Common Name For Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
Juapaving
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
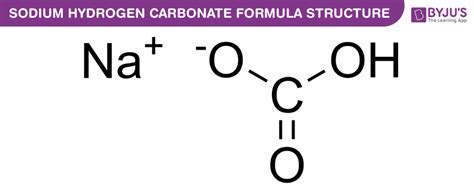
Table of Contents
The Common Name for Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate: Baking Soda and Beyond
Sodium hydrogen carbonate, a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO₃, is ubiquitous in homes and industries worldwide. While its formal chemical name might sound intimidating, its common name, baking soda, is far more familiar. This article delves deep into the common name, its various applications, historical context, and why it's so much more than just a baking ingredient.
Baking Soda: The Household Staple
The most prevalent common name for sodium hydrogen carbonate is baking soda. This moniker perfectly encapsulates its primary domestic use: leavening agent in baking. Baking soda's ability to release carbon dioxide gas when exposed to an acidic environment is crucial for creating light and fluffy baked goods like cakes, cookies, and bread. This reaction, a classic acid-base neutralization, is the heart of baking soda's magic.
The Chemistry of Baking: Acid-Base Reaction
The chemical reaction behind baking soda's leavening power is a fundamental principle of chemistry. When baking soda (a base) reacts with an acidic ingredient (like buttermilk, lemon juice, or vinegar), it produces carbon dioxide gas (CO₂), water (H₂O), and a salt. The CO₂ gas gets trapped within the batter or dough, creating air pockets that cause the baked goods to rise. Understanding this reaction is key to successfully using baking soda in recipes.
The reaction can be simplified as follows:
NaHCO₃ (baking soda) + H⁺ (acid) → CO₂ (carbon dioxide) + H₂O (water) + Na⁺ (salt)
Baking Soda vs. Baking Powder: Key Differences
Often confused with baking powder, baking soda requires an acidic ingredient to activate its leavening properties. Baking powder, on the other hand, contains both an acid and a base, making it a self-acting leavening agent. Choosing between baking soda and baking powder depends entirely on the recipe. Recipes that already incorporate acidic ingredients, such as those using buttermilk or sour cream, are ideal candidates for baking soda. Recipes without acidic components will require baking powder.
Beyond Baking: The Diverse Applications of Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
While baking is the most well-known application, the versatility of sodium hydrogen carbonate extends far beyond the kitchen. Its uses span various industries and everyday life, highlighting its multifaceted nature.
Cleaning Powerhouse: Removing Stains and Odors
Baking soda's mildly abrasive nature and ability to neutralize odors makes it a remarkable cleaning agent. It effectively scrubs away tough stains from cookware, countertops, and even clothes. Its deodorizing properties are equally impressive, eliminating unpleasant smells from refrigerators, carpets, and even pet areas. Simply sprinkle baking soda on the affected area, let it sit, and then wipe or vacuum it away for a fresh, clean result.
Health and Beauty Benefits: A Natural Remedy
Sodium hydrogen carbonate finds its place in various health and beauty regimes. Its mild alkalinity can help soothe skin irritations and neutralize excess acidity. It can be used as a natural toothpaste, a gentle exfoliant, and even a remedy for heartburn or indigestion. However, it's crucial to note that these are anecdotal uses, and consulting a healthcare professional before using baking soda for medicinal purposes is always recommended.
Industrial Applications: A Versatile Chemical
The industrial applications of sodium hydrogen carbonate are extensive. It's a crucial component in fire extinguishers, where its reaction with an acid produces carbon dioxide, effectively extinguishing flames. It's also used in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and various other products. Its buffering properties, ability to regulate pH levels, and its relative safety make it invaluable across various industries.
Historical Context: A Long and Rich History
The use of sodium hydrogen carbonate dates back centuries. While the precise details of its initial discovery remain somewhat unclear, its presence in various cultures throughout history is evident. Early methods of production likely involved extracting it from natural sources, like certain mineral deposits. The development of efficient industrial production methods greatly increased its availability and led to its widespread use.
Early Uses and Discoveries: Natural Sources and Early Applications
Before industrial production became commonplace, sodium hydrogen carbonate was likely obtained from naturally occurring sources. Its presence in mineral deposits and its association with certain geological formations were likely observed, leading to its early use in various applications. These early applications might have been limited to areas where these natural sources were readily available.
Industrial Production: Revolutionizing Availability and Use
The advent of industrial production methods revolutionized the accessibility and affordability of sodium hydrogen carbonate. This allowed for its large-scale application in various industries and households. Modern manufacturing processes have made baking soda readily available to consumers globally, cementing its role as a household staple.
Safety Precautions: Handling Baking Soda Responsibly
Despite its generally safe nature, it's important to handle sodium hydrogen carbonate responsibly. While it's non-toxic, excessive ingestion can lead to adverse effects. Always store it in a cool, dry place, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Additionally, avoid inhaling large quantities of baking soda dust, as it can irritate the respiratory system.
Avoiding Overconsumption: Moderation is Key
While occasional ingestion of small amounts of baking soda is generally considered harmless, overconsumption should be avoided. Excessive intake can disrupt the body's electrolyte balance and potentially lead to health problems.
Proper Storage and Handling: Maintaining Quality and Safety
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of baking soda. Keeping it in an airtight container in a cool, dry environment will prevent clumping and degradation. Avoid exposure to moisture or high temperatures, as these conditions can compromise its effectiveness.
Conclusion: An Everyday Wonder
Sodium hydrogen carbonate, commonly known as baking soda, is a remarkable chemical compound with a wide range of applications. Its use in baking, cleaning, and various industrial processes highlights its versatility and importance in both household and industrial settings. Understanding its chemical properties and handling it responsibly allows us to harness its many benefits safely and effectively. From its role as a leavening agent to its efficacy as a cleaning agent, baking soda continues to be an everyday wonder, a testament to the power of simple chemistry. Its enduring popularity speaks volumes about its practical utility and its enduring presence in our daily lives. The common name, baking soda, while simple, perfectly encapsulates its essential role in our homes and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
D How Is The Energy Produced By Respiration Stored
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Functional And Structural Unit Of The Kidneys Is The
Apr 04, 2025
-
To Pour Water On Calcium Oxide
Apr 04, 2025
-
Evaluate The Trigonometric Function At The Quadrantal Angle
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many Kilometers Is 11 Miles
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Name For Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
