According To The Law Of Conservation Of Mass
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
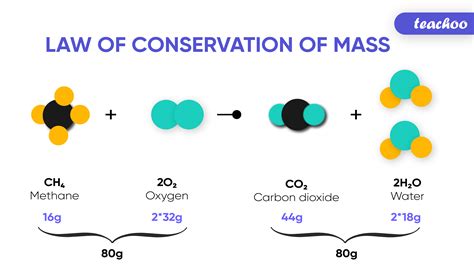
Table of Contents
According to the Law of Conservation of Mass: A Deep Dive into Matter's Unchanging Nature
The Law of Conservation of Mass, a cornerstone of chemistry and physics, asserts a fundamental truth about the universe: matter cannot be created or destroyed. This seemingly simple statement underpins countless scientific principles and has profound implications across various fields, from basic chemical reactions to complex astrophysical phenomena. This comprehensive article will explore the law's implications, historical context, limitations, and its crucial role in understanding the physical world.
A Historical Perspective: From Lavoisier to Modern Science
The formal articulation of the Law of Conservation of Mass is largely attributed to Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier, a renowned 18th-century French chemist often hailed as the "father of modern chemistry." Through meticulous experimentation, particularly his work with combustion reactions, Lavoisier demonstrated that the total mass of the reactants (the substances undergoing change) always equaled the total mass of the products (the substances formed after the reaction). His famous quote, "Nothing is lost, nothing is created, everything is transformed," encapsulates the essence of this fundamental law.
Prior to Lavoisier's work, the understanding of chemical reactions was less precise. The phlogiston theory, a prevailing belief at the time, proposed the existence of a fire-like element called phlogiston that was released during combustion. This theory failed to account for the observed mass changes during reactions. Lavoisier's experiments, conducted with careful measurements using sealed vessels, definitively refuted the phlogiston theory and established the Law of Conservation of Mass as a fundamental principle.
Understanding the Law: Mass Remains Constant
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that in a closed system, the total mass remains constant during any physical or chemical change. This means that even though substances may transform into different forms – a solid might melt into a liquid, or reactants might combine to form new products – the total amount of matter involved remains unchanged.
Let's consider a simple example: the combustion of methane gas (CH₄) with oxygen (O₂). The balanced chemical equation is:
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
According to the Law of Conservation of Mass, the total mass of methane and oxygen reacting will be precisely equal to the total mass of carbon dioxide and water produced. No mass is lost or gained during this transformation; it simply changes form.
This principle is crucial for stoichiometry, the branch of chemistry dealing with quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. By applying the law, chemists can accurately predict the amounts of products formed from given amounts of reactants, ensuring precise control over chemical processes in various industrial applications.
Applications Across Diverse Scientific Fields
The Law of Conservation of Mass isn't confined to the realm of basic chemistry; its implications extend to numerous fields:
1. Nuclear Reactions: A Seemingly Contradictory Exception?
While the Law of Conservation of Mass holds true for most chemical reactions, it needs a slight modification when dealing with nuclear reactions. In nuclear reactions, a small amount of mass is converted into energy, as famously described by Einstein's equation, E=mc². This mass-energy equivalence doesn't invalidate the law entirely; it simply highlights that mass and energy are interconvertible. A more accurate, overarching principle is the Law of Conservation of Mass-Energy, which states that the total mass-energy of a closed system remains constant.
2. Astrophysics and Cosmology: Understanding Stellar Evolution
In astrophysics, the Law of Conservation of Mass is essential for understanding the processes occurring within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis, the process by which stars create heavier elements from lighter ones, obeys this principle. While energy is released in the process, the total mass-energy of the system remains conserved. Studying the mass balance in stellar evolution helps scientists model the life cycle of stars and understand the origin of elements in the universe.
3. Environmental Science: Tracking Pollutants and Waste Management
In environmental science, the Law of Conservation of Mass helps track pollutants and manage waste. For example, understanding the mass balance of pollutants in an ecosystem allows scientists to assess the sources and pathways of contamination. Effective waste management strategies rely on applying this principle to minimize environmental impact and ensure proper disposal or recycling of materials.
4. Engineering and Industrial Processes: Ensuring Efficiency and Safety
In engineering and industrial applications, the Law of Conservation of Mass ensures efficient and safe operations. Chemical engineers use it to design reactors and optimize processes, ensuring that reactants are completely converted into products, minimizing waste, and maximizing efficiency. Understanding mass balances is crucial in designing safe and efficient industrial processes.
Limitations and Considerations
While the Law of Conservation of Mass is a powerful and generally applicable principle, it has certain limitations:
- Open Systems: The law strictly applies to closed systems where there is no exchange of matter with the surroundings. In open systems, the mass within the system can change due to the inflow or outflow of matter.
- Nuclear Reactions: As previously mentioned, nuclear reactions involving mass-energy conversion require the more comprehensive Law of Conservation of Mass-Energy.
- Relativistic Effects: At extremely high velocities approaching the speed of light, relativistic effects become significant, and the classical Law of Conservation of Mass needs to be modified to incorporate relativistic mass.
The Law's Enduring Significance
Despite its limitations, the Law of Conservation of Mass remains a cornerstone of scientific understanding. Its simplicity and broad applicability make it a fundamental concept taught in early science education, laying the foundation for more advanced studies in chemistry, physics, and other related fields. The law's enduring significance lies in its ability to provide a framework for understanding and quantifying changes in matter, underpinning countless scientific advancements and technological applications. It reminds us that even amidst the complexities of the universe, certain fundamental principles remain steadfast, guiding our understanding of the world around us.
Further Exploration and Deeper Understanding
To deepen your understanding of the Law of Conservation of Mass, consider exploring the following topics:
- Stoichiometry Calculations: Practice solving problems involving balanced chemical equations and mass relationships to solidify your grasp of the law's practical applications.
- Thermodynamics: Explore the relationship between the law and the First Law of Thermodynamics, which deals with the conservation of energy.
- Relativistic Mass: Investigate how the concept of mass changes at high velocities, requiring modifications to the classical law.
- Nuclear Chemistry: Delve into the fascinating world of nuclear reactions and the conversion of mass into energy.
By exploring these areas, you'll gain a more comprehensive understanding of this fundamental law and its implications in various scientific disciplines. The Law of Conservation of Mass isn't just a theoretical concept; it's a practical tool used daily to understand and manipulate the world around us. Its continued relevance underlines its importance as a cornerstone of scientific knowledge.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats The Square Root Of 400
Mar 10, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 12
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Cubic Inches In A Cubic Ft
Mar 10, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 3 And 7
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 50 Metres
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about According To The Law Of Conservation Of Mass . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
