Which Of The Following Is A Site For Lipid Synthesis
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
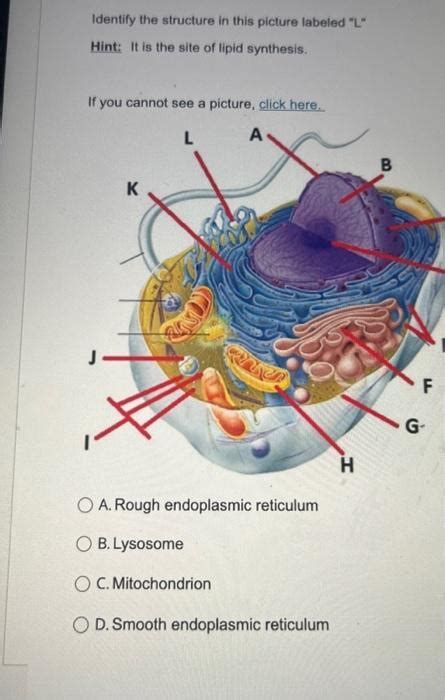
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Is A Site For Lipid Synthesis
- Table of Contents
- Which of the following is a site for lipid synthesis? A Deep Dive into Cellular Lipid Metabolism
- Understanding Lipids and Their Diverse Roles
- Key Types of Lipids and Their Synthesis Pathways
- Specific Organelles and Their Roles in Lipid Synthesis
- 1. Cytosol: The Central Hub for Fatty Acid and Triglyceride Synthesis
- 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The Membrane Factory for Phospholipids and Sphingolipids
- 3. Golgi Apparatus: The Sorting and Modification Center for Sphingolipids
- 4. Mitochondria: A Supporting Role in Lipid Metabolism
- Factors Regulating Lipid Synthesis
- Clinical Implications of Dysregulated Lipid Synthesis
- Conclusion: A Complex and Essential Process
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the following is a site for lipid synthesis? A Deep Dive into Cellular Lipid Metabolism
The question, "Which of the following is a site for lipid synthesis?" requires a nuanced answer, as lipid synthesis occurs in multiple cellular compartments, depending on the type of lipid and the organism. This article will delve into the intricate world of lipid biosynthesis, exploring the key sites and processes involved in the creation of these essential biomolecules. We'll examine the specifics of various lipid types and the organelles responsible for their synthesis, highlighting the critical roles these processes play in cellular function and overall health.
Understanding Lipids and Their Diverse Roles
Before delving into the sites of lipid synthesis, let's first establish a foundational understanding of lipids themselves. Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic or amphipathic molecules, meaning they either repel water or have both water-loving and water-repelling regions. This characteristic significantly influences their biological functions and location within the cell.
Lipids are essential components of cell membranes, providing structural integrity and regulating permeability. They also serve as energy storage molecules, providing a significant source of fuel for cellular processes. Beyond these core functions, lipids play critical roles in signaling pathways, acting as hormones and messengers that trigger various cellular responses. Their diverse functions necessitate their synthesis in specific locations within the cell, optimized for each particular lipid type and its ultimate destination.
Key Types of Lipids and Their Synthesis Pathways
The diverse nature of lipids dictates that their synthesis occurs in various locations within the cell. Here are some key lipid types and their primary sites of synthesis:
-
Fatty Acids: The building blocks of many complex lipids, fatty acids are synthesized primarily in the cytosol. The process, called de novo fatty acid synthesis, involves a series of enzymatic reactions that add two-carbon units to a growing acyl chain. The key enzyme is fatty acid synthase (FAS), a large multi-enzyme complex. The newly synthesized fatty acids are then used to build more complex lipids.
-
Triglycerides: These are the primary energy storage lipids in animals, consisting of three fatty acids esterified to a glycerol molecule. Their synthesis, known as triglyceride synthesis or esterification, primarily takes place in the cytosol of liver cells and adipocytes (fat cells). The glycerol-3-phosphate pathway is a crucial step in this process.
-
Phospholipids: Major components of cell membranes, phospholipids are amphipathic molecules with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails. Their synthesis occurs predominantly in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), specifically the smooth ER. The ER membrane provides the necessary environment for the assembly of these complex molecules, with the newly synthesized phospholipids often inserted directly into the ER membrane.
-
Cholesterol: This crucial steroid is a vital component of cell membranes and a precursor for many steroid hormones. Cholesterol synthesis primarily occurs in the cytosol, with many enzymatic steps involved. The rate-limiting step is catalyzed by HMG-CoA reductase, a key enzyme targeted by statin drugs used to lower cholesterol levels.
