Biuret Test Shows The Presence Of
Juapaving
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
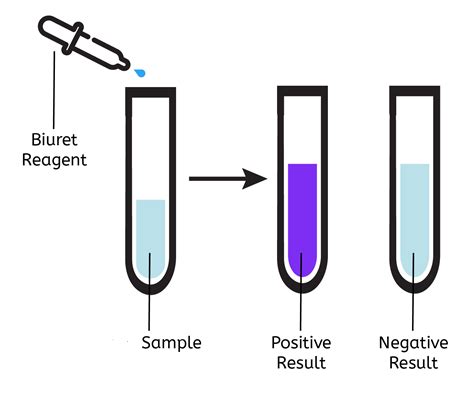
Table of Contents
Biuret Test: Unveiling the Presence of Peptide Bonds
The Biuret test is a widely used chemical test employed to detect the presence of peptide bonds. This simple yet powerful technique provides a quick and reliable way to identify the presence of proteins and other compounds containing two or more peptide linkages. Understanding the principles behind the Biuret test, its applications, limitations, and interpretations is crucial for various fields, including biochemistry, clinical diagnostics, and food science. This comprehensive article delves deep into the Biuret test, explaining its mechanism, procedure, and significance in different contexts.
The Chemistry Behind the Biuret Reaction
The Biuret test relies on a chemical reaction between copper(II) ions (Cu²⁺) and peptide bonds under alkaline conditions. Specifically, the test detects the presence of nitrogen atoms linked to a carbonyl group (–CO–) and a second nitrogen atom, which is the characteristic structural feature of a peptide bond.
The Mechanism
When a solution containing peptide bonds is treated with an alkaline copper(II) sulfate solution, a coordination complex forms between the copper(II) ions and the nitrogen atoms of the peptide bonds. This complex formation results in a distinctive violet-colored solution. The intensity of the violet color is directly proportional to the number of peptide bonds present in the sample. This color change is the hallmark of a positive Biuret test.
The reaction mechanism involves the coordination of the copper(II) ions with the nitrogen atoms of the peptide bonds, forming a chelate complex. This complex absorbs light in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, causing the observed color change. The alkaline conditions are crucial because they ensure that the peptide bonds are in their deprotonated form, making them more readily available for complexation with the copper(II) ions.
Key Reagents: A Closer Look
The two key components of the Biuret reagent are:
- Copper(II) Sulfate (CuSO₄): Provides the copper(II) ions essential for complex formation with the peptide bonds.
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) or Potassium Hydroxide (KOH): Creates the alkaline environment needed for the reaction to proceed effectively. The strong base deprotonates the peptide bonds, enhancing their reactivity with the copper(II) ions.
The exact composition of the Biuret reagent can vary depending on the specific application, but it typically includes a mixture of copper(II) sulfate, sodium/potassium hydroxide, and often a potassium sodium tartrate to help keep the copper(II) ions in solution.
Conducting the Biuret Test: A Step-by-Step Guide
Performing the Biuret test is relatively straightforward. The procedure typically involves the following steps:
-
Sample Preparation: The sample, which could be a protein solution, a food extract, or any other material suspected to contain peptide bonds, needs to be prepared appropriately. This might involve dissolving the sample in water or a suitable buffer solution.
-
Reagent Addition: A small amount of the Biuret reagent is added to the prepared sample. The reagent should be added dropwise, ensuring thorough mixing.
-
Observation: The mixture is then carefully observed for a change in color. The appearance of a violet or purple color indicates a positive Biuret test, signifying the presence of peptide bonds. The intensity of the color corresponds to the concentration of peptide bonds. A weak color indicates a low concentration of peptide bonds, while a strong color suggests a high concentration.
-
Control: It is essential to include a negative control (a solution without peptide bonds) and a positive control (a solution containing a known concentration of peptide bonds) to validate the test's accuracy. The negative control should not show any color change, while the positive control should exhibit a clear violet color.
Interpreting the Results: Positive, Negative, and Ambiguous Cases
-
Positive Result: A violet or purple color indicates the presence of peptide bonds, confirming the presence of proteins or other compounds containing at least two peptide linkages. The intensity of the color provides a qualitative estimation of the concentration.
-
Negative Result: The absence of any color change (remaining blue or clear) suggests the absence of peptide bonds. This indicates a lack of proteins or other compounds with two or more peptide linkages in the tested sample.
-
Ambiguous Results: Occasionally, the test might yield ambiguous results. This could be due to interfering substances in the sample or an insufficient amount of peptide bonds. In such cases, further analysis is necessary to confirm the presence or absence of peptide bonds. Interfering substances might include reducing sugars, which can react with the copper(II) ions and produce a different color change.
Applications of the Biuret Test: A Wide Spectrum of Uses
The versatility of the Biuret test makes it an invaluable tool in diverse fields:
1. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology:
The Biuret test is a fundamental technique in biochemistry and molecular biology laboratories for the quick screening and estimation of protein concentration in various samples. This is invaluable for protein purification, quantification, and analysis.
2. Clinical Diagnostics:
The test can be used in clinical settings for preliminary protein analysis in body fluids such as serum or urine. Abnormal protein levels can indicate various medical conditions. However, it's crucial to remember that the Biuret test is a preliminary test, and further, more specific tests are often required for accurate diagnosis.
3. Food Science and Nutrition:
The Biuret test finds application in food analysis to determine the protein content of different food products. This is important for nutritional labeling and quality control purposes. It can help assess the protein quality and quantity in various food sources.
4. Environmental Monitoring:
In environmental science, the Biuret test can be utilized to detect the presence of proteins in water samples or soil extracts. This can aid in monitoring pollution and assessing environmental quality.
Limitations of the Biuret Test: Considerations and Alternatives
Despite its wide applications, the Biuret test has certain limitations:
-
Sensitivity: The Biuret test is not highly sensitive and may not detect small amounts of proteins or peptides. For more sensitive detection, techniques like Bradford assay or Lowry assay are preferred.
-
Specificity: While the Biuret test is specific to peptide bonds, certain compounds might interfere with the reaction and produce false-positive or false-negative results.
-
Quantitative Limitations: Although the intensity of the color provides a qualitative estimate of protein concentration, it is not suitable for precise quantitative measurements. Spectrophotometric techniques are preferred for accurate quantification.
-
Interferences: Compounds such as ammonium ions, reducing sugars, and certain buffers can interfere with the Biuret reaction and lead to inaccurate results.
Despite these limitations, the Biuret test remains a valuable tool because of its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and wide applicability. When used appropriately, along with proper controls and considerations for potential interferences, it provides a valuable method for detecting the presence of peptide bonds.
Conclusion: A Simple Test with Far-Reaching Implications
The Biuret test, despite its simplicity, represents a powerful and versatile tool for detecting peptide bonds. Its widespread applications across biochemistry, clinical diagnostics, food science, and environmental monitoring highlight its importance. While understanding its limitations, including its sensitivity and potential interferences, is crucial for accurate interpretation, the Biuret test continues to be a valuable technique for the qualitative detection of proteins and peptides, providing a foundational step in more comprehensive analyses. Its ease of execution and cost-effectiveness make it a cornerstone method in many laboratories worldwide. Remember always to use appropriate controls to ensure reliable and meaningful results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Plant Is Where Photosynthesis Takes Place
Apr 02, 2025
-
12 Cm Is How Many Inches
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Most Abundant Gas In The Earths Atmosphere Is
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is Rubbing Alcohol And Denatured Alcohol The Same
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is 17 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Biuret Test Shows The Presence Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
