Charge Mass Ratio Of An Electron
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
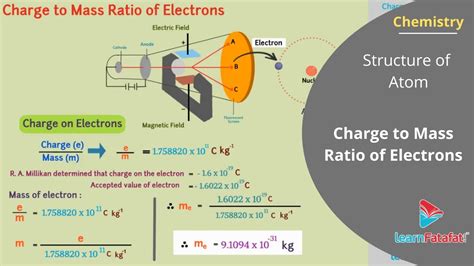
Table of Contents
Charge-to-Mass Ratio of an Electron: A Deep Dive
The charge-to-mass ratio (e/m) of an electron is a fundamental physical constant that plays a crucial role in our understanding of atomic structure and particle physics. This ratio represents the amount of electric charge an electron possesses relative to its mass. Accurately determining this value has been a cornerstone of numerous scientific breakthroughs, from the development of early atomic models to the advancements in modern particle accelerators. This article will explore the history, significance, methods of determination, and applications of the electron's charge-to-mass ratio.
The Historical Context: Unveiling the Electron
Before delving into the specifics of e/m, it's crucial to understand the historical context of its discovery. The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed a revolutionary period in physics, largely driven by advancements in understanding electricity and magnetism. Scientists were grappling with the nature of cathode rays, mysterious streams of particles emitted from a negatively charged electrode (cathode) in a vacuum tube.
J.J. Thomson's Groundbreaking Experiment: In 1897, J.J. Thomson performed a series of experiments using cathode ray tubes that proved pivotal in determining the e/m ratio of the electron. He meticulously studied the deflection of cathode rays under the influence of both electric and magnetic fields. By carefully balancing the forces exerted by these fields, he could deduce the ratio of the charge to the mass of the particles constituting the rays. This experiment was groundbreaking because it provided the first concrete evidence for the existence of subatomic particles—particles smaller than the atom itself—shattering the prevailing notion of the atom as the fundamental indivisible unit of matter.
Thomson's experiment not only determined the e/m ratio but also established that these particles carried a negative charge, far lighter than any known atom. He named these particles "corpuscles," which later became known as electrons.
Determining the Charge-to-Mass Ratio: Methods and Techniques
Several methods have been employed over the years to precisely determine the e/m ratio of the electron. Thomson's method, while groundbreaking, laid the foundation for more refined techniques. Let's explore some of the key approaches:
1. Thomson's Method: A Classic Approach
Thomson's method involved applying both electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to the direction of the cathode rays. The electric field exerts a force on the charged electrons, causing them to deflect. Similarly, the magnetic field exerts a force, causing a deflection in the opposite direction. By carefully adjusting the strengths of the electric and magnetic fields, Thomson achieved a condition where the two forces balanced each other, resulting in no net deflection of the electron beam. This balance allowed him to derive a relationship between the charge (e), mass (m), velocity (v), electric field strength (E), and magnetic field strength (B). The equation derived was:
e/m = E/(Bv)
This equation highlights that the e/m ratio could be calculated if the electric and magnetic field strengths and the velocity of the electrons were known. Thomson cleverly determined the electron velocity by measuring the deflection of the beam when only the magnetic field was applied.
2. Modern Techniques: Enhanced Precision
Modern techniques for determining e/m have evolved significantly, employing advanced instrumentation and refined experimental designs. These approaches often incorporate more sophisticated methods for measuring the electron's velocity and the applied fields. For example, techniques utilizing electron spectrometers and sophisticated detectors allow for far more precise measurements. The advanced techniques offer a higher level of accuracy and allow for the exploration of relativistic effects at higher electron velocities.
3. Cyclotron Resonance: A High-Precision Method
Cyclotron resonance is another technique used to determine the e/m ratio with high precision. This method utilizes the cyclotron motion of electrons in a uniform magnetic field. Electrons moving perpendicular to the magnetic field experience a Lorentz force that causes them to move in a circular path. The frequency of this circular motion, known as the cyclotron frequency, is directly proportional to the e/m ratio and the magnetic field strength. By measuring the cyclotron frequency, one can precisely determine the e/m ratio. This method provides very high accuracy because the frequency can be measured with great precision.
The Significance of the Charge-to-Mass Ratio
The precise determination of the e/m ratio has profound implications across various fields of physics:
-
Atomic Structure: The e/m ratio provided crucial evidence for the existence of the electron as a fundamental subatomic particle, revolutionizing our understanding of atomic structure. It helped establish the model of the atom with a positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons, replacing the earlier, less accurate models.
-
Particle Physics: The e/m ratio is a fundamental constant in particle physics, appearing in numerous equations and calculations related to particle behavior and interactions. Its accurate determination is essential for validating theoretical models and understanding the fundamental forces governing the universe.
-
Electromagnetism: The e/m ratio is inextricably linked to the laws of electromagnetism. Its precise value is crucial for calibrating instruments and for making accurate predictions in various electromagnetic phenomena.
-
Material Science: The e/m ratio is used in the study of materials, for example in understanding electron transport in solids and the behavior of electrons in different materials.
-
Technological Applications: The accurate understanding of electron behavior, in part derived from the e/m ratio, plays a vital role in the development and refinement of numerous technologies including electronics, medical imaging, and particle accelerators.
Beyond the Basics: Relativistic Effects and Variations
At high electron velocities, relativistic effects become significant, causing a noticeable change in the measured e/m ratio. Relativity dictates that the mass of an object increases with its velocity, approaching infinity as the velocity approaches the speed of light. Therefore, at relativistic speeds, the observed e/m ratio will appear lower than at low speeds. This relativistic effect is crucial to consider for accurate measurements, especially in high-energy experiments involving accelerated electrons.
Variations in the e/m ratio can also occur depending on the environment in which the measurement is made. For instance, the ratio might vary slightly in different materials due to interactions between electrons and the surrounding atoms. Such variations are typically small, but they can be significant in specific applications requiring extremely high precision.
Conclusion: A Constant with Enduring Importance
The charge-to-mass ratio of the electron, a seemingly simple constant, has played a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the universe. From its initial discovery through increasingly refined measurement techniques, the e/m ratio continues to be a vital parameter in numerous fields of physics and related technologies. Its accurate determination has underpinned significant advancements in atomic physics, particle physics, and countless technological applications. The ongoing pursuit of ever-more precise measurements of this fundamental constant serves as a testament to humanity's relentless quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe at its most fundamental levels. Further research and advancements in measurement techniques will undoubtedly continue to refine our understanding and unlock new possibilities in the realm of fundamental physics. The legacy of J.J. Thomson's pioneering work lives on, inspiring generations of physicists to explore the fundamental building blocks of matter and the universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Adjectives That Start With The Letter B
Mar 10, 2025
-
Electric Field Of A Charged Surface
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Phosphorus Have
Mar 10, 2025
-
Is Baking Soda An Acid Or Base
Mar 10, 2025
-
Moment Of Inertia Of A Solid Sphere
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Charge Mass Ratio Of An Electron . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
