What Is The Lcm Of 9 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 4 min read
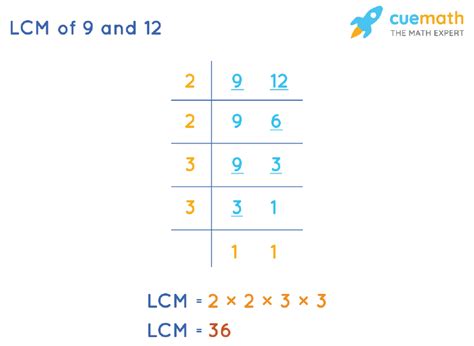
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 9 and 12? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly useful in various areas like fractions, simplifying expressions, and solving real-world problems. This article will explore the LCM of 9 and 12 in detail, explaining different methods to calculate it and providing practical examples to illustrate its applications. We'll also touch upon the broader mathematical concepts surrounding LCMs and their significance.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before diving into the specific calculation for 9 and 12, let's establish a clear understanding of what an LCM is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors.
For instance, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14... and multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods to Calculate the LCM of 9 and 12
There are several effective methods to determine the LCM of 9 and 12. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward approach, especially useful for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60...
The smallest number that appears in both lists is 36. Therefore, the LCM of 9 and 12 is 36.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. We first find the prime factorization of each number:
- Prime factorization of 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
- Prime factorization of 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations and multiply them together:
LCM(9, 12) = 2² x 3² = 4 x 9 = 36
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor). The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is always equal to the product of the two numbers. Therefore, we can find the LCM using the following formula:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
First, we need to find the GCD of 9 and 12. Using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization, we find that the GCD(9, 12) = 3.
Now, we can calculate the LCM:
LCM(9, 12) = (9 x 12) / 3 = 108 / 3 = 36
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of LCM isn't confined to theoretical mathematics; it finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
1. Scheduling and Timing
Imagine two buses departing from the same station at different intervals. One bus departs every 9 minutes, and the other every 12 minutes. To determine when both buses will depart simultaneously again, we need to find the LCM of 9 and 12. The LCM, 36, indicates that both buses will depart together again after 36 minutes.
2. Fraction Operations
LCM plays a crucial role in adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add 1/9 and 1/12, we need to find a common denominator, which is the LCM of 9 and 12. The LCM is 36, so we rewrite the fractions as 4/36 and 3/36 respectively, allowing for easy addition.
3. Measurement Conversions
In scenarios involving conversions between different units of measurement, LCM can be helpful. Consider converting between inches and centimeters. Understanding the LCM of the conversion factors can streamline the process and minimize errors.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For example, to find the LCM of 9, 12, and 15, we would follow the same prime factorization method:
- Prime factorization of 9: 3²
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
The LCM would be 2² x 3² x 5 = 4 x 9 x 5 = 180
Conclusion: The Significance of LCM in Mathematics
The least common multiple is a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications across various mathematical fields. Understanding how to calculate the LCM, using different methods, allows for efficient problem-solving in numerous situations. From scheduling events to performing fraction operations, the application of LCM extends beyond theoretical calculations into practical real-world problems. Mastering this concept is crucial for a strong foundation in mathematics and its applications. The detailed exploration of calculating the LCM of 9 and 12, using multiple methods and illustrating real-world examples, provides a comprehensive understanding of this important mathematical tool. Remember that consistent practice and exploration of various problems will further solidify your understanding and ability to apply the LCM effectively in different contexts. Keep practicing, and you'll find this seemingly simple concept becomes a powerful asset in your mathematical toolkit.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Organisms That Make Their Own Food
Mar 10, 2025
-
Adjectives Beginning With The Letter V
Mar 10, 2025
-
Describe The Features Of The Globe
Mar 10, 2025
-
The Part Of The Seed That Develops Into The Shoot
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Most Abundant Gas In The Atmosphere
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 9 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