-
Sphingolipids: These lipids are enriched in the nervous system and play roles in cell signaling and membrane structure. Their synthesis takes place in the ER and the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi apparatus is crucial for the modification and sorting of sphingolipids to their final destinations within the cell.
Specific Organelles and Their Roles in Lipid Synthesis
Now, let's delve deeper into the specific organelles involved in lipid synthesis:
1. Cytosol: The Central Hub for Fatty Acid and Triglyceride Synthesis
The cytosol, the fluid portion of the cytoplasm, plays a critical role as the primary location for de novo fatty acid synthesis and triglyceride synthesis. The presence of the necessary enzymes, substrates, and coenzymes within the cytosol makes it an ideal environment for these reactions. The newly synthesized fatty acids and triglycerides are then transported to other locations within the cell, either for membrane incorporation or energy storage. The regulated expression of enzymes in the cytosol fine-tunes lipid synthesis in response to energy demands and nutritional status.
2. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The Membrane Factory for Phospholipids and Sphingolipids
The ER, a vast network of interconnected membranes, is crucial for the synthesis of phospholipids and sphingolipids. The ER membrane provides a platform for assembling these complex lipids and inserting them directly into the membrane bilayer. The smooth ER, in particular, is enriched in enzymes involved in lipid metabolism. The newly synthesized phospholipids are utilized for membrane expansion and repair, while sphingolipids are further modified and sorted in the Golgi apparatus for delivery to their target locations.
3. Golgi Apparatus: The Sorting and Modification Center for Sphingolipids
The Golgi apparatus receives newly synthesized sphingolipids from the ER and undergoes further modification and processing. This includes the addition of various sugar molecules, leading to the formation of glycosphingolipids. The Golgi also plays a critical role in sorting sphingolipids for delivery to their appropriate destinations within the cell, such as the plasma membrane or lysosomes. This precise sorting is essential for maintaining the functional integrity of different cellular compartments.
4. Mitochondria: A Supporting Role in Lipid Metabolism
While not a primary site of de novo lipid synthesis, mitochondria play a vital supporting role. They are involved in the beta-oxidation of fatty acids, a process that breaks down fatty acids to generate acetyl-CoA, which can then be used in various metabolic pathways, including lipid synthesis under certain conditions. Furthermore, mitochondria also contribute to the synthesis of specific lipid components, such as cardiolipin, a unique phospholipid found in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Factors Regulating Lipid Synthesis
The synthesis of lipids is a tightly regulated process influenced by various factors, including:
-
Nutritional Status: The availability of dietary carbohydrates and fats significantly impacts lipid synthesis. Abundant carbohydrate intake can lead to increased de novo fatty acid synthesis, while a high-fat diet can suppress this process.
-
Hormonal Regulation: Hormones such as insulin, glucagon, and glucocorticoids play crucial roles in regulating lipid metabolism. Insulin stimulates lipid synthesis, while glucagon and glucocorticoids inhibit it.
-
Enzyme Activity: The activity of key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis, such as fatty acid synthase and HMG-CoA reductase, is tightly regulated at both transcriptional and post-translational levels.
-
Cellular Energy Status: The cellular energy charge (ATP/ADP ratio) influences lipid metabolism. Under conditions of high energy, lipid synthesis is favored, while under energy depletion, lipid breakdown is promoted.
Clinical Implications of Dysregulated Lipid Synthesis
Dysregulation of lipid synthesis is implicated in various pathological conditions, including:
-
Obesity: Excessive lipid accumulation in adipose tissue is a hallmark of obesity, often associated with impaired lipid metabolism and insulin resistance.
-
Cardiovascular Disease: Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, and stroke.
-
Fatty Liver Disease: Excessive accumulation of lipids in the liver can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a growing health concern.
-
Neurological Disorders: Dysregulation of sphingolipid metabolism can contribute to various neurological disorders, such as lysosomal storage diseases.
Conclusion: A Complex and Essential Process
Lipid synthesis is a complex and tightly regulated process occurring in multiple cellular compartments. The cytosol, ER, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria all contribute to the biosynthesis of diverse lipid molecules, each playing a crucial, specialized role. Understanding the sites and mechanisms of lipid synthesis is critical for comprehending cellular function and health. Dysregulation of these processes can lead to various diseases, highlighting the importance of maintaining balanced lipid metabolism. Future research in this field will continue to unveil further intricacies of lipid biosynthesis, paving the way for new therapeutic strategies for various lipid-related disorders.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Storage Form Of Carbohydrates In Plants Is
Mar 18, 2025
-
Inspiratory And Expiratory Centers Are Located In The
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Feet Are In 300 Yards
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Storage Form Of Glucose In Plants Is
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Chemical Name For Milk
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Site For Lipid Synthesis . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
