Common Factors Of 4 And 6
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
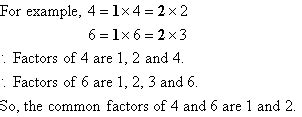
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Common Factors of 4 and 6: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic exercise, but it's a fundamental concept in number theory with far-reaching applications in mathematics and computer science. This article delves deep into the common factors of 4 and 6, exploring various methods to identify them, understanding their significance, and extending the concept to more complex scenarios. We'll also touch upon related concepts like greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM), illustrating their practical relevance.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we pinpoint the common factors of 4 and 6, let's solidify our understanding of fundamental terms. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. For instance, the factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3, and 6 because each of these numbers divides 6 evenly. Similarly, the factors of 4 are 1, 2, and 4.
Divisibility rules are shortcuts to determine if a number is divisible by another. For example:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, or 8).
- Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 4: A number is divisible by 4 if its last two digits are divisible by 4.
Identifying the Common Factors of 4 and 6
Now, let's focus on finding the common factors of 4 and 6. We can list all the factors of each number and then identify those that appear in both lists:
Factors of 4: 1, 2, 4
Factors of 6: 1, 2, 3, 6
By comparing the two lists, we see that the common factors of 4 and 6 are 1 and 2. These are the numbers that divide both 4 and 6 without leaving a remainder.
Prime Factorization: A Powerful Tool
Prime factorization is a crucial technique in number theory. It involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors – numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
Let's find the prime factorization of 4 and 6:
- 4 = 2 x 2 = 2²
- 6 = 2 x 3
Notice that both 4 and 6 share a common prime factor: 2. This reinforces our earlier finding that 1 and 2 are the common factors. The number 1 is considered a factor of every number but isn't a prime number.
The Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The greatest common divisor (GCD), also known as the highest common factor (HCF), is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. In the case of 4 and 6, the GCD is 2. Finding the GCD is crucial in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems.
There are several methods for calculating the GCD:
- Listing Factors: As we did earlier, list all factors and select the largest common one.
- Prime Factorization: Find the prime factorization of each number. The GCD is the product of the common prime factors raised to the lowest power. For 4 and 6, the common prime factor is 2, and its lowest power is 2¹ (from the factorization of 6), hence the GCD is 2.
- Euclidean Algorithm: This efficient algorithm involves repeated division until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCD.
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) is the smallest number that is a multiple of both given numbers. Understanding the LCM is essential in various applications like finding the least common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions.
We can find the LCM of 4 and 6 using several methods:
- Listing Multiples: List the multiples of each number and find the smallest common one. Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16... Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18... The LCM is 12.
- Prime Factorization: Find the prime factorization of each number. The LCM is the product of all prime factors raised to the highest power. For 4 (2²) and 6 (2 x 3), the LCM is 2² x 3 = 12.
Applications of Common Factors and GCD/LCM
The concepts of common factors, GCD, and LCM are not merely abstract mathematical ideas; they have practical applications in diverse fields:
- Fraction Simplification: The GCD is used to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 6/4 can be simplified to 3/2 by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCD (2).
- Scheduling Problems: The LCM is used to solve scheduling problems. For instance, if two events occur every 4 days and 6 days, respectively, they will occur simultaneously every LCM(4, 6) = 12 days.
- Modular Arithmetic: GCD and LCM play a crucial role in modular arithmetic, which has applications in cryptography and computer science.
- Geometry: Finding common factors can be helpful in solving geometric problems involving scaling and ratios.
Extending the Concept: More Than Two Numbers
The concepts of common factors and GCD extend seamlessly to scenarios involving more than two numbers. To find the common factors of multiple numbers, we list the factors of each number and identify the numbers present in all lists. The GCD of multiple numbers is the largest number that divides all of them. The LCM of multiple numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. Prime factorization and the Euclidean algorithm can also be extended to find the GCD and LCM of more than two numbers.
Conclusion: A Foundation of Number Theory
Understanding common factors, GCD, and LCM is fundamental to grasping more advanced concepts in number theory and its applications. While finding the common factors of 4 and 6 may seem straightforward, the underlying principles and their broader applications are vast and profound. This exploration provides a solid foundation for delving deeper into the fascinating world of number theory, opening doors to a deeper understanding of mathematical structures and their practical significance. By mastering these fundamental concepts, you enhance your mathematical problem-solving skills and broaden your appreciation for the elegance and utility of number theory. From simplifying fractions to scheduling complex events, the principles discussed here are invaluable tools applicable across many domains.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Abiotic
Mar 11, 2025
-
What Do Arrows Mean In A Food Chain
Mar 11, 2025
-
Is Sugar Dissolving In Water A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 11, 2025
-
Which Step In Cellular Respiration Produces The Most Atp
Mar 11, 2025
-
How Many Sides Are There In A Dodecagon
Mar 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Factors Of 4 And 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
