Are Mitochondria Found In Most Animal Cells
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
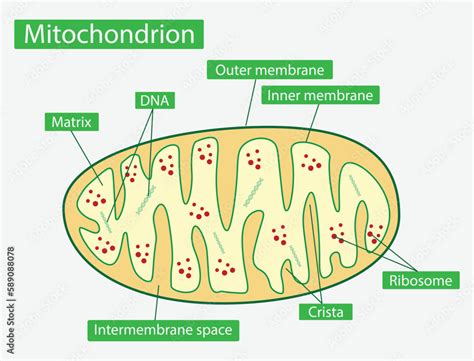
Table of Contents
Are Mitochondria Found in Most Animal Cells? A Deep Dive into the Powerhouses of the Cell
Mitochondria, often dubbed the "powerhouses of the cell," are essential organelles found within the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells. This article delves deep into the ubiquitous nature of mitochondria in animal cells, exploring their crucial role in cellular respiration, their unique structure, and the exceptions where they might be absent or significantly altered. We'll also touch upon the fascinating implications of mitochondrial dysfunction and the ongoing research in this vital area of cell biology.
The Ubiquity of Mitochondria in Animal Cells: A Fundamental Truth
Yes, mitochondria are found in the vast majority of animal cells. Their presence is a defining characteristic of eukaryotic cells, which distinguishes them from prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) that lack membrane-bound organelles. The fundamental role of mitochondria in ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production—the cell's primary energy currency—makes their presence virtually indispensable for the survival and function of most animal cells.
The Crucial Role of Mitochondria in Cellular Respiration
Mitochondria are the primary sites of cellular respiration, a metabolic process that converts nutrients into ATP. This process involves three main stages:
- Glycolysis: This initial step takes place in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose into pyruvate.
- Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Pyruvate is transported into the mitochondrial matrix, where it enters the Krebs cycle, a series of chemical reactions that release carbon dioxide and generate high-energy electron carriers.
- Electron Transport Chain (ETC): The electron carriers from the Krebs cycle deliver electrons to the ETC, located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This electron flow drives the pumping of protons across the membrane, creating a proton gradient. This gradient then powers ATP synthase, an enzyme that produces ATP.
This intricate process is fundamental to virtually all energy-demanding cellular activities, from muscle contraction and nerve impulse transmission to protein synthesis and cell division. The efficiency of mitochondrial ATP production is vital for the overall health and function of the animal organism.
The Structure of Mitochondria: A Closer Look
Understanding the structure of mitochondria helps explain their remarkable functionality. Each mitochondrion is characterized by a double membrane system:
- Outer Mitochondrial Membrane: This smooth outer membrane acts as a barrier, regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the organelle.
- Inner Mitochondrial Membrane: This highly folded membrane contains the ETC and ATP synthase. The folds, known as cristae, significantly increase the surface area available for ATP production. The compartment enclosed by the inner membrane is called the mitochondrial matrix.
The mitochondrial matrix houses the enzymes responsible for the Krebs cycle and other crucial metabolic reactions. Mitochondria also possess their own DNA (mtDNA), ribosomes, and the machinery for protein synthesis. This unique characteristic supports the endosymbiotic theory, which proposes that mitochondria were once independent prokaryotic organisms that formed a symbiotic relationship with early eukaryotic cells.
Exceptions to the Rule: Cells with Few or Modified Mitochondria
While mitochondria are prevalent in animal cells, there are some exceptions and variations:
-
Mature Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes): These cells, responsible for oxygen transport, lack mitochondria. Their energy needs are met through glycolysis, a less efficient process. The absence of mitochondria is crucial to maximize the space available for hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein.
-
Corneal Epithelial Cells: These cells also exhibit significantly reduced numbers of mitochondria to maintain transparency. High mitochondrial density would scatter light, impairing vision.
-
Cells with Specialized Energy Metabolism: Some cells, like those in certain muscle types, might have modified mitochondrial morphology or numbers depending on their energy demands. For instance, highly active muscle cells often possess a large number of mitochondria to support their high energy requirements.
These exceptions highlight the adaptability of cells and their ability to optimize their energy production mechanisms based on their specific functions and environmental conditions.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Disease: The Consequences of Impaired Energy Production
Malfunctioning mitochondria can have profound consequences for cell and organismal health. Mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in a wide range of diseases, collectively known as mitochondrial disorders. These disorders are often characterized by impaired ATP production, leading to a variety of symptoms depending on the affected tissues and the severity of the dysfunction.
Some common mitochondrial disorders include:
- Mitochondrial myopathies: These affect muscle function, leading to weakness, fatigue, and muscle pain.
- Neurological disorders: Mitochondrial dysfunction can impact brain function, resulting in conditions like epilepsy, stroke-like episodes, and developmental delays.
- Cardiomyopathies: These affect the heart muscle, causing heart failure and other cardiovascular problems.
- Diabetes: Mitochondrial dysfunction can contribute to impaired insulin production and glucose metabolism.
The diverse range of symptoms associated with mitochondrial disorders highlights the critical role of mitochondria in maintaining the health and proper functioning of various organ systems throughout the body.
Research and Future Directions: Unraveling the Mysteries of Mitochondria
Ongoing research continues to uncover the complexities of mitochondrial biology and its role in health and disease. Areas of active investigation include:
- Mitochondrial dynamics: The processes of mitochondrial fission (division) and fusion (merging) are essential for maintaining mitochondrial health and function. Understanding these processes is crucial for developing therapies for mitochondrial disorders.
- Mitochondrial biogenesis: The process of generating new mitochondria is a complex interplay of nuclear and mitochondrial genes. Regulating this process might offer therapeutic opportunities for diseases involving mitochondrial deficiency.
- Mitochondrial quality control: Mechanisms for eliminating damaged or dysfunctional mitochondria are critical for maintaining cellular health. Research is exploring ways to enhance these processes to prevent or treat mitochondrial diseases.
- Mitochondria and aging: Mitochondrial dysfunction is strongly associated with the aging process. Studies are investigating ways to maintain mitochondrial health throughout life to promote healthy aging.
The ongoing research in this area promises to further illuminate the intricate role of mitochondria in cellular function, aging, and disease, leading to improved diagnostic tools and effective therapies for a wide range of debilitating conditions.
Conclusion: Mitochondria – Essential Organelles in the Animal Cell
In conclusion, mitochondria are indeed found in the vast majority of animal cells, playing a pivotal role in energy production and cellular function. Their ubiquitous presence underscores their critical importance for survival and health. While exceptions exist, the fundamental role of these "powerhouses" remains undeniable. Further research into mitochondrial biology will continue to unveil their secrets, paving the way for novel therapeutic strategies to address diseases linked to mitochondrial dysfunction and improve overall human health. Understanding the intricate structure and function of mitochondria is a cornerstone of modern cell biology, and its significance extends to various fields, including medicine, genetics, and aging research.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 21 And 24
Mar 23, 2025
-
Rank The Following Chemical Bonds According To Their Strength
Mar 23, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 15 And 21
Mar 23, 2025
-
How To Convert Hexadecimal To Octal
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Organelles Are Only Found In Plant Cells
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Are Mitochondria Found In Most Animal Cells . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
