Which Of The Following Is A Multiple Of 4
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
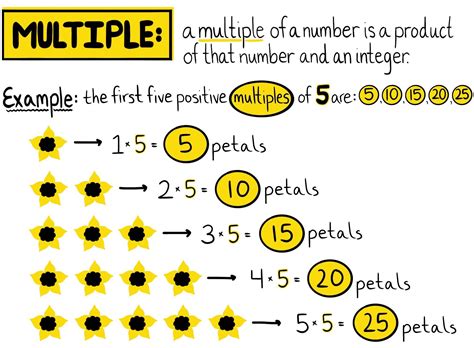
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Multiple of 4? A Deep Dive into Divisibility Rules and Number Theory
Understanding multiples is a fundamental concept in mathematics, essential for various applications from basic arithmetic to advanced number theory. This article delves deep into the concept of multiples, specifically focusing on identifying multiples of 4. We'll explore the divisibility rule for 4, practical applications, and even touch on some related number theory concepts.
What are Multiples?
A multiple of a number is the result of multiplying that number by any integer (whole number). For instance, multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on. These are obtained by multiplying 2 by 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and so forth. Similarly, multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on.
Key takeaway: Multiples are the products of a number and any integer.
Identifying Multiples of 4: The Divisibility Rule
The most efficient way to determine if a number is a multiple of 4 is to use the divisibility rule for 4. This rule simplifies the process significantly, avoiding the need for lengthy division.
The divisibility rule for 4 states: A number is divisible by 4 if its last two digits are divisible by 4.
Let's break this down with examples:
- 124: The last two digits are 24, and 24 is divisible by 4 (24 ÷ 4 = 6). Therefore, 124 is a multiple of 4.
- 736: The last two digits are 36, and 36 is divisible by 4 (36 ÷ 4 = 9). Therefore, 736 is a multiple of 4.
- 917: The last two digits are 17, and 17 is not divisible by 4. Therefore, 917 is not a multiple of 4.
- 2000: The last two digits are 00, and 00 is divisible by 4 (00 ÷ 4 = 0). Therefore, 2000 is a multiple of 4.
Important Note: This rule only works for checking divisibility by 4. It cannot be used to find the other multiples of 4.
Practical Applications of Identifying Multiples of 4
The ability to quickly identify multiples of 4 has numerous practical applications across various fields:
- Basic Arithmetic: Simplifying fractions, performing calculations involving division, and solving word problems often require identifying multiples.
- Algebra: Solving equations and inequalities may involve recognizing multiples of 4 to find solutions.
- Geometry: Calculating areas and volumes of shapes often involves multiples of 4, especially when dealing with squares, rectangles, and other related figures.
- Computer Science: In programming, understanding multiples is critical for tasks such as loop control, array manipulation, and memory allocation. Many algorithms rely on the ability to quickly identify multiples of 4 or other numbers.
- Real-World Scenarios: Think about scenarios involving packaging, arranging items in groups of four, or dividing resources evenly. Recognizing multiples of 4 becomes essential. For example, if you need to arrange 24 chairs into equal rows of 4, understanding that 24 is a multiple of 4 allows you to easily determine the number of rows needed.
Beyond the Divisibility Rule: Deeper Understanding of Multiples
While the divisibility rule provides a shortcut, understanding the underlying mathematical principles enhances your problem-solving abilities.
Prime Factorization and Multiples
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. This technique can help us understand why a number is a multiple of 4. A number is a multiple of 4 if and only if its prime factorization contains at least two factors of 2 (because 4 = 2 x 2).
For example:
- 12: The prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3. It contains two factors of 2, so 12 is a multiple of 4.
- 20: The prime factorization of 20 is 2 x 2 x 5. It contains two factors of 2, so 20 is a multiple of 4.
- 15: The prime factorization of 15 is 3 x 5. It doesn't contain two factors of 2, so 15 is not a multiple of 4.
Modular Arithmetic and Multiples
Modular arithmetic provides another lens through which to view multiples. When a number is divided by 4, the remainder can be 0, 1, 2, or 3. A number is a multiple of 4 if and only if its remainder is 0 when divided by 4. This is expressed mathematically as:
x ≡ 0 (mod 4)
Where 'x' represents the number, and the notation '≡ 0 (mod 4)' means 'x' is congruent to 0 modulo 4 (meaning it leaves a remainder of 0 when divided by 4).
Relationship between Multiples and Factors
It's important to understand the relationship between multiples and factors. If 'a' is a multiple of 'b', then 'b' is a factor of 'a'. Conversely, if 'b' is a factor of 'a', then 'a' is a multiple of 'b'. For example, since 20 is a multiple of 4, 4 is a factor of 20.
Advanced Concepts: Multiples of 4 in Number Theory
Delving deeper into number theory, multiples of 4 play a role in various interesting concepts:
- Even and Odd Numbers: All multiples of 4 are even numbers, but not all even numbers are multiples of 4.
- Arithmetic Progressions: A sequence of numbers where the difference between consecutive terms is constant is called an arithmetic progression. We can form arithmetic progressions consisting solely of multiples of 4. For example: 4, 8, 12, 16,...
- Patterns in Multiples: Examining multiples of 4 reveals interesting patterns. For example, the last two digits of multiples of 4 cycle through multiples of 4 (00, 04, 08, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36...).
- Congruences: As mentioned earlier, modular arithmetic and congruences provide a powerful framework for studying properties of numbers, including multiples.
Practical Exercises to Strengthen Understanding
To solidify your understanding, try these exercises:
- Identify whether the following numbers are multiples of 4: 328, 157, 840, 2912, 573, 1004.
- Find five consecutive multiples of 4.
- Explain why 24 is a multiple of 4 using prime factorization.
- Determine if a number formed by concatenating two identical two-digit numbers is always a multiple of 4 (e.g., 2727).
- Can you find a six-digit number that is a multiple of 4, and whose digits are all odd?
By working through these exercises, you'll reinforce your understanding of multiples and their properties.
Conclusion: Mastering Multiples of 4 and Beyond
Understanding multiples, particularly those of 4, is a fundamental skill with broad applications in mathematics and various other fields. This article has explored the divisibility rule for 4, practical applications, and even touched on advanced concepts in number theory. Remember, mastering this concept isn't just about applying a rule; it's about gaining a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles and how they connect to the wider world of numbers. By practicing and exploring these concepts, you'll build a strong foundation in mathematics, enhancing your problem-solving skills and fostering a deeper appreciation for the beauty and elegance of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Nuclear Membrane Reforms During Which Phase Of Mitosis
May 09, 2025
-
How To Calculate The Bandwidth Of A Signal
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Are In 1 Coulomb
May 09, 2025
-
How To Find The Average Cost Of A Function
May 09, 2025
-
How Does A Switch Work In A Circuit
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Multiple Of 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.