Which Of The Following Is Not Found Within Dna
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
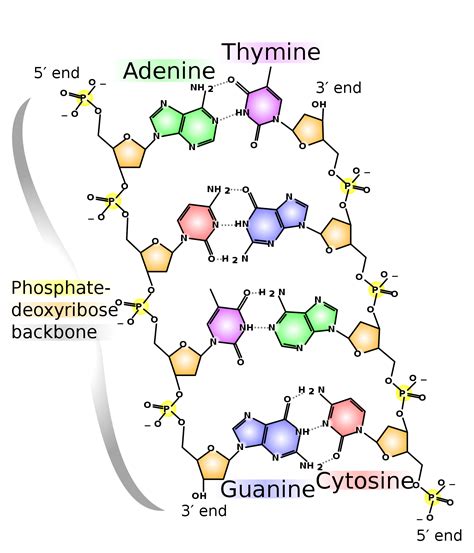
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is NOT Found Within DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is the fundamental building block of life, carrying the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. Understanding its composition is crucial to comprehending the complexities of biology and genetics. This article will delve into the components found within DNA, and more importantly, those that are conspicuously absent. We'll explore the nuanced differences between DNA and RNA, and clarify common misconceptions about the molecules that interact with DNA.
The Core Components of DNA: A Recap
Before we address what's not found in DNA, let's briefly review its essential components. DNA is a double-stranded helix composed of:
-
Deoxyribose Sugar: This five-carbon sugar forms the backbone of the DNA molecule. It's the "deoxy" in deoxyribonucleic acid that distinguishes it from ribose sugar found in RNA. The absence of a hydroxyl (-OH) group on the 2' carbon is a key structural difference.
-
Phosphate Groups: These negatively charged groups link the deoxyribose sugars together, creating the sugar-phosphate backbone. This backbone gives DNA its overall negative charge.
-
Nitrogenous Bases: These are the "letters" of the genetic code. There are four main nitrogenous bases in DNA:
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
- Cytosine (C)
- Thymine (T) These bases pair specifically with each other: A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C via hydrogen bonds. This specific base pairing is fundamental to DNA's structure and function.
What is NOT Found in DNA? A Comprehensive List
Now, let's tackle the main question: what molecules or structures are not typically found within the DNA double helix itself?
1. Ribose Sugar
As mentioned earlier, DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, not ribose sugar. Ribose sugar is a key component of RNA (ribonucleic acid), another crucial nucleic acid involved in protein synthesis. The presence of the hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon of ribose makes RNA more reactive and less stable than DNA. This difference is crucial for their distinct roles in the cell.
2. Uracil (U)
Uracil is one of the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA, replacing thymine (T) which is specific to DNA. While both uracil and thymine are pyrimidines, they differ structurally, and uracil's presence in RNA is related to its functional role in protein synthesis and RNA's overall instability. The methylation of uracil to thymine in DNA provides additional protection against spontaneous mutations.
3. Free-Floating Nucleotides
While nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA, they aren't typically found freely within the double helix structure itself. The nucleotides are covalently bonded together to form the polynucleotide chains. Free nucleotides, however, are abundant in the cell's cytoplasm and are essential for DNA replication and repair processes. They act as the raw materials for constructing new DNA strands.
4. Proteins (Directly Integrated into the Double Helix)
While proteins are intimately involved in DNA replication, transcription, and repair, they are not directly integrated into the DNA double helix structure itself. Proteins, like histones, bind to DNA and play crucial structural and regulatory roles. They help package and organize DNA into chromatin, but they don't form part of the double helix's backbone or base pairs.
5. Lipids
Lipids, or fats, are not structural components of DNA. While cell membranes, which are composed of lipids, are essential for protecting and compartmentalizing DNA within the nucleus, lipids are not directly incorporated into the DNA molecule itself.
6. Carbohydrates (Other than Deoxyribose)
Apart from the deoxyribose sugar forming the backbone, other types of carbohydrates are not integral structural components of the DNA molecule. While carbohydrates can be attached to DNA (glycosylation), it's not a common or primary structural element.
7. Amino Acids
Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. They are not found directly incorporated into the DNA double helix. The sequence of bases in DNA dictates the sequence of amino acids in a protein through the processes of transcription and translation. However, amino acids themselves are not part of the DNA structure.
Understanding the Interactions Around DNA
It's crucial to differentiate between what's within the DNA double helix and what interacts with it. Many molecules and structures interact dynamically with DNA, influencing its function and stability. This includes:
- Histones: These proteins help package and organize DNA into chromatin, regulating gene expression.
- Transcription Factors: These proteins bind to specific DNA sequences to regulate gene transcription.
- Enzymes: Various enzymes, such as DNA polymerase and ligase, are essential for DNA replication and repair.
- RNA Polymerase: This enzyme transcribes DNA into RNA.
- Non-Coding RNAs: Various types of RNA molecules interact with DNA, influencing gene expression.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
There are some misconceptions about what's found in DNA:
-
Water: While DNA resides in an aqueous environment within the cell nucleus, water molecules are not within the DNA double helix structure itself. They surround and interact with the molecule, affecting its stability and interactions.
-
Ions: Ions, such as Mg²⁺, are crucial for various enzymatic processes related to DNA, but they aren't structurally incorporated into the double helix. They influence the stability and interactions of the DNA molecule.
The Significance of Understanding DNA's Composition
Understanding the precise composition of DNA—what's included and, critically, what's excluded—is fundamental to comprehending the mechanisms of heredity, genetic expression, and evolution. Knowing what doesn't belong to the DNA molecule itself allows us to appreciate the intricate network of interactions that govern its functions and regulation within the cell. The specificity of DNA's components is key to its stability, its ability to store vast amounts of genetic information, and the precise transmission of this information from one generation to the next.
This detailed analysis emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between the core components of the DNA double helix and the various molecules that interact with and regulate its function within the complex cellular environment. Future advancements in genetics and molecular biology will rely heavily on this fundamental understanding of DNA’s composition and its dynamic interactions with other cellular components. The precision of its structure and the specificity of its interactions are testament to the elegance and efficiency of biological systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Produce Antibodies
Mar 19, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 5 And 7
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 6 And 10
Mar 19, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 24
Mar 19, 2025
-
When Dissolved In Water Acid Produce
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Not Found Within Dna . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
