A Quadrilateral Where Each Angle Is A Right Angle
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
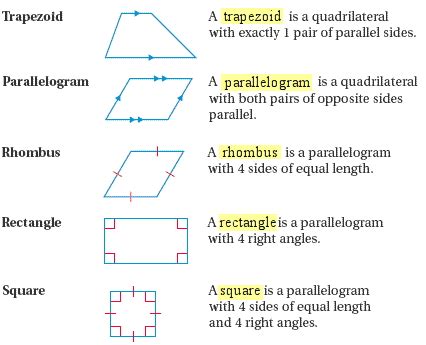
Table of Contents
A Quadrilateral Where Each Angle is a Right Angle: Exploring the Properties of Rectangles and Squares
A quadrilateral, by definition, is a polygon with four sides and four angles. When each of these angles measures exactly 90 degrees, we enter the fascinating world of rectangles and squares – special cases within the broader family of quadrilaterals. This article delves deep into the properties, theorems, and applications of these unique shapes, exploring their characteristics and distinctions. We'll move beyond simple definitions and delve into the mathematical elegance that underpins their significance.
Defining Rectangles and Squares: More Than Just Right Angles
While all squares are rectangles, not all rectangles are squares. This subtle yet crucial difference hinges on the lengths of their sides. Let's define each:
Rectangle: The Fundamental Characteristics
A rectangle is a quadrilateral where:
- All four angles are right angles (90 degrees). This is the defining characteristic.
- Opposite sides are parallel and equal in length. This ensures the shape's stability and predictability.
These two properties lead to numerous other characteristics, including:
- Diagonals bisect each other: The lines connecting opposite corners intersect precisely at their midpoints.
- Diagonals are equal in length: Both diagonals have identical measurements.
- Opposite sides are congruent: They possess the same length.
Square: The Perfect Rectangle
A square takes the properties of a rectangle one step further. It's a quadrilateral where:
- All four angles are right angles (90 degrees). Inherited from its rectangular nature.
- All four sides are equal in length. This adds symmetry and regularity.
This additional property of equal sides grants the square additional characteristics:
- Diagonals bisect each other at right angles: Not only do they bisect, but they also intersect at a perfect 90-degree angle.
- Diagonals bisect the angles: Each diagonal splits its corresponding angles into two 45-degree angles.
- Possesses rotational symmetry: A square looks identical after a 90-degree rotation.
- Possesses reflectional symmetry: A square can be reflected across multiple lines of symmetry and still appear unchanged.
Proofs and Theorems: Understanding the Mathematical Underpinnings
The properties of rectangles and squares aren't arbitrary; they're derived from rigorous mathematical proofs. Let's examine a few key examples:
Proof: Opposite Sides of a Rectangle are Equal
Consider a rectangle ABCD. We can prove that AB = CD and BC = AD using the concept of congruent triangles.
- Draw diagonals AC and BD.
- In triangles ABC and ADC, we have:
- AB = AB (common side)
- ∠BAC = ∠DCA = 90° (angles of a rectangle)
- ∠BCA = ∠DAC (alternate interior angles, since AB || CD)
- By Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) congruence, triangles ABC and CDA are congruent.
- Therefore, AB = CD and BC = AD (corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent).
Proof: Diagonals of a Rectangle Bisect Each Other
Let's again use rectangle ABCD with diagonals AC and BD intersecting at point O.
- In triangles ABO and CDO, we have:
- ∠BAO = ∠DCO (alternate interior angles)
- ∠ABO = ∠CDO (alternate interior angles)
- AB = CD (opposite sides of a rectangle are equal)
- By Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) congruence, triangles ABO and CDO are congruent.
- Therefore, AO = CO and BO = DO (corresponding parts of congruent triangles). This proves that the diagonals bisect each other.
Applications: Rectangles and Squares in the Real World
The geometric perfection of rectangles and squares makes them ubiquitous in our world. Their practicality extends across numerous disciplines:
Architecture and Construction
- Building foundations: The stability and strength of rectangles make them ideal for building foundations and supporting structures.
- Room layouts: Rectangular rooms are common due to their efficient use of space and ease of furnishing.
- Window and door frames: The right angles ensure proper fitting and sealing.
- Bricklaying: Rectangular bricks are easily stacked to create walls and structures.
Design and Art
- Graphic design: Rectangles and squares form the basis of many layouts and designs, offering visual balance and order.
- Painting and sculpture: Artists often utilize these shapes to create composition and structure within their works.
- Packaging: Boxes and containers frequently employ rectangular and square shapes for their practicality and efficiency.
Engineering and Technology
- Circuit boards: The precise dimensions and right angles are crucial for the placement of electronic components.
- Computer screens: Rectangular screens are the standard for displays.
- Machining and manufacturing: Many manufactured parts are rectangular or square due to their ease of production and compatibility with standard tools.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
The study of rectangles and squares extends beyond their fundamental properties. Let's briefly touch upon some related concepts:
Area and Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles and squares is straightforward:
- Rectangle:
- Area = length × width
- Perimeter = 2 × (length + width)
- Square:
- Area = side × side = side²
- Perimeter = 4 × side
These formulas are fundamental in various applications, from land surveying to material estimation.
Tessellations: Covering Surfaces Without Gaps
Rectangles and squares are perfect for creating tessellations – patterns that completely cover a surface without any gaps or overlaps. Their right angles and consistent dimensions make them uniquely suited for this purpose. This property is evident in tiled floors, brick walls, and even honeycomb structures.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Rectangles and Squares
From the simplest building blocks to the most complex engineering feats, rectangles and squares play a pivotal role in our world. Their inherent stability, ease of construction, and mathematical elegance have cemented their place as fundamental geometric shapes. Understanding their properties, theorems, and applications is essential for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of geometry and its pervasive influence on our lives. This exploration has only scratched the surface; continued study will reveal even more fascinating facets of these seemingly simple yet profoundly important shapes. The beauty of mathematics often lies in its ability to reveal order and predictability within the world around us, and the properties of rectangles and squares are a prime example of this elegance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Layers Of The Sun In Order
Mar 26, 2025
-
Scanner Is Input Device Or Output Device
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is The Absolute Value Of A Number Always Positive
Mar 26, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 3 And 5
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Edges Does A Rectangular Prism Has
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Quadrilateral Where Each Angle Is A Right Angle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
