Which Of The Following Is A Product Of Photosynthesis
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
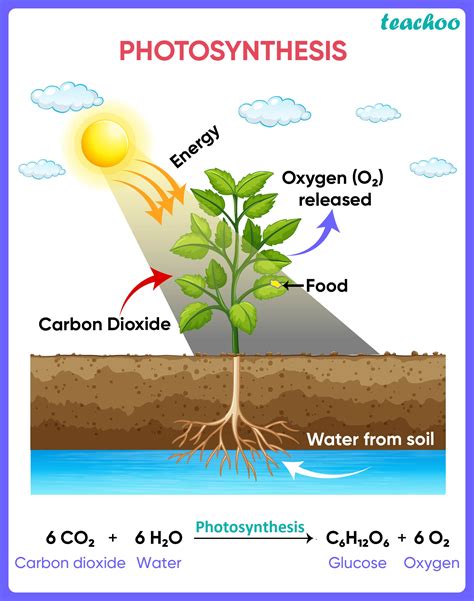
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Product of Photosynthesis? Unraveling the Secrets of Plant Energy Production
Photosynthesis, the remarkable process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods from carbon dioxide and water, is fundamental to life on Earth. Understanding its products is key to appreciating its vital role in our ecosystem. This in-depth exploration delves into the primary products of photosynthesis, exploring the intricacies of the process and the significance of its outputs.
The Core Products: Glucose and Oxygen
The most well-known products of photosynthesis are glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and oxygen (O₂). These two molecules represent the culmination of a complex series of biochemical reactions within chloroplasts, the plant cell's energy factories.
Glucose: The Energy Currency of Plants
Glucose is a simple sugar, a fundamental carbohydrate. It acts as the primary source of energy for plants, fueling their growth, reproduction, and all metabolic processes. Plants utilize glucose in several ways:
- Cellular Respiration: Glucose undergoes cellular respiration, a process that breaks down glucose in the presence of oxygen, releasing energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's energy currency. This energy powers various cellular activities.
- Storage: Excess glucose is converted into other carbohydrates, like starch and sucrose, for storage. Starch is stored in roots, stems, and seeds, providing a reserve energy source for later use. Sucrose is the primary sugar transported throughout the plant via phloem.
- Biosynthesis: Glucose serves as a building block for the synthesis of other essential biomolecules, including cellulose (the main component of plant cell walls), proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. It's the cornerstone of plant structure and function.
The formation of glucose during photosynthesis is a crucial step in the carbon cycle. Plants capture atmospheric carbon dioxide, incorporating it into organic molecules like glucose, effectively sequestering carbon from the atmosphere. This process plays a vital role in regulating Earth's climate.
Oxygen: A Byproduct with Immense Significance
Oxygen, a byproduct of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, is released into the atmosphere. While not directly used by the plant in the same way as glucose, its release has had a profound impact on the planet.
- Aerobic Respiration: Oxygen is essential for aerobic respiration, the process by which most living organisms, including animals and many microorganisms, obtain energy from glucose. The oxygen we breathe is a direct consequence of photosynthesis.
- Ozone Layer Formation: Oxygen in the upper atmosphere forms ozone (O₃), which absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, protecting life on Earth from its damaging effects.
- Oxidative Processes: Oxygen participates in various oxidative processes within the plant itself, contributing to metabolism and cellular signaling.
The evolution of photosynthesis and the subsequent release of oxygen fundamentally changed Earth's atmosphere, paving the way for the development of complex aerobic life.
Beyond Glucose and Oxygen: Other Photosynthetic Products
While glucose and oxygen are the primary outputs, photosynthesis also yields several other important products, albeit in smaller quantities. These include:
Water: A Reactant and a Product
Water (H₂O) is both a reactant and a product of photosynthesis. It's used in the light-dependent reactions to provide electrons and protons, crucial for the electron transport chain. However, water is also produced during the photorespiration process, a metabolic pathway that competes with photosynthesis under certain conditions. Photorespiration, while less efficient than photosynthesis, can help plants avoid the harmful effects of excess light energy.
