Distinguish Between Private And Public Sector Organization.
Juapaving
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
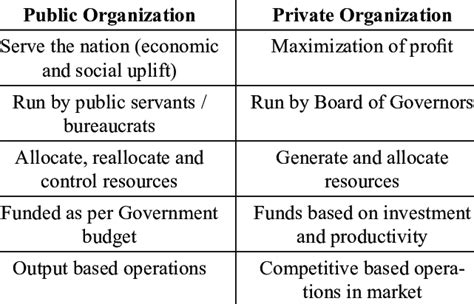
Table of Contents
Distinguishing Between Private and Public Sector Organizations: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the differences between private and public sector organizations is crucial for anyone navigating the business world, seeking employment, or simply understanding how our economies function. While both types of organizations contribute to society, their goals, structures, and operations differ significantly. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into these distinctions, exploring their contrasting characteristics and the implications for individuals and society as a whole.
Defining the Sectors: A Foundation for Understanding
Before diving into the nuances, let's establish a clear definition of each sector:
The Public Sector:
The public sector encompasses organizations owned and operated by the government at local, regional, or national levels. These entities are funded primarily through taxation and aim to provide essential services to citizens. Examples include government departments (e.g., education, healthcare, defense), public utilities (e.g., water, electricity), and public corporations (e.g., postal services, transportation authorities). The core mission of public sector organizations revolves around serving the public interest and fulfilling societal needs.
The Private Sector:
The private sector comprises organizations owned and operated by private individuals or groups. Their primary objective is usually profit maximization, although some private organizations may also pursue social responsibility goals. Examples include corporations, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), partnerships, and sole proprietorships. These entities operate independently of government control, except for adherence to regulations and laws.
Key Differences: A Comparative Analysis
The distinctions between the public and private sectors extend beyond simple ownership. A comprehensive understanding necessitates examining several key differences:
1. Ownership and Control:
- Public Sector: Owned and controlled by the government, ultimately accountable to the electorate. Decisions are often influenced by political considerations and public policy.
- Private Sector: Owned and controlled by private individuals or shareholders. Decisions are primarily driven by profit motives and shareholder value.
2. Primary Goal:
- Public Sector: Providing essential services to the public, promoting social welfare, and achieving policy objectives. Profit is not the primary driver.
- Private Sector: Generating profit for owners and shareholders. While social responsibility is increasingly important, profit remains the central focus.
3. Funding and Revenue Sources:
- Public Sector: Primarily funded through taxation, government grants, and public borrowing. Revenue may also come from fees for services rendered.
- Private Sector: Funding comes from a variety of sources, including private investment, loans, equity financing, and revenue generated from the sale of goods or services.
4. Accountability and Transparency:
- Public Sector: Subject to greater scrutiny and accountability mechanisms. Operations are typically more transparent due to Freedom of Information laws and public audits. Performance is frequently measured against publicly stated objectives.
- Private Sector: Accountability is primarily to shareholders and stakeholders. While regulatory compliance is mandatory, transparency levels vary depending on the organization’s size and nature.
5. Decision-Making Processes:
- Public Sector: Decision-making often involves bureaucratic processes, consultations, and political considerations. This can lead to slower decision-making compared to the private sector.
- Private Sector: Decision-making is generally faster and more streamlined, with a greater emphasis on efficiency and profitability. However, this can sometimes lead to overlooking ethical considerations or long-term sustainability.
6. Performance Measurement:
- Public Sector: Performance is often measured against targets related to service delivery, efficiency, and social impact. Qualitative measures alongside quantitative data are often used.
- Private Sector: Performance is typically measured in terms of profitability, market share, return on investment (ROI), and shareholder value. Quantitative data is the primary focus.
7. Risk Tolerance:
- Public Sector: Often more risk-averse due to the need for stability and the potential for negative public backlash. Innovation may be slower.
- Private Sector: May be more willing to take risks to pursue innovation and growth. This can lead to greater dynamism but also higher potential for failure.
8. Employee Compensation and Benefits:
- Public Sector: Compensation and benefits are usually determined by government regulations and collective bargaining agreements. Salaries might be lower compared to the private sector, but job security is often higher.
- Private Sector: Compensation and benefits are more variable, often depending on performance, market conditions, and company profitability. Higher salaries are common, but job security can be less certain.
9. Regulations and Legal Framework:
- Public Sector: Subject to strict regulations, oversight, and accountability frameworks. Their actions must comply with existing legislation and public policy.
- Private Sector: While subject to regulations (depending on the industry), they generally have more operational flexibility. The regulatory environment shapes business operations, but allows for greater autonomy.
10. Social Responsibility:
- Public Sector: Inherent social responsibility as the primary function is to serve the public good.
- Private Sector: Social responsibility is becoming increasingly important, driven by stakeholder expectations and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives. However, the primary focus usually remains on profit maximization.
Blurring the Lines: Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
In recent decades, the distinction between the public and private sectors has become less clear-cut due to the rise of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs). These collaborations involve the sharing of resources, risks, and responsibilities between government entities and private companies to deliver public services. PPPs can offer advantages such as:
- Increased efficiency and effectiveness: Private sector expertise can improve the delivery of public services.
- Reduced public expenditure: Private investment can reduce the financial burden on the government.
- Access to innovation and technology: Private companies can bring innovative solutions to public service challenges.
However, PPPs also present potential drawbacks, such as:
- Increased complexity: Managing partnerships can be challenging and require strong governance structures.
- Potential for conflicts of interest: Balancing the interests of the public and private partners requires careful negotiation and monitoring.
- Concerns about transparency and accountability: The lack of transparency in some PPPs can raise concerns about accountability and fairness.
Conclusion: Understanding the Interplay
The differences between private and public sector organizations are significant and impact various aspects of our lives, from the services we receive to the economic landscape we inhabit. While their primary goals and operating principles differ, both sectors play crucial roles in society. Understanding these differences is vital for effective policymaking, informed decision-making, and a comprehensive understanding of the complex interplay between government and the private sector. The increasing prevalence of PPPs further highlights the interconnectedness and the need for a nuanced perspective on the distinctions between these two important organizational sectors. As we move forward, recognizing the strengths and limitations of each sector, and fostering collaboration where appropriate, will be crucial for building resilient and prosperous communities. Continued research and analysis of the evolving relationship between public and private organizations are essential to navigate the complex dynamics of the modern world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Phosphorus A Metal Or Nonmetal
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 17 Inches
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 14 Inches
Apr 07, 2025
-
Is Capacity And Volume The Same
Apr 07, 2025
-
Is Potassium Oxide Ionic Or Covalent
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Distinguish Between Private And Public Sector Organization. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
