Write The Prime Factorization Of 18
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
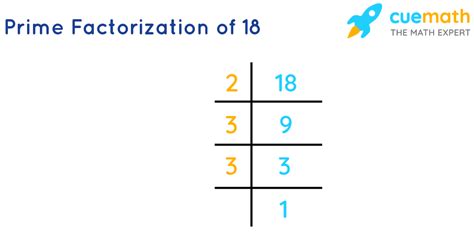
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Prime Factorization of 18: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 18?", opens a gateway into the fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, the journey to understanding how we arrive at that answer reveals fundamental concepts crucial to mathematics and computer science. This article will not only provide the prime factorization of 18 but will also delve into the underlying principles, exploring related concepts like prime numbers, composite numbers, and the fundamental theorem of arithmetic. We'll also touch upon the practical applications of prime factorization in cryptography and other fields.
Understanding Prime and Composite Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 18, let's establish a solid foundation by defining key terms.
Prime Numbers: The Building Blocks
A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Prime numbers are considered the fundamental building blocks of all other whole numbers. Their unique properties make them crucial in various mathematical fields.
Composite Numbers: Built from Primes
A composite number is a whole number greater than 1 that is not prime. This means it can be divided evenly by at least one whole number other than 1 and itself. For instance, 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), and 9 (3 x 3) are all composite numbers. Every composite number can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers – this is the essence of prime factorization.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 18
Now, let's address the central question: What is the prime factorization of 18?
The prime factorization of a number is the expression of that number as a product of its prime factors. To find the prime factorization of 18, we systematically break it down into smaller factors until we are left with only prime numbers.
One common method is to use a factor tree:
18
/ \
2 9
/ \
3 3
Starting with 18, we find the smallest prime number that divides it evenly, which is 2. 18 divided by 2 is 9. Now we look at 9. The smallest prime number that divides 9 is 3. 9 divided by 3 is 3, which is also a prime number. Therefore, the prime factorization of 18 is 2 x 3 x 3, or 2 x 3².
Another method involves repeated division:
- Divide 18 by the smallest prime number, 2: 18 ÷ 2 = 9
- Divide the result (9) by the smallest prime number that divides it, which is 3: 9 ÷ 3 = 3
- The result (3) is a prime number.
This again confirms that the prime factorization of 18 is 2 x 3 x 3 or 2 x 3².
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The success of our prime factorization of 18 is guaranteed by a cornerstone theorem in number theory: the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This uniqueness is incredibly important in many areas of mathematics. It provides a fundamental building block for various mathematical structures and operations.
Applications of Prime Factorization
While finding the prime factorization of 18 might seem like a simple exercise, the concept of prime factorization has far-reaching implications across various fields.
Cryptography: Securing Our Digital World
Prime factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in the RSA algorithm, one of the most widely used public-key cryptosystems. RSA relies on the fact that multiplying two large prime numbers is computationally easy, but factoring the resulting product back into its original prime factors is incredibly difficult. This computational asymmetry is what makes RSA secure. The difficulty of factoring large numbers underpins the security of many online transactions, protecting sensitive data like financial information and personal communications.
Other Applications
Beyond cryptography, prime factorization finds applications in:
- Coding Theory: Error detection and correction codes often utilize prime numbers to enhance their efficiency and robustness.
- Computer Science: Prime factorization is used in algorithm design and analysis, particularly in areas dealing with number theory and cryptography.
- Mathematics Research: Prime factorization continues to be an area of active research, with unsolved problems like the distribution of prime numbers driving ongoing investigation.
Exploring Further: Advanced Concepts
The seemingly simple task of finding the prime factorization of 18 opens doors to more complex and fascinating mathematical concepts. Here are a few avenues for further exploration:
- Sieve of Eratosthenes: This ancient algorithm provides an efficient method for finding all prime numbers up to a specified limit. Understanding how it works can deepen your appreciation for prime numbers.
- Prime Number Theorem: This theorem provides an approximate estimate for the number of prime numbers less than or equal to a given number. It's a landmark result in number theory, illustrating the distribution of prime numbers.
- Mersenne Primes: These are prime numbers of the form 2<sup>p</sup> - 1, where p is also a prime number. The search for Mersenne primes continues to be a driving force in computational number theory.
- Twin Primes: These are pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2 (e.g., 3 and 5, 11 and 13). The twin prime conjecture, which posits that there are infinitely many twin primes, remains one of the most challenging unsolved problems in mathematics.
Conclusion: The Significance of a Simple Factorization
The prime factorization of 18, while seemingly trivial at first glance, serves as a gateway to understanding fundamental concepts in number theory and its profound applications. From the building blocks of numbers to the security of our digital world, prime factorization plays a crucial role. Exploring this seemingly simple concept reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical ideas, highlighting the beauty and elegance of this foundational area of mathematics. The simplicity of the answer—2 x 3²—masks the depth and significance of the principles underlying its derivation. This exploration encourages a deeper appreciation of the intricate world of numbers and their profound impact on our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Label The Anatomy Of The Male
May 09, 2025
-
Electrical Resistivity Of A Given Metallic Wire Depends Upon
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Stereoisomers Are Possible For
May 09, 2025
-
14 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Si Unit For Distance
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write The Prime Factorization Of 18 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.