Which Of The Following Is Secondary Pollutant
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
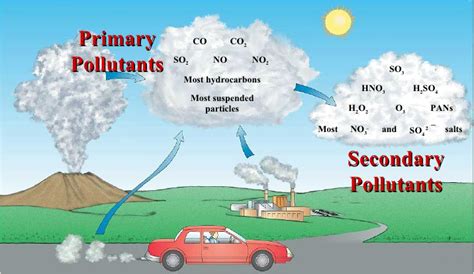
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Secondary Pollutant? Understanding Air Pollution
Air pollution is a significant global environmental problem, impacting human health and the planet's ecosystems. Understanding the different types of pollutants is crucial to tackling this issue effectively. This article delves into the concept of secondary pollutants, differentiating them from primary pollutants and exploring several examples. We will examine various sources and the chemical processes involved in their formation. Finally, we will discuss the implications of secondary pollutants on human health and the environment.
Primary vs. Secondary Pollutants: A Fundamental Distinction
Before we identify which pollutants are secondary, it's crucial to grasp the distinction between primary and secondary pollutants. This fundamental difference dictates how we approach pollution control strategies.
Primary pollutants are emitted directly from a source into the atmosphere. Examples include:
- Carbon monoxide (CO): Released from vehicle exhaust and industrial processes.
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2): Emitted from burning fossil fuels, particularly coal.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): Produced from combustion processes in vehicles and power plants.
- Particulate matter (PM): Includes dust, soot, and other solid or liquid particles directly released into the air.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Emitted from various sources, including vehicles, industrial processes, and solvents.
Secondary pollutants, on the other hand, are not directly emitted. Instead, they are formed in the atmosphere through chemical reactions between primary pollutants and other atmospheric components. This transformation often involves sunlight (photochemical reactions) and atmospheric moisture. This is where the complexity arises, as the exact composition and concentration of secondary pollutants can vary widely depending on atmospheric conditions, geographic location, and the mix of primary pollutants present.
Identifying Secondary Pollutants: Key Characteristics
Several characteristics help us identify secondary pollutants:
- Formation in the Atmosphere: The defining characteristic. They are not directly emitted but are formed through chemical reactions.
- Dependence on Primary Pollutants: Their existence relies on the presence of specific primary pollutants. Removing or reducing primary pollutants will invariably impact the formation of secondary pollutants.
- Variability in Concentration: Their concentration can fluctuate significantly based on meteorological factors like sunlight intensity, temperature, and humidity.
- Complex Chemical Processes: The formation pathways often involve multiple steps and intermediate species, making modeling their behavior challenging.
Examples of Secondary Pollutants: A Detailed Look
Let's examine some common secondary pollutants and their formation pathways:
1. Ozone (O3) at Ground Level (Tropospheric Ozone):
This is arguably the most important and widely discussed secondary pollutant. Ground-level ozone is a significant component of smog. It's formed through a complex series of photochemical reactions involving NOx and VOCs.
Formation Process:
- NOx emissions: Vehicles and power plants release NOx (NO and NO2).
- VOC emissions: Various sources, like solvents and industrial processes, release VOCs.
- Sunlight: UV radiation from the sun initiates photochemical reactions.
- Reaction sequence: A complex sequence of reactions occurs, involving the oxidation of NO to NO2, followed by reactions involving VOCs and oxygen molecules (O2), ultimately leading to the formation of ozone (O3).
Health and Environmental Impacts: Ground-level ozone is a respiratory irritant, causing coughing, wheezing, and reduced lung function. It can also damage vegetation and ecosystems.
2. Peroxyacetyl Nitrate (PAN):
PAN is another significant secondary pollutant formed through photochemical reactions involving NOx and VOCs. It's a strong oxidizing agent and a major component of photochemical smog.
Formation Process: Similar to ozone formation, PAN formation involves a series of reactions initiated by sunlight. Acetaldehyde, a common VOC, is a key precursor.
Health and Environmental Impacts: PAN is a respiratory irritant and can damage vegetation. It's also a component of smog, reducing visibility and affecting air quality.
3. Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4):
While sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a primary pollutant, it reacts in the atmosphere to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4), a secondary pollutant. This transformation often involves water vapor.
Formation Process:
- SO2 emissions: Burning fossil fuels releases SO2.
- Oxidation: SO2 reacts with oxygen and water vapor in the atmosphere.
- Sulfuric acid formation: This reaction forms sulfuric acid, which can exist as a vapor or condense into aerosol particles.
Health and Environmental Impacts: Sulfuric acid contributes to acid rain, damaging ecosystems, buildings, and infrastructure. As an aerosol, it can also affect respiratory health.
4. Nitric Acid (HNO3):
Similar to sulfuric acid, nitric acid (HNO3) is a secondary pollutant formed from the oxidation of nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the atmosphere.
Formation Process: NOx reacts with hydroxyl radicals (OH) and other atmospheric components, leading to the formation of nitric acid.
Health and Environmental Impacts: Nitric acid contributes to acid rain and can cause respiratory irritation. It's also a component of atmospheric aerosols.
The Interplay of Primary and Secondary Pollutants: A Complex System
The formation of secondary pollutants is a complex interplay between primary pollutants and atmospheric conditions. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of addressing both primary and secondary pollution sources for effective air quality management. Reducing emissions of primary pollutants, such as NOx and VOCs, is a crucial step in mitigating the formation of harmful secondary pollutants like ozone and PAN.
Addressing the Issue of Secondary Pollutants: Mitigation Strategies
Effectively managing secondary pollutants requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on source reduction and atmospheric chemistry manipulation. Strategies include:
- Reducing primary pollutant emissions: This is the most fundamental step. Stricter emission controls on vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes can significantly reduce the precursors for secondary pollutant formation.
- Cleaner energy sources: Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower reduces emissions of SO2 and NOx from fossil fuel combustion.
- Improved vehicle technologies: Advances in engine technology and the use of catalytic converters can reduce NOx and VOC emissions from vehicles.
- Urban planning and transportation management: Promoting public transportation, cycling, and walking can reduce reliance on private vehicles, thus reducing emissions.
- Industrial process optimization: Implementing cleaner production technologies and optimizing industrial processes can minimize VOC emissions.
- Air quality monitoring and modeling: Sophisticated monitoring systems and atmospheric models help us understand the formation and dispersion of secondary pollutants, informing effective control strategies.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Secondary Pollutants
Understanding the formation, characteristics, and impacts of secondary pollutants is critical for effective air pollution management. These pollutants are not merely byproducts; they are significant contributors to environmental damage and human health problems. By addressing both primary and secondary sources, implementing cleaner technologies, and improving urban planning, we can strive for cleaner air and a healthier environment for all. The interconnected nature of air pollution demands a comprehensive and integrated strategy, requiring collaboration among governments, industries, and individuals. Only through a unified effort can we effectively reduce the detrimental effects of secondary pollutants and safeguard the planet's air quality.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
300 Square Meters In Square Feet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Bacteria Forms Irregular Cluster That Resemble Grapes
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Planets Closest To The Sun Are Known As The
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Purpose Of The Filament
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 10 And 11
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Secondary Pollutant . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
