Which Of The Following Is A Semilunar Valve
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
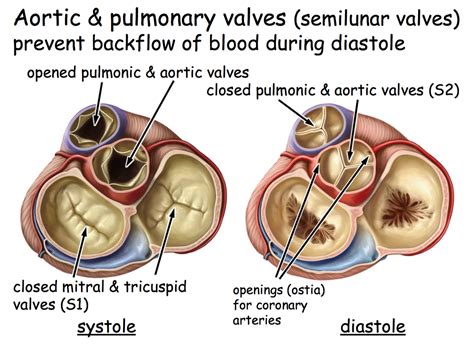
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Semilunar Valve? A Deep Dive into Cardiac Valves
The human heart, a remarkable organ, tirelessly pumps blood throughout our bodies. This intricate process relies heavily on a series of valves that ensure unidirectional blood flow. Understanding these valves, particularly the semilunar valves, is crucial to comprehending cardiovascular health. This article will comprehensively explore semilunar valves, comparing them to other heart valves and clarifying their crucial role in maintaining circulatory efficiency.
Understanding Heart Valves: A Necessary Overview
Before delving into the specifics of semilunar valves, let's establish a foundational understanding of the heart's valvular system. The heart possesses four valves, each strategically positioned to regulate blood flow between its chambers and the major blood vessels: the aorta and the pulmonary artery. These valves are categorized into two groups based on their structure and function:
-
Atrioventricular (AV) Valves: These valves are located between the atria (upper chambers) and the ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart. Their primary function is to prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles into the atria during ventricular contraction (systole). There are two AV valves:
- Tricuspid Valve: Situated between the right atrium and the right ventricle. It's named for its three cusps (leaflets).
- Mitral Valve (Bicuspid Valve): Located between the left atrium and the left ventricle. It has two cusps.
-
Semilunar Valves: These valves are positioned at the exits of the ventricles, preventing backflow of blood from the arteries back into the ventricles during ventricular relaxation (diastole). There are two semilunar valves:
- Pulmonary Valve: Located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, which carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- Aortic Valve: Situated between the left ventricle and the aorta, the body's largest artery, which carries oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
The Distinguishing Features of Semilunar Valves
Semilunar valves are structurally different from atrioventricular valves. Their key differentiating characteristics include:
-
Three Cusps (Leaflets): Unlike the bicuspid mitral valve and the tricuspid valve, semilunar valves possess three half-moon-shaped cusps. These cusps are composed of fibrous connective tissue covered by endothelium, the smooth lining of blood vessels.
-
No Chordae Tendineae: AV valves are anchored to the ventricular walls by strong fibrous cords called chordae tendineae, which are attached to papillary muscles. These structures are essential for preventing eversion (prolapse) of the AV valves during ventricular contraction. Semilunar valves lack chordae tendineae; their cusps are held in place by the pressure differences between the ventricles and the arteries.
-
Pocket-like Structure: The cusps of semilunar valves are arranged in a way that creates a pocket-like structure. When the ventricles contract, the pressure pushes the cusps open, allowing blood to flow into the arteries. When the ventricles relax, the backflow of blood fills the pockets, causing the cusps to close tightly and preventing regurgitation.
-
Location and Function: Their location at the arterial outflow tracts of the ventricles is critical to their function. They prevent the backflow of blood from the pulmonary artery and aorta into the ventricles during diastole.
Why Semilunar Valve Function is Crucial for Cardiovascular Health
The proper functioning of the semilunar valves is paramount to maintaining efficient blood circulation and overall cardiovascular health. Failure of these valves can lead to serious complications:
-
Aortic Valve Stenosis: Narrowing of the aortic valve restricts blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta. This can lead to decreased cardiac output, shortness of breath (dyspnea), chest pain (angina), and even heart failure.
-
Aortic Valve Regurgitation (Insufficiency): Incomplete closure of the aortic valve allows blood to leak back into the left ventricle during diastole. This increases the workload on the heart, potentially leading to heart enlargement (cardiomegaly) and heart failure.
-
Pulmonary Valve Stenosis: Narrowing of the pulmonary valve obstructs blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. This reduces the amount of blood reaching the lungs for oxygenation, potentially causing shortness of breath and cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin).
-
Pulmonary Valve Regurgitation (Insufficiency): Incomplete closure of the pulmonary valve allows blood to leak back into the right ventricle during diastole. While often less severe than aortic regurgitation, it can still lead to right ventricular enlargement and heart failure.
Differentiating Semilunar Valves from Atrioventricular Valves: A Comparative Analysis
The following table highlights the key differences between semilunar and atrioventricular valves:
| Feature | Semilunar Valves | Atrioventricular Valves |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Between ventricles and arteries (aorta & pulmonary artery) | Between atria and ventricles |
| Number of Cusps | Three | Two (mitral) or three (tricuspid) |
| Chordae Tendineae | Absent | Present |
| Papillary Muscles | Absent | Present |
| Function | Prevent backflow from arteries to ventricles | Prevent backflow from ventricles to atria |
| Valve Type | Pulmonary and Aortic | Mitral and Tricuspid |
Clinical Significance and Diagnostic Methods
Understanding semilunar valve function is crucial for diagnosing and managing various cardiovascular diseases. Several diagnostic methods are used to assess the health and function of these valves:
-
Echocardiography: This non-invasive ultrasound technique provides detailed images of the heart, allowing clinicians to visualize valve structure, assess valve function, and detect abnormalities such as stenosis or regurgitation.
-
Cardiac Catheterization: A more invasive procedure involving the insertion of a catheter into a blood vessel to access the heart chambers and visualize the valves directly. This allows for precise measurements of pressure gradients across the valves and can be used for therapeutic interventions.
-
Electrocardiography (ECG): While not directly visualizing the valves, an ECG can detect indirect signs of valve disease, such as changes in heart rhythm or electrical activity.
Therapeutic Interventions for Semilunar Valve Disease
Depending on the severity and type of semilunar valve disease, various therapeutic interventions are available:
-
Medical Management: For mild cases, medical management may involve medications to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
-
Valve Repair: In some cases, surgical repair of the damaged valve may be possible, restoring its function without the need for replacement.
-
Valve Replacement: For severe valve disease that cannot be repaired, valve replacement surgery is often necessary. This involves replacing the damaged valve with a prosthetic valve, which can be either mechanical or biological.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Semilunar Valves
The semilunar valves – the pulmonary and aortic valves – play a vital role in maintaining efficient unidirectional blood flow within the circulatory system. Their unique structural characteristics, including their three cusps and lack of chordae tendineae, are crucial for their function in preventing backflow of blood from the arteries to the ventricles. Understanding their structure and function is fundamental for recognizing and managing various cardiovascular conditions. Early diagnosis and appropriate interventions are essential in mitigating the potential complications associated with semilunar valve disease, ensuring optimal cardiovascular health and overall well-being. Further research continues to refine our understanding of these critical valves and improve treatment strategies for associated diseases. The continued advancements in cardiovascular medicine promise improved outcomes and a higher quality of life for individuals affected by semilunar valve disorders. Remember, regular health checkups and a healthy lifestyle are key to preventing and managing cardiovascular disease.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Multiply A 3x3 Matrix By A 3x1 Matrix
May 09, 2025
-
What X Value Makes The Set Of Ratios Equivalent
May 09, 2025
-
Average Height Of A 9th Grader
May 09, 2025
-
Picture Of Prokaryotic Cell And Eukaryotic Cell
May 09, 2025
-
Five Letter Word With I E
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Semilunar Valve . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.