Common Multiple Of 8 And 14
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
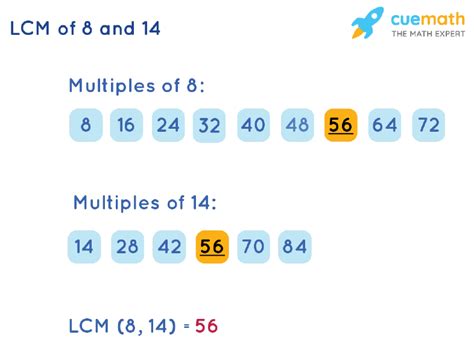
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 8 and 14: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with applications spanning various fields, from scheduling to music theory. This comprehensive guide delves into the process of determining the LCM of 8 and 14, exploring multiple methods and providing a thorough understanding of the underlying principles. We'll cover not just the calculation but also the significance of LCM and its broader implications.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we dive into calculating the LCM of 8 and 14, let's establish a firm understanding of what an LCM actually is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the original numbers as factors.
For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30...
The common multiples of 2 and 3 are the numbers that appear in both lists: 6, 12, 18, 24... The least common multiple is the smallest of these common multiples, which is 6.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 8 and 14
There are several effective methods for calculating the LCM of two numbers. Let's explore the most common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80...
- Multiples of 14: 14, 28, 42, 56, 70, 84, 98, 112, 126, 140...
By comparing the lists, we see that the smallest common multiple is 56. Therefore, the LCM(8, 14) = 56. This method is simple but can become tedious with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method utilizes the prime factorization of each number. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
- Prime factorization of 8: 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
- Prime factorization of 14: 2 x 7
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization and multiply them together.
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 7: 7¹ = 7
LCM(8, 14) = 8 x 7 = 56
This method is more efficient than listing multiples, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It provides a systematic approach and is less prone to errors.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method leverages the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The GCD is the largest positive integer that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. The formula relating LCM and GCD is:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
First, we need to find the GCD of 8 and 14. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide the larger number (14) by the smaller number (8): 14 = 8 x 1 + 6
- Replace the larger number with the remainder (6) and repeat: 8 = 6 x 1 + 2
- Repeat until the remainder is 0: 6 = 2 x 3 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is the GCD, which is 2.
Now, we can calculate the LCM:
LCM(8, 14) = (8 x 14) / 2 = 112 / 2 = 56
This method is also efficient and provides a structured approach, particularly useful for larger numbers where prime factorization might become cumbersome.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends beyond simple mathematical exercises. It finds practical applications in various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have two machines that operate on different cycles. One machine completes a task every 8 hours, and another every 14 hours. To determine when both machines will complete a task simultaneously, we need to find the LCM of 8 and 14. The LCM (56) represents the time, in hours, when both machines will finish their tasks at the same time.
2. Music Theory
In music, LCM plays a role in determining the least common denominator for rhythmic patterns. For example, if one musical phrase has a length of 8 beats and another has a length of 14 beats, the LCM (56) represents the shortest length of time at which both phrases would repeat simultaneously.
3. Fractions and Least Common Denominator (LCD)
When adding or subtracting fractions, we need a common denominator. The least common denominator (LCD) is the LCM of the denominators. For instance, to add 1/8 and 1/14, we find the LCM of 8 and 14 (which is 56), and then convert the fractions to have a denominator of 56 before adding them.
4. Modular Arithmetic
LCM plays a crucial role in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with applications in cryptography and computer science. Understanding LCM helps solve congruence problems and analyze cyclical patterns.
5. Engineering and Construction
In construction projects, LCM can be used to determine the optimal time intervals for certain tasks that need to align. This efficient planning can save resources and time in large-scale projects.
Beyond the Basics: Extending LCM to More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, we simply consider all prime factors from all the numbers, taking the highest power of each. For the GCD method, we can iteratively apply the process to pairs of numbers.
For example, to find the LCM of 8, 14, and 6:
-
Prime factorization:
- 8 = 2³
- 14 = 2 x 7
- 6 = 2 x 3
-
LCM(8, 14, 6) = 2³ x 3 x 7 = 8 x 3 x 7 = 168
Conclusion: Mastering LCM for Practical Applications
Understanding and calculating the least common multiple is a fundamental skill with a wide range of applications across various disciplines. Whether using the listing multiples method, prime factorization, or the GCD method, choosing the most appropriate approach depends on the complexity of the numbers involved. By mastering these techniques, you equip yourself with a powerful tool for solving problems in mathematics, scheduling, music, and various other fields. The LCM of 8 and 14, determined to be 56 through various methods, serves as a practical example illustrating the importance and versatility of this mathematical concept. Understanding LCM not only helps solve specific problems but also builds a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 9 And 12
Mar 10, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 7 And 8
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The 15 Of 200
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 120 Minutes In Hours
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Quarts In 2 Cubic Feet
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Multiple Of 8 And 14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
