Definition Of Uniform Motion In Physics
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
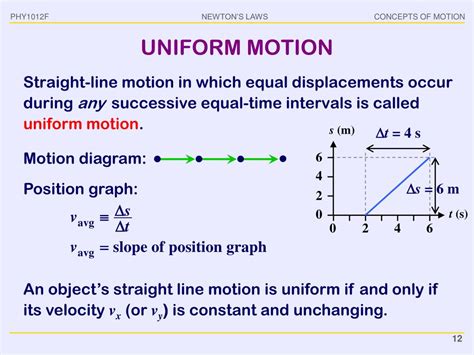
Table of Contents
Uniform Motion in Physics: A Comprehensive Guide
Uniform motion, also known as constant velocity motion, is a fundamental concept in classical mechanics. Understanding it is crucial for grasping more complex physics principles. This comprehensive guide will delve into the definition, characteristics, equations, examples, and applications of uniform motion. We'll explore its nuances and differentiate it from other types of motion, equipping you with a thorough understanding of this cornerstone of physics.
Defining Uniform Motion
In the simplest terms, uniform motion describes the movement of an object at a constant velocity. This means the object's speed and direction remain unchanged throughout its journey. It's important to emphasize both aspects:
-
Constant Speed: The object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. Think of a car cruising on a straight highway at a steady 60 mph.
-
Constant Direction: The object maintains a straight-line path. Any deviation from this straight line signifies a change in velocity, thereby negating uniform motion.
Therefore, uniform motion is characterized by the absence of any acceleration. Acceleration, the rate of change of velocity, is zero in uniform motion. This contrasts sharply with non-uniform motion, where velocity changes over time due to factors like acceleration, deceleration, or changes in direction.
Key Characteristics of Uniform Motion
Let's summarize the key characteristics that define uniform motion:
-
Constant Velocity: The object's velocity remains constant throughout its motion. This encompasses both constant speed and constant direction.
-
Zero Acceleration: The rate of change of velocity is zero. There are no forces causing a change in the object's velocity.
-
Straight-Line Path: The object travels along a straight line. Any curvature indicates a change in direction and, therefore, a change in velocity.
-
Predictable Motion: The object's position at any given time can be precisely predicted using simple equations of motion.
Equations of Motion for Uniform Motion
The simplicity of uniform motion allows us to use straightforward equations to describe its behavior. The most basic equation is:
Distance = Speed x Time
or, more formally:
s = vt
Where:
- s represents the distance traveled.
- v represents the constant velocity.
- t represents the time elapsed.
This equation assumes the motion starts at a reference point (s=0 at t=0). If there's an initial displacement, the equation becomes:
s = s₀ + vt
Where:
- s₀ represents the initial displacement.
While seemingly simple, this equation is incredibly powerful. It allows us to calculate any of the three variables (distance, velocity, or time) if we know the other two.
Examples of Uniform Motion (Idealized Scenarios)
In reality, achieving perfectly uniform motion is challenging due to various external forces like friction and air resistance. However, several idealized scenarios approximate uniform motion:
-
An object sliding on a frictionless surface: In a hypothetical environment without friction, an object given an initial push would continue moving at a constant velocity in a straight line.
-
A puck sliding on an air hockey table: The air cushion minimizes friction, allowing the puck to move with relatively uniform motion.
-
A satellite orbiting Earth (at a constant distance and speed): While technically undergoing circular motion, if we consider only a small section of its orbit, its velocity can be approximated as uniform.
-
A perfectly calibrated train moving on a straight track: While real-world trains experience friction and variations in speed, a theoretical train with negligible resistance and constant power could approximate uniform motion.
It's crucial to understand that these examples are idealized. Real-world scenarios always involve some degree of non-uniformity.
Differentiating Uniform Motion from Other Types of Motion
Understanding uniform motion requires differentiating it from other types of motion:
-
Non-uniform motion: This encompasses any motion where the velocity is not constant. This includes accelerated motion (increasing velocity), decelerated motion (decreasing velocity), and motion with changing direction.
-
Accelerated motion: This is motion where the velocity changes over time. The acceleration can be constant (e.g., an object falling under gravity) or varying (e.g., a car accelerating and then braking).
-
Circular motion: This involves movement along a circular path. Although the speed might be constant, the direction is constantly changing, meaning the velocity is not constant. Therefore, circular motion is not uniform motion.
-
Projectile motion: This involves an object launched into the air, subject to gravity. The object's velocity changes both in magnitude (speed) and direction throughout its trajectory.
Applications of Uniform Motion
While perfectly uniform motion is rare in reality, the concept provides a crucial foundation for understanding more complex scenarios:
-
Calculating travel time and distance: The basic equation (s = vt) is extensively used for estimating travel times and distances, particularly in navigation and transportation planning.
-
Understanding inertial frames of reference: Uniform motion is key to understanding inertial frames of reference, where Newton's laws of motion hold true. An observer in uniform motion experiences the same physics as an observer at rest.
-
Simplifying complex motion: Analyzing complex motions often involves breaking them down into smaller segments that approximate uniform motion. This simplifies calculations and provides a reasonable estimate of the overall motion.
-
Modeling simple systems: Uniform motion is a building block for creating simple models of more complex systems in physics and engineering.
-
Foundation for more advanced concepts: A solid grasp of uniform motion is essential for understanding more complex topics like relative velocity, momentum, and energy.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several common misconceptions surround uniform motion:
-
Constant speed implies uniform motion: While constant speed is a necessary condition for uniform motion, it is not sufficient. The direction must also remain constant.
-
Uniform motion only occurs in idealized scenarios: While perfectly uniform motion is rare, many real-world scenarios can be approximated by uniform motion for simplification.
-
Uniform motion means no forces are acting: While no net force is acting on an object in uniform motion (Newton's First Law), individual forces might be present but cancel each other out. For example, a car cruising at a constant speed experiences forces like friction and engine thrust that balance each other.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Uniform Motion
Uniform motion, despite its apparent simplicity, is a cornerstone of classical mechanics. A thorough understanding of its definition, characteristics, and equations is essential for grasping more advanced concepts in physics. While perfectly uniform motion is rarely observed in the real world, its idealized nature provides a crucial foundation for analyzing, modeling, and predicting more complex forms of movement. Mastering this fundamental concept unlocks a deeper understanding of the world around us and paves the way for tackling more challenging problems in physics and engineering. By appreciating the nuances of uniform motion and differentiating it from other types of motion, you develop a robust foundation for future studies in physics and related fields. Remember, even in complex scenarios, understanding the principles of uniform motion allows for simplification and accurate estimations, making it an invaluable tool in various scientific and engineering applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Endpoints Does A Segment Have
Mar 20, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 4 And 12
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Outermost Layer Of Earth
Mar 20, 2025
-
Alternation Of Generations Means That Plants Produce
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Hours Are In 1 Week
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Definition Of Uniform Motion In Physics . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
