inconsistencies, is paramount for international commerce and communication. Businesses need to coordinate schedules, meetings, and transactions across multiple countries and continents. Accurate and consistent timekeeping ensures efficient operations and prevents costly misunderstandings.
Air Travel and Navigation: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
Air travel relies heavily on precise timekeeping. Pilots, air traffic controllers, and other aviation professionals use time zones to coordinate flight plans, avoid collisions, and maintain safety standards. The precise calculation of flight times and adherence to schedules heavily depend on the accurate understanding of time zone differences.
Data Synchronization and Global Networks: The Backbone of Modern Technology
Our modern digital infrastructure operates across time zones. Data synchronization, network management, and global communication networks rely on the careful management and coordination of time. The accurate transmission of data and the functionality of global networks hinge upon the consistent application of time zones, however irregular those zones might be.
Science and Research: Studying and Understanding Temporal Phenomena
Scientists involved in various fields, from astronomy and meteorology to biology and environmental studies, require precise timekeeping across global locations. Accurate time synchronization is essential for comparative studies, data collection, and monitoring global phenomena. Understanding the nuances of time zones allows for more accurate and globally relevant scientific analysis.
The Unanswerable Question: A Definitive Count
Returning to the original question, "How many time zones are there?", the answer remains surprisingly elusive. There's no single definitive number. While the foundational system points to 24, the practical reality includes many more due to irregular boundaries, fractional zones, and the seasonal changes implemented by Daylight Saving Time. Trying to pinpoint an exact number becomes a semantic exercise rather than a factual calculation. The dynamic nature of political boundaries and the ongoing adjustments to time zones prevent a fixed and unchanging count.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity
The system of time zones, despite its complexities, remains a testament to human ingenuity and our efforts to navigate a globally connected world. The seemingly simple question of how many time zones exist opens a window into the intricate interplay between geography, politics, technology, and the very human need for synchronization and order. Instead of seeking a definitive numerical answer, it's more valuable to appreciate the complexities and understand the system's role in facilitating our interconnected lives. The system may be irregular, but it's a testament to our collaborative efforts to make sense of our shared planet and the passage of time.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Miles Is A 1k Run
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Two Purines Bases In Dna Are
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Are The Multiples Of Eight
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Element Does Not Contain Any Neutrons
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is One Fifth As A Percentage
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Earth Is Divided Into How Many Time Zones . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