ATP and NADPH: Energy Carriers
Photosynthesis isn't a single reaction but a series of interconnected reactions. The light-dependent reactions produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are energy-carrying molecules. They act as temporary energy stores, transferring the captured light energy to the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) where glucose is synthesized. These molecules are crucial intermediaries, ensuring efficient energy transfer within the photosynthetic process.
Other Metabolites: A Rich Array of Compounds
Photosynthesis produces a diverse array of metabolites beyond glucose and oxygen. These include:
- Fatty Acids: Plants synthesize fatty acids through photosynthesis, which are essential components of cell membranes and storage lipids.
- Amino Acids: Photosynthesis provides the carbon skeletons and energy required for the synthesis of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins.
- Vitamins: Certain vitamins are produced or their synthesis is facilitated by photosynthetic pathways.
- Secondary Metabolites: These compounds have various functions in plant defense mechanisms, attraction of pollinators, and other ecological interactions. Examples include alkaloids, terpenoids, and phenols. They contribute significantly to the diversity of plant life and their interactions with the environment.
Factors Influencing Photosynthetic Product Yields
The quantities of glucose and oxygen produced during photosynthesis are influenced by several factors:
- Light Intensity: Increased light intensity generally leads to higher photosynthetic rates, resulting in increased glucose and oxygen production, up to a point of saturation. Beyond this point, further increases in light intensity may lead to photoinhibition, damaging photosynthetic machinery.
- Carbon Dioxide Concentration: Higher carbon dioxide levels generally enhance photosynthesis, increasing glucose production. However, extremely high levels can have negative effects.
- Temperature: Optimal temperatures are essential for efficient enzyme activity in photosynthesis. Temperatures that are too high or too low can significantly reduce photosynthetic rates.
- Water Availability: Water is a crucial reactant in photosynthesis. Water stress can severely limit photosynthetic activity.
- Nutrient Availability: Essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and magnesium, are vital for the synthesis of chlorophyll and other components of the photosynthetic machinery. Deficiencies in these nutrients can significantly reduce photosynthetic output.
The Significance of Photosynthetic Products in the Ecosystem
The products of photosynthesis underpin the entire food web. Plants, through their photosynthetic activity, form the base of most terrestrial and many aquatic ecosystems. The glucose they produce serves as the primary energy source for herbivores, which are then consumed by carnivores and omnivores. Oxygen released during photosynthesis is crucial for the respiration of most organisms, enabling the flow of energy throughout the ecosystem.
The carbon sequestered by plants during photosynthesis also plays a critical role in regulating the Earth's carbon cycle and climate. Forests and other plant communities act as significant carbon sinks, helping to mitigate the effects of human-induced climate change. The disruption of photosynthetic processes through deforestation and other human activities can have severe consequences for both the environment and human society.
Conclusion: Photosynthesis – A Cornerstone of Life
Photosynthesis is a fundamental biological process with far-reaching consequences. The primary products, glucose and oxygen, are essential for life on Earth. However, a deeper understanding reveals a broader range of photosynthetic products, from energy carriers like ATP and NADPH to a diverse array of metabolites that contribute to plant structure, function, and ecological interactions. The efficiency and output of photosynthesis are influenced by several factors, highlighting the intricate interplay between plants and their environment. Appreciating the complexities of photosynthesis and its vital products is paramount to understanding the intricate web of life and the importance of preserving our planet's biodiversity. The impact of photosynthesis extends beyond the individual plant, shaping ecosystems, regulating climate, and supporting the very existence of countless organisms. It's a process worthy of continued study and appreciation for its immense significance to life as we know it.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
3 1 4 As Improper Fraction
May 09, 2025
-
What Organelles Involved In Protein Synthesis
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 25 Centimeters
May 09, 2025
-
Size Chart In Cm And Inches
May 09, 2025
-
How Heat Is Different From Temperature
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Product Of Photosynthesis . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.