3 And 2/5 As A Decimal
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
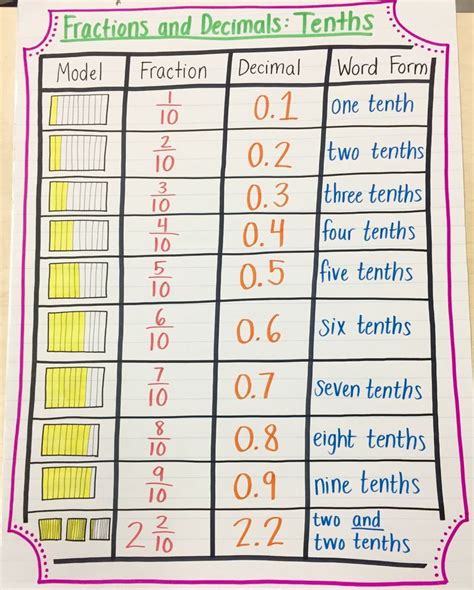
Table of Contents
3 and 2/5 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics with applications spanning various fields, from simple everyday calculations to complex scientific computations. This comprehensive guide delves into the process of converting the mixed number 3 and 2/5 into its decimal equivalent, exploring different methods and offering insights into the underlying principles. We'll also touch upon the broader context of fraction-to-decimal conversion, providing a solid foundation for understanding this important mathematical concept.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Fractions
Before diving into the conversion process, let's briefly review the concepts of mixed numbers and fractions. A mixed number, like 3 and 2/5, combines a whole number (3 in this case) and a proper fraction (2/5). A fraction, such as 2/5, represents a part of a whole, where the numerator (2) indicates the number of parts and the denominator (5) indicates the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
Method 1: Converting the Fraction to a Decimal
The most straightforward method for converting 3 and 2/5 to a decimal involves focusing on the fractional component first. To convert the fraction 2/5 to a decimal, we perform a simple division: we divide the numerator (2) by the denominator (5).
2 ÷ 5 = 0.4
Therefore, the fraction 2/5 is equivalent to the decimal 0.4. Since the mixed number is 3 and 2/5, we simply add the whole number component:
3 + 0.4 = 3.4
Therefore, 3 and 2/5 as a decimal is 3.4.
Method 2: Converting to an Improper Fraction First
An alternative approach involves first converting the mixed number into an improper fraction. To do this, we multiply the whole number by the denominator and add the numerator, keeping the same denominator.
(3 × 5) + 2 = 17
So, 3 and 2/5 is equivalent to the improper fraction 17/5. Now, we divide the numerator by the denominator:
17 ÷ 5 = 3.4
Again, we arrive at the decimal equivalent 3.4.
Understanding Decimal Place Value
It's crucial to understand the concept of decimal place value. The number 3.4 can be broken down as follows:
- 3: Represents 3 ones (or units).
- 4: Represents 4 tenths (0.4).
The decimal point separates the whole number part from the fractional part. Each position to the right of the decimal point represents a decreasing power of 10: tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on.
Practical Applications of Decimal Conversion
The ability to convert fractions to decimals has numerous practical applications:
-
Financial Calculations: Dealing with monetary amounts often requires converting fractions of currency units to decimals (e.g., calculating sales tax, discounts, or interest).
-
Measurement: Many measurement systems, such as the metric system, use decimal notation. Converting fractional measurements to decimals is essential for accurate calculations and comparisons.
-
Scientific and Engineering Calculations: In scientific and engineering contexts, precise calculations often involve converting fractions to decimals for greater accuracy and ease of computation.
-
Data Analysis: Data analysis often involves working with decimal numbers. Converting fractional data to decimals is necessary for consistent data handling and analysis.
-
Everyday Life: Many everyday situations require converting fractions to decimals, such as calculating tips, dividing recipes, or determining fuel efficiency.
Other Examples of Fraction-to-Decimal Conversions
Let's explore a few more examples to solidify our understanding of the conversion process:
- 1/4 as a decimal: 1 ÷ 4 = 0.25
- 3/8 as a decimal: 3 ÷ 8 = 0.375
- 5/2 as a decimal: 5 ÷ 2 = 2.5
- 7/10 as a decimal: 7 ÷ 10 = 0.7
- 12/25 as a decimal: 12 ÷ 25 = 0.48
These examples showcase the versatility of the division method in converting various fractions into their decimal equivalents.
Repeating Decimals
It's important to note that not all fractions result in terminating decimals (decimals with a finite number of digits). Some fractions produce repeating decimals, which have a sequence of digits that repeat infinitely. For example, 1/3 = 0.3333... (the 3 repeats infinitely). These repeating decimals are often represented using a bar over the repeating digit(s), such as 0.3̅.
Terminating vs. Repeating Decimals: A Deeper Look
The nature of a decimal representation (terminating or repeating) depends on the denominator of the fraction when it's simplified to its lowest terms. If the denominator only contains prime factors of 2 and/or 5, the decimal will terminate. If the denominator contains prime factors other than 2 and 5, the decimal will repeat.
Advanced Techniques: Using Place Value and Equivalent Fractions
While the division method is the most straightforward, other approaches can enhance your understanding:
-
Place Value: Recognizing place value is helpful, particularly with simple fractions. For example, 2/10 is directly understood as 0.2 because the denominator is a power of 10.
-
Equivalent Fractions: Creating equivalent fractions with denominators that are powers of 10 can simplify the conversion. For example, to convert 3/4 to a decimal, you can find an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 100: 3/4 = 75/100 = 0.75. This method becomes particularly useful when dealing with more complex fractions.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
When converting fractions to decimals, some common mistakes can occur:
-
Incorrect Division: Carefully performing the division is crucial. Double-check your calculations to avoid errors.
-
Misunderstanding of Place Value: Make sure you correctly interpret the decimal place values.
-
Ignoring the Whole Number: Remember to include the whole number when working with mixed numbers.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction-to-Decimal Conversions
Converting 3 and 2/5 to a decimal, resulting in 3.4, is a fundamental skill with broad applications. Understanding the different methods, including the direct division of the fraction and the conversion to an improper fraction, provides flexibility in tackling various fraction-to-decimal conversion problems. Furthermore, grasping the concept of decimal place value, the distinction between terminating and repeating decimals, and the potential use of equivalent fractions will strengthen your mathematical abilities and expand your problem-solving skills. Remember to practice consistently to build fluency and confidence in performing these conversions accurately and efficiently. This solid foundation will empower you to handle a vast array of mathematical tasks with ease and precision, whether in academic settings or practical applications in everyday life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Push Or A Pull Is Called
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 And 2/5 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
