Which Of The Following Is Part Of The Hydrosphere
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
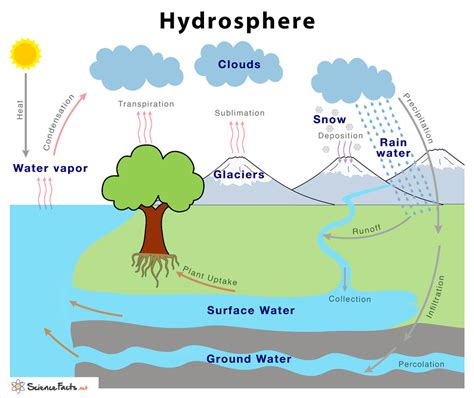
Table of Contents
Which of the following is part of the hydrosphere? A Deep Dive into Earth's Water Systems
The hydrosphere, a term encompassing all the water on Earth, is a crucial component of our planet's dynamic systems. Understanding what constitutes the hydrosphere is fundamental to grasping the complexities of climate, weather patterns, ecosystems, and the very sustenance of life itself. This comprehensive guide will explore the hydrosphere in detail, clarifying which elements belong and highlighting the interconnectedness of its various parts. We'll explore the vastness of oceans, the intricate workings of groundwater, the importance of glaciers and ice caps, and even the role of atmospheric water vapor.
Defining the Hydrosphere: More Than Just Oceans
When we think of water on Earth, our minds often leap to the vast expanse of the oceans. While the oceans undeniably represent the largest portion of the hydrosphere, it’s crucial to remember that the hydrosphere encompasses much more than just saltwater. It's a complex, interconnected system of water in all its forms and locations:
-
Oceans: Covering approximately 71% of the Earth's surface, the oceans are the dominant feature of the hydrosphere. They contain the vast majority of Earth's water, influencing global climate, weather patterns, and supporting an incredible diversity of marine life. The salinity, temperature, and currents of oceans play critical roles in shaping global ecosystems and biogeochemical cycles.
-
Lakes and Rivers: These freshwater bodies, while smaller in volume compared to oceans, are vital components of the hydrosphere. Lakes act as reservoirs, storing freshwater crucial for human consumption, agriculture, and industrial use. Rivers, acting as dynamic conduits, transport water from land to the oceans, shaping landscapes and contributing to nutrient cycles along their paths. The size and type of lake or river (e.g., meandering river vs. braided river, oligotrophic lake vs. eutrophic lake) impact their ecological roles and the surrounding ecosystems.
-
Groundwater: This often-overlooked component is arguably one of the most critical parts of the hydrosphere. Groundwater represents water stored beneath the Earth's surface in aquifers – layers of permeable rock and soil. It acts as a massive reservoir, providing a crucial source of freshwater for human consumption, agriculture, and industry. Groundwater replenishment rates vary greatly, dependent on geological factors and precipitation, making sustainable management critical. Over-extraction can lead to depletion of aquifers and land subsidence, highlighting the delicate balance within this part of the hydrosphere.
-
Glaciers and Ice Caps: These massive reservoirs of frozen freshwater play a significant role in the hydrosphere and global climate. Glaciers and ice caps, particularly those in Greenland and Antarctica, represent a substantial portion of Earth's freshwater reserves. Their melting contributes to rising sea levels, impacting coastal communities and ecosystems worldwide. The study of glaciers and ice caps provides crucial insights into past climates and the impacts of current climate change. Understanding their mass balance (accumulation versus ablation) is essential for predicting future sea-level rise and associated consequences.
-
Water Vapor: While less visually apparent than other hydrosphere components, atmospheric water vapor plays a critical role in the hydrological cycle and weather patterns. Water evaporates from various sources, including oceans, lakes, and soil, forming clouds and contributing to precipitation. The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere influences humidity, cloud formation, and ultimately, rainfall patterns. This dynamic component links the hydrosphere closely with the atmosphere.
-
Soil Moisture: The water retained in the soil plays a crucial role in plant growth and overall terrestrial ecosystems. This moisture influences the infiltration of rainwater into groundwater, and also the rate of evaporation back into the atmosphere. Soil moisture levels are highly variable depending on rainfall, soil type, and vegetation.
The Interconnectedness of the Hydrosphere: The Water Cycle
The various components of the hydrosphere are not isolated entities; they're dynamically interconnected through the water cycle (also known as the hydrological cycle). This continuous process involves the movement of water among the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere (Earth's solid crust), and biosphere (all living organisms). The water cycle includes several key stages:
- Evaporation: The transformation of liquid water (from oceans, lakes, rivers, and soil) into water vapor.
- Transpiration: The release of water vapor from plants into the atmosphere.
- Evapotranspiration: The combined effect of evaporation and transpiration.
- Condensation: The transformation of water vapor into liquid water, forming clouds.
- Precipitation: The release of water from clouds in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
- Infiltration: The movement of water from the surface into the soil.
- Runoff: The flow of water over the land surface, eventually reaching rivers, lakes, and oceans.
Understanding the water cycle is vital for comprehending how water moves through the hydrosphere, influencing climate, ecosystems, and human activities. Changes in any part of the cycle (e.g., increased evaporation due to rising temperatures) can have cascading effects on other components, leading to droughts, floods, and disruptions to water availability.
Human Impact on the Hydrosphere: A Growing Concern
Human activities significantly impact the hydrosphere, often with negative consequences. These impacts include:
- Pollution: The introduction of pollutants (such as chemicals, plastics, and sewage) into water bodies, contaminating freshwater resources and harming aquatic life.
- Over-extraction of Groundwater: Depleting aquifers beyond their sustainable recharge rates, leading to water shortages and land subsidence.
- Dam Construction: Altering river flows and disrupting aquatic ecosystems.
- Deforestation: Reducing infiltration and increasing runoff, leading to soil erosion and altered water cycles.
- Climate Change: Altering precipitation patterns, increasing evaporation rates, and causing glacial melt, leading to sea-level rise and disruptions to the water cycle.
The consequences of these impacts are far-reaching, affecting water availability, ecosystem health, and human well-being. Sustainable water management practices, conservation efforts, and mitigation of climate change are crucial for preserving the health of the hydrosphere and ensuring access to clean water for future generations.
Conclusion: Protecting Our Precious Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is a complex, interconnected system that sustains life on Earth. From the vast oceans to the smallest groundwater droplets, each component plays a vital role in maintaining the planet's delicate balance. Understanding the hydrosphere's various parts, their interactions, and the human impacts upon it is crucial for effective environmental stewardship. Protecting this precious resource requires a multifaceted approach encompassing sustainable practices, conservation efforts, and global cooperation to address the challenges of climate change and pollution. The future health of our planet hinges on our ability to safeguard the hydrosphere for generations to come. Only through a concerted global effort can we ensure the continued well-being of this vital component of our planet's life support system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 28 A Multiple Of 7
Mar 23, 2025
-
5 Letter Words That Start With T H I
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is 24 A Multiple Of 6
Mar 23, 2025
-
9 Is A Multiple Of 3
Mar 23, 2025
-
A Pair Of Angles That Add Up To 180
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Part Of The Hydrosphere . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
