84 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
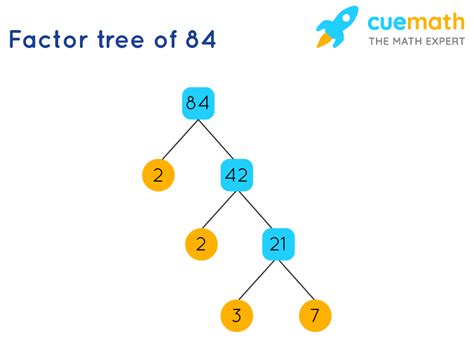
Table of Contents
84 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, the process of breaking down a composite number into its prime number components, is a fundamental concept in number theory. Understanding prime factorization allows us to simplify complex mathematical operations, solve problems related to greatest common divisors (GCD) and least common multiples (LCM), and opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts. This article will delve into the prime factorization of 84, exploring the process step-by-step and highlighting its broader implications within the field of mathematics.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before diving into the factorization of 84, let's establish a firm understanding of the key concepts:
What are Prime Numbers?
A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it cannot be expressed as the product of two smaller whole numbers. Examples of prime numbers include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite.
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of expressing a composite number (a whole number greater than 1 that is not prime) as a product of its prime factors. Each composite number has a unique prime factorization, a fact known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This uniqueness is crucial in various mathematical applications.
Finding the Prime Factors of 84
Now, let's apply the concept of prime factorization to the number 84. We'll use a method often called the "factor tree" to visually represent the process.
Step-by-Step Factorization of 84:
-
Start with the number 84: We begin with our target number, 84.
-
Find the smallest prime factor: The smallest prime number is 2. Since 84 is an even number, it's divisible by 2. We divide 84 by 2 to get 42. Our initial factorization looks like this: 84 = 2 x 42.
-
Continue factoring: Now we focus on 42. Again, 42 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. Dividing 42 by 2 gives us 21. Our factorization becomes: 84 = 2 x 2 x 21.
-
Identify the next prime factor: 21 is no longer divisible by 2. The next prime number is 3. Since 21 is divisible by 3 (21 / 3 = 7), we have: 84 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 7.
-
Reach prime factors: Both 3 and 7 are prime numbers. We've successfully broken down 84 into its prime factors.
The Prime Factorization of 84:
Therefore, the prime factorization of 84 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 7, which can also be written as 2² x 3 x 7. This means that 84 can only be expressed as the product of these prime numbers.
Visual Representation: The Factor Tree
A factor tree is a helpful visual aid for prime factorization. For 84, the factor tree would look like this:
84
/ \
2 42
/ \
2 21
/ \
3 7
Each branch represents a division by a prime factor until all the leaves are prime numbers.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The ability to find the prime factorization of a number is crucial in several areas of mathematics and its applications:
1. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM):
Prime factorization is the most efficient method for finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) and the least common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
For example, let's find the GCD and LCM of 84 and 126:
- Prime factorization of 84: 2² x 3 x 7
- Prime factorization of 126: 2 x 3² x 7
GCD: The common prime factors are 2, 3, and 7. The lowest power of each common factor is used: 2¹ x 3¹ x 7¹ = 42. Therefore, the GCD(84, 126) = 42.
LCM: We take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization: 2² x 3² x 7¹ = 4 x 9 x 7 = 252. Therefore, the LCM(84, 126) = 252.
2. Simplifying Fractions:
Prime factorization helps in simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. By finding the prime factors of the numerator and denominator, we can cancel out common factors, reducing the fraction to its simplest form.
For example, consider the fraction 84/126. Using the prime factorizations above:
84/126 = (2² x 3 x 7) / (2 x 3² x 7) = 2/3
3. Cryptography:
Prime numbers and their properties play a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. The security of these systems relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components.
4. Modular Arithmetic:
Prime factorization is also fundamental to modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory that deals with remainders after division. Many applications in computer science and cryptography rely on the properties of modular arithmetic, which are intrinsically linked to prime numbers.
Advanced Concepts Related to Prime Factorization
Beyond the basic process, several more advanced concepts relate to prime factorization:
1. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic:
This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This uniqueness is a cornerstone of number theory.
2. Mersenne Primes:
Mersenne primes are prime numbers that are one less than a power of two (2<sup>p</sup> - 1, where p is a prime number). Finding Mersenne primes is an active area of research, with the Great Internet Mersenne Prime Search (GIMPS) project contributing significantly to the discovery of some of the largest known prime numbers.
3. Distribution of Prime Numbers:
The distribution of prime numbers among integers is a complex and fascinating subject. While there's no simple formula to predict the next prime number, mathematicians have developed sophisticated theories and approximations related to the distribution of primes, such as the Prime Number Theorem.
4. Algorithms for Prime Factorization:
Various algorithms have been developed to find the prime factors of large numbers. Some of these algorithms, like trial division and the Pollard rho algorithm, are relatively straightforward. However, factoring very large numbers remains computationally challenging, forming the basis of the security of many cryptographic systems.
Conclusion: The Significance of 84's Prime Factorization
This in-depth exploration of the prime factorization of 84 demonstrates the fundamental importance of this concept in number theory and its diverse applications. From simplifying fractions to securing online transactions, understanding how to break down composite numbers into their prime components is a crucial skill for anyone interested in mathematics and its real-world applications. The seemingly simple act of finding the prime factors of 84 (2² x 3 x 7) serves as a gateway to understanding a vast and complex area of mathematics. Its seemingly simple nature belies the profound implications it holds within the realm of number theory and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Find The Relative Abundance
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Are The Factors For 86
Mar 26, 2025
-
Electric Field Due To Infinite Line Charge
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Chromosomes Does Gametes Have
Mar 26, 2025
-
Whats The Greatest Common Factor Of 12 And 18
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 84 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
