Which Is Greater Megabytes Or Gigabytes
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
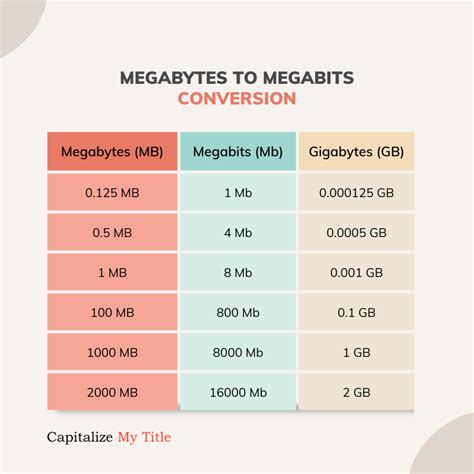
Table of Contents
Megabytes vs. Gigabytes: Understanding the Difference and Their Importance in the Digital World
In today's digital landscape, we constantly encounter terms like megabytes (MB) and gigabytes (GB) when dealing with computer storage, internet speeds, and file sizes. Understanding the difference between these units is crucial for navigating the digital world effectively. This comprehensive guide will not only clarify the difference between megabytes and gigabytes but also delve into their practical implications and how they affect our daily digital experiences.
Understanding the Metric System and Data Measurement
Before diving into the comparison, it's essential to establish a foundational understanding of how digital data is measured. The system used is based on powers of 1024 (2<sup>10</sup>), not 1000, which is a common misconception. This stems from the binary system used by computers, where data is stored and processed in bits (0s and 1s).
-
Bit (b): The smallest unit of data, representing a single binary digit (0 or 1).
-
Byte (B): Eight bits make up one byte, the basic unit for measuring digital information.
From here, we move to larger units:
- Kilobyte (KB): 1024 bytes (approximately 1,000 bytes)
- Megabyte (MB): 1024 kilobytes (approximately 1,000,000 bytes)
- Gigabyte (GB): 1024 megabytes (approximately 1,000,000,000 bytes)
- Terabyte (TB): 1024 gigabytes (approximately 1,000,000,000,000 bytes)
- Petabyte (PB): 1024 terabytes
- Exabyte (EB): 1024 petabytes
- Zettabyte (ZB): 1024 exabytes
- Yottabyte (YB): 1024 zettabytes
Megabytes: A Closer Look
A megabyte (MB) represents a significant amount of data, sufficient to store various types of files. Think of it as a medium-sized container for your digital belongings.
Examples of Files Measured in Megabytes:
- High-resolution images: A single high-quality photograph can easily range from a few MB to tens of MB, depending on its resolution and format (JPEG, TIFF, etc.).
- Short audio files: Music tracks in compressed formats (MP3) typically range from several MB to tens of MB, while uncompressed formats (WAV) can be significantly larger.
- Documents: Word processing documents, presentations, and spreadsheets usually range from a few KB to several MB depending on their size and complexity.
- Short videos: Short videos can range from a few MB to hundreds of MBs, but the file size will dramatically increase with resolution, length and video quality.
Practical Implications of Megabytes:
Understanding megabytes helps you make informed decisions regarding:
- Storage capacity: When purchasing a USB drive, SD card, or cloud storage, you'll need to consider the storage capacity expressed in gigabytes or terabytes to ensure sufficient space for your data.
- Download speeds: Downloading large files, like movies or games, often takes time and depends heavily on your internet speed.
- Email attachments: Sending large email attachments, especially high-resolution photos or videos, can cause delays and potential problems with email delivery.
Gigabytes: The Larger Picture
A gigabyte (GB), being 1024 times larger than a megabyte, signifies a much larger storage capacity. It's the standard unit for measuring the storage capacity of many common devices.
Examples of Files Measured in Gigabytes:
- High-definition videos: A single high-definition movie can easily take up several GBs of space, and this increases exponentially with higher resolutions (4K, 8K) and longer durations.
- Software applications: Modern software applications, especially games, often require several GBs of installation space.
- Music collections: A substantial music library containing hundreds of songs in uncompressed formats can quickly accumulate to many gigabytes.
- Operating systems: Operating systems themselves, such as Windows or macOS, occupy multiple gigabytes on your hard drive.
- Large databases: Businesses and organizations work with databases that can store terabytes and petabytes of data. A single database table could measure in the gigabytes.
Practical Implications of Gigabytes:
Gigabytes are crucial when:
- Choosing storage devices: Hard drives, SSDs, and cloud storage are typically measured in gigabytes or terabytes. Understanding the GB capacity is essential for determining how much data you can store.
- Managing computer performance: Insufficient free space on your hard drive can severely impact your computer's performance and speed.
- Understanding internet plans: Internet plans are often advertised with download and upload speeds measured in megabits per second (Mbps) and gigabits per second (Gbps). These influence your ability to quickly download and upload large files. (Note: bits and bytes are different; 8 bits = 1 byte).
- Gaming: Many modern PC and console games require tens of gigabytes of storage space. Understanding this will help you manage your game library effectively.
Megabytes vs. Gigabytes: The Key Differences
The primary difference between megabytes and gigabytes lies in their magnitude:
-
Scale: A gigabyte is 1024 times larger than a megabyte. This significant difference highlights the vastly different amounts of data they can hold. Visualize a megabyte as a small suitcase and a gigabyte as a large moving truck!
-
Applications: Megabytes are commonly used for smaller files, while gigabytes are used for larger ones. The size of your files dictates which unit is appropriate for measuring them.
-
Storage: You'll see megabytes used in the context of smaller storage devices, like USB flash drives with lower capacities, while gigabytes are used for the storage capacity of hard drives, SSDs, and cloud storage plans.
Real-world scenarios illustrating the difference:
Scenario 1: Downloading a movie: A high-definition movie might be 5 GB in size. A standard definition movie could be 1.5 GB. It's quite clear the difference in size and storage required. Downloading the HD version will take much longer and require more bandwidth than the standard definition version.
Scenario 2: Storing photos: A single high-resolution photograph may take up 5-10 MB of space. A collection of 1000 such photos would amount to roughly 5-10 GB, requiring significant storage.
Scenario 3: Software Installation: Modern video games can often consume over 50 GB of hard drive space. Smaller applications might need only a few hundred MB. This showcases the huge variance in software size.
Scenario 4: Internet Speed: A high-speed internet connection might offer download speeds of 1 Gbps (gigabits per second), while a lower speed connection may be around 100 Mbps (megabits per second). The difference in download speeds is substantial. Remember 8 bits = 1 byte.
Conclusion: Understanding the Importance
The distinction between megabytes and gigabytes is fundamental to understanding digital data storage and transfer. Knowing the difference allows you to make informed decisions when purchasing storage devices, choosing internet plans, managing files, and comprehending file sizes in the digital realm. As technology continues to evolve and file sizes continue to grow, this knowledge will become increasingly important for navigating the constantly expanding digital world. By understanding the relationship between these units and their practical implications, you can optimize your digital experiences and ensure seamless interactions with the technology that powers our daily lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Building Block Of All Matter
Mar 04, 2025
-
15 5 2b Equivalent Expression Worksheet
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Are Biotic Factors And Abiotic Factors
Mar 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Planets Has No Moon
Mar 04, 2025
-
The Swim Bladder Of Bony Fishes Functions In
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Is Greater Megabytes Or Gigabytes . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
