How Many Valence Electrons Does Phosphorus Have
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
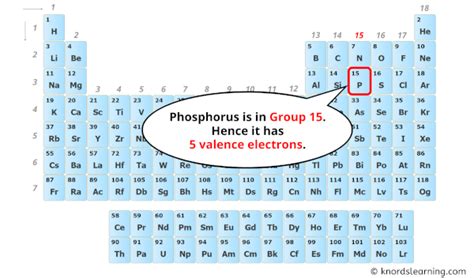
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Does Phosphorus Have? A Deep Dive into Phosphorus Chemistry
Phosphorus, a crucial element in biological systems and a cornerstone of numerous industrial applications, boasts a fascinating chemistry largely dictated by its valence electrons. Understanding the number of valence electrons in phosphorus is key to unlocking its reactivity and explaining its diverse range of compounds. This article delves deep into the electronic structure of phosphorus, explaining its valence electron count, its implications for bonding, and its role in various chemical contexts.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Before we focus on phosphorus specifically, let's establish a foundational understanding of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell (the highest principal energy level) of an atom. These electrons are the most loosely held and are therefore the ones primarily involved in chemical bonding. The number of valence electrons determines an element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form.
The number of valence electrons can be readily determined from an element's position on the periodic table. For the main group elements (groups 1-18), the group number (using the older numbering system) directly corresponds to the number of valence electrons. However, this rule doesn't apply to transition metals, which have more complex electron configurations.
Determining Phosphorus's Valence Electrons
Phosphorus (P) is located in Group 15 (or VA) of the periodic table. Following the rule for main group elements, phosphorus has five valence electrons. This can be further confirmed by examining its electron configuration.
Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, meaning it has 15 protons and 15 electrons in a neutral atom. Its electron configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p³. The outermost shell is the third shell (n=3), which contains both the 3s and 3p electrons. Therefore, the total number of electrons in the outermost shell (3s²3p³ = 2 + 3 = 5) confirms that phosphorus possesses five valence electrons.
Implications of Five Valence Electrons: Bonding Behavior
The presence of five valence electrons profoundly influences phosphorus's chemical behavior and bonding capabilities. Phosphorus exhibits a variety of bonding patterns, including:
1. Covalent Bonding:
Given its five valence electrons, phosphorus readily forms covalent bonds with other nonmetals. It can achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in its outermost shell) by either sharing electrons to form single, double, or triple bonds. This ability allows phosphorus to form a diverse array of compounds, such as:
-
Phosphine (PH₃): Phosphorus forms three single covalent bonds with three hydrogen atoms, utilizing three of its valence electrons. The remaining two electrons exist as a lone pair.
-
Phosphorus Trichloride (PCl₃): Similar to phosphine, phosphorus shares three electrons to form three single bonds with three chlorine atoms. Again, a lone pair remains.
-
Phosphorus Pentachloride (PCl₅): In this case, phosphorus utilizes all five of its valence electrons to form five single bonds with five chlorine atoms. This expands the octet of phosphorus, a phenomenon observed in larger atoms of the third period and beyond.
-
Phosphorus Oxides (P₄O₁₀ and P₄O₆): These oxides showcase complex bonding involving multiple covalent bonds between phosphorus and oxygen atoms.
2. Coordinate Covalent (Dative) Bonding:
Phosphorus can also participate in coordinate covalent bonding, where both electrons in the shared pair originate from the same atom (phosphorus in this case). This is often observed in the formation of complexes with transition metals.
3. Ionic Bonding (Less Common):
Although less common than covalent bonding, phosphorus can form ionic bonds with highly electronegative elements under certain circumstances. For example, in the presence of a very strong oxidizing agent, phosphorus can lose its valence electrons to form the phosphide ion (P³⁻). This ion has a noble gas configuration and is stable. However, this type of bonding is less frequently observed compared to covalent bonding.
