Common Factors Of 12 And 24
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
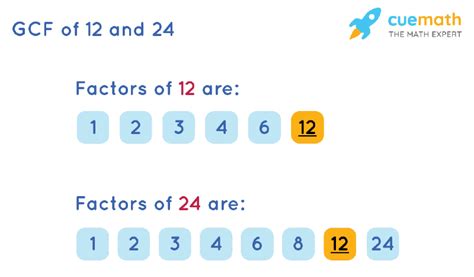
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Common Factors of 12 and 24: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple task, especially for smaller numbers like 12 and 24. However, understanding the underlying principles involved opens the door to a fascinating world of number theory, with implications far beyond basic arithmetic. This article will delve into the common factors of 12 and 24, exploring various methods to identify them and connecting the concept to broader mathematical concepts like prime factorization, greatest common divisor (GCD), and least common multiple (LCM). We'll also touch upon the practical applications of understanding common factors in various fields.
Understanding Factors and Common Factors
Before we dive into the specifics of 12 and 24, let's establish a clear understanding of what factors and common factors are.
A factor of a number is a whole number that divides the number evenly, without leaving a remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving any remainder.
A common factor is a number that is a factor of two or more numbers. For example, if we consider the numbers 12 and 18, their factors are:
- Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
- Factors of 18: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18
The common factors of 12 and 18 are 1, 2, 3, and 6, as these numbers divide both 12 and 18 evenly.
Finding the Common Factors of 12 and 24
Now, let's focus on our main subject: the common factors of 12 and 24. We can approach this problem in several ways:
Method 1: Listing the Factors
The most straightforward method is to list all the factors of each number and then identify the common ones.
- Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
- Factors of 24: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
By comparing the two lists, we can easily see that the common factors of 12 and 24 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a powerful technique for finding common factors. It involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
- Prime factorization of 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 24: 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = 2³ x 3
To find the common factors, we look at the common prime factors and their lowest powers. Both 12 and 24 share two prime factors: 2 and 3. The lowest power of 2 is 2¹ (or simply 2), and the lowest power of 3 is 3¹. Therefore, the common factors are formed by combining these prime factors and their powers:
- 2¹ = 2
- 3¹ = 3
- 2¹ x 3¹ = 6
- 2² x 3¹ = 12
- 2⁰ x 3⁰ = 1 (This represents the case where no common prime factors are used)
Combining these, we get the same common factors as before: 1, 2, 3, 6, and 12. Notice that we missed 4 (2²) because we only initially considered the lowest powers. A more thorough approach to constructing common factors from prime factorizations involves considering all possible combinations of the common prime factors and their powers up to the lowest power present in either factorization. Thus 2², which is 4, is also a common factor of 12 and 24.
This highlights the importance of a systematic approach when using prime factorization to identify common factors.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The greatest common divisor (GCD) is the largest number that divides two or more numbers without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCD provides a shortcut to identifying all common factors.
Several methods exist to calculate the GCD, including:
- Euclidean Algorithm: This efficient algorithm involves repeatedly applying the division algorithm until the remainder is zero. The last non-zero remainder is the GCD.
- Prime Factorization Method: Comparing the prime factorizations, as shown above, allows us to easily identify the GCD. The GCD is the product of the common prime factors raised to their lowest powers.
For 12 and 24:
- Prime factorization method: The common prime factors are 2 and 3. The lowest power of 2 is 2¹, and the lowest power of 3 is 3¹. Therefore, the GCD is 2¹ x 3¹ = 6.
Once we have the GCD (which is 12 for 12 and 24), we know that all the factors of the GCD are also common factors of the original numbers. The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12; these are precisely the common factors of 12 and 24.
Connecting to Broader Concepts
Understanding common factors allows us to explore related concepts:
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. The LCM and GCD are related through the following formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
For 12 and 24:
- GCD(12, 24) = 12
- LCM(12, 24) = 24
This formula helps verify the relationship between the GCD and LCM.
Applications of Common Factors and GCD
Understanding common factors and the GCD has practical applications in various fields:
-
Simplification of Fractions: Finding the GCD allows us to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 24/12 can be simplified to 2/1 (or simply 2) by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCD, which is 12.
-
Solving Problems Involving Ratios and Proportions: GCD is used to simplify ratios and proportions, making them easier to understand and work with.
-
Cryptography: Number theory, including concepts like GCD and prime factorization, plays a crucial role in modern cryptography algorithms that secure online communication and transactions.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms related to GCD are essential for various computational tasks, including simplifying fractions, finding the least common multiple, and implementing some cryptographic techniques.
-
Music Theory: Common factors and multiples are fundamental concepts used in musical harmony and the creation of scales and chords.
Conclusion
Finding the common factors of 12 and 24, while seemingly basic, opens up a gateway to a rich understanding of number theory. Through different methods, such as listing factors, prime factorization, and using the GCD, we've uncovered the common factors (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12) and established connections to other essential mathematical concepts like the LCM. The practical applications of these concepts extend across various fields, highlighting the importance of understanding these foundational mathematical principles. This exploration underscores the inherent beauty and practicality of number theory and its far-reaching implications in both theoretical and practical contexts. By understanding these fundamental concepts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and utility of mathematics in our daily lives and various technological applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Electric Field Of A Charged Surface
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Phosphorus Have
Mar 10, 2025
-
Is Baking Soda An Acid Or Base
Mar 10, 2025
-
Moment Of Inertia Of A Solid Sphere
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 62 Inches
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Factors Of 12 And 24 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
