Circle How Many Lines Of Symmetry
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
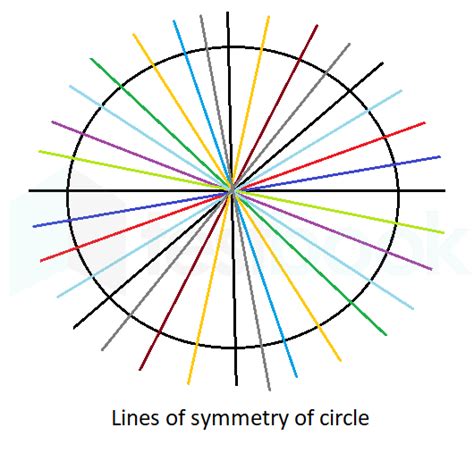
Table of Contents
Circle: How Many Lines of Symmetry Does It Have? Exploring the Infinite Symmetry of a Circle
The humble circle. A shape so ubiquitous, it's easy to overlook its fascinating mathematical properties. One such property, and the focus of this article, is its lines of symmetry. Unlike squares or triangles with a finite number of lines of symmetry, a circle possesses an infinite number. Understanding why this is the case requires exploring the very definition of symmetry and how it applies to circular shapes.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
Before diving into the specifics of a circle, let's establish a clear understanding of what a line of symmetry actually is. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap.
Consider a square. It has four lines of symmetry: two that run diagonally through opposite corners and two that run horizontally and vertically through the center. Fold a square along any of these lines, and the two halves align perfectly. A regular hexagon, with its six equal sides, boasts six lines of symmetry.
Exploring the Symmetry of the Circle
Now, let's shift our attention to the circle. A circle is defined as a set of points equidistant from a central point (the center). This equidistance is the key to understanding its infinite lines of symmetry.
Imagine drawing a line through the center of the circle. This line divides the circle into two perfectly congruent semicircles. These semicircles are mirror images of each other; if you were to fold the circle along this line, the two halves would perfectly overlap. Therefore, this line is a line of symmetry.
But we can draw another line through the center, at a different angle. This new line also divides the circle into two identical semicircles, and it, too, is a line of symmetry. We can continue this process, drawing countless lines through the center, each one acting as a line of symmetry.
This is the crucial point: Because we can draw an infinite number of lines through the center of a circle, a circle has an infinite number of lines of symmetry. There's no limit to the number of angles at which we can draw a line through the center, resulting in an infinite set of lines of symmetry.
Visualizing Infinite Symmetry
Visualizing infinity can be challenging, but consider this: Imagine rotating a circle by even the smallest fraction of a degree. The circle remains unchanged. This continuous rotational symmetry is intimately connected to its infinite lines of symmetry. Every rotation corresponds to a line of symmetry passing through the center. Since the circle can be rotated infinitely many times, it follows logically that it possesses an infinite number of lines of symmetry.
The Mathematical Proof of Infinite Lines of Symmetry in a Circle
While the visual explanation is compelling, we can also approach this from a mathematical standpoint. The equation of a circle centered at the origin (0,0) with radius 'r' is:
x² + y² = r²
Any line passing through the origin can be represented by the equation y = mx, where 'm' is the slope of the line. This line represents a line of symmetry because for every point (x,y) on the circle, the point (-x,-y) is also on the circle, and these points are reflections of each other across the line y=mx. Since 'm' can take on any real value (including infinity, represented by a vertical line), there are infinitely many lines of symmetry.
Further solidifying this, we can consider the concept of rotational symmetry. A circle exhibits rotational symmetry around its center for any angle of rotation. This implies an infinite number of rotational symmetries, directly correlating to the infinite number of lines of symmetry.
Comparing Circle Symmetry to Other Shapes
Let's contrast the circle's infinite lines of symmetry with shapes possessing finite lines of symmetry:
- Equilateral Triangle: Has three lines of symmetry, one through each vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
- Square: Has four lines of symmetry: two diagonals and two lines parallel to the sides through the center.
- Regular Pentagon: Has five lines of symmetry, one through each vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
- Regular Hexagon: Has six lines of symmetry, analogous to the pentagon.
The pattern is clear: regular polygons have a number of lines of symmetry equal to the number of their sides. The circle, however, transcends this pattern because it's not a polygon—it's a continuous curve with an infinite number of points.
Real-world Applications of Circular Symmetry
The infinite symmetry of a circle is not just a mathematical curiosity. It has practical applications in various fields:
- Engineering: Circular designs are prevalent in engineering due to their strength and even distribution of stress. Wheels, gears, and pipes are just a few examples. The symmetrical nature ensures balanced performance and stability.
- Architecture: Circular structures like domes and rotundas are visually appealing and offer structural advantages. The symmetry aids in stability and even distribution of weight.
- Nature: Many natural phenomena exhibit circular symmetry, from the rings of Saturn to the ripples created when a stone is dropped into water. This inherent symmetry often reflects underlying physical principles.
- Design: The circle's aesthetic appeal in design is undeniable. Its symmetry creates a sense of balance and harmony, making it a popular choice in logos, artwork, and decorative patterns.
Conclusion: The Enduring Elegance of Circular Symmetry
The infinite lines of symmetry in a circle are a testament to its unique mathematical elegance. This property, far from being an abstract concept, has significant implications in various real-world applications. Understanding the infinite symmetry of a circle enriches our appreciation for the fundamental principles of geometry and its profound influence on the world around us. From the microcosm of cellular structures to the macrocosm of planetary orbits, the circle’s inherent symmetry continues to fascinate and inspire. Its enduring beauty lies not just in its visual appeal but also in the boundless mathematical concepts it embodies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Kingdom Does Euglena Belong To
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lcm Of 5 4 And 2
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Action Is A Reflex Action
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Shape With 7 Sides Called
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of One Sixth
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Circle How Many Lines Of Symmetry . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