Phosphorus's Role in Biological Systems: The Importance of Valence Electrons
The unique bonding capabilities of phosphorus, driven by its five valence electrons, are essential to life. Phosphorus is a vital component of:
-
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): ATP is the primary energy currency of cells. The high-energy phosphate bonds in ATP, critically involving phosphorus, are responsible for powering numerous metabolic processes.
-
DNA and RNA: The phosphodiester bonds linking nucleotides in DNA and RNA are crucial for storing and transmitting genetic information. These bonds directly involve phosphorus atoms.
-
Phospholipids: These molecules form the cell membranes, separating the intracellular and extracellular environments. The phosphate group in phospholipids plays a key role in membrane structure and function.
In all these crucial biomolecules, the unique bonding properties of phosphorus, made possible by its five valence electrons, are indispensable for life as we know it.
Industrial Applications of Phosphorus: A Consequence of its Valence Electrons
Beyond its biological significance, phosphorus and its compounds find widespread industrial applications, including:
-
Fertilizers: Phosphate minerals are essential ingredients in fertilizers, providing phosphorus, a vital nutrient for plant growth. The effectiveness of these fertilizers is directly linked to the chemical reactivity of phosphorus compounds.
-
Detergents: Phosphate compounds were once commonly used as builders in detergents, but their use is now restricted in many regions due to environmental concerns.
-
Flame Retardants: Organophosphorus compounds are utilized as flame retardants in various materials, offering fire safety.
-
Semiconductors: Phosphorus is a vital dopant in semiconductor manufacturing, altering the electrical properties of silicon-based materials. This usage leverages the unique electronic properties arising from its electron configuration and valence electron count.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Phosphorus Chemistry
The discussion so far has primarily focused on the simpler aspects of phosphorus chemistry. However, the richness of phosphorus chemistry extends far beyond these basics. Some more advanced topics include:
-
Allotropes of Phosphorus: Phosphorus exists in several allotropic forms, including white phosphorus (highly reactive and toxic), red phosphorus (relatively less reactive), and black phosphorus (a semiconductor). These different forms exhibit varying chemical properties due to differences in their bonding structures and electronic configurations, ultimately originating from the same core of five valence electrons.
-
Phosphorous Acids: Various phosphorous acids, such as orthophosphoric acid (H₃PO₄), pyrophosphoric acid (H₄P₂O₇), and metaphosphoric acid (HPO₃), demonstrate differing structural arrangements based on the bonding possibilities enabled by its five valence electrons.
-
Organophosphorus Chemistry: This branch explores the vast world of phosphorus-carbon bonded compounds, used in pesticides, herbicides, and nerve agents. The reactivity and chemical behavior of these organophosphorus compounds are deeply rooted in the properties of phosphorus's valence electrons.
-
Coordination Chemistry of Phosphorus: Phosphorus and its compounds can act as ligands in coordination complexes with transition metals. The diversity of bonding modes and the resulting complex structures are closely related to the number and availability of its valence electrons.
The complexity and diversity of phosphorus chemistry continue to be an area of active research, revealing new insights into the behavior of this vital element and its compounds.
Conclusion: The Significance of Phosphorus's Five Valence Electrons
In conclusion, phosphorus's five valence electrons are the driving force behind its rich and diverse chemistry. This relatively simple number dictates its bonding behavior, impacting its role in biological systems, its industrial applications, and the extensive field of phosphorus-based research. Understanding the number of valence electrons is not merely an academic exercise; it is the key to unlocking a deep understanding of this element’s significance in various fields, from the molecular machinery of life to advanced materials science and industrial processes. Further exploration into phosphorus chemistry unveils a complex and fascinating world, firmly grounded in the fundamental properties dictated by its five valence electrons.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Describe The Features Of The Globe
Mar 10, 2025
-
The Part Of The Seed That Develops Into The Shoot
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Most Abundant Gas In The Atmosphere
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Litres Are In 5 Gallons
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 72 In
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Does Phosphorus Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
