What's The Square Root Of 4
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
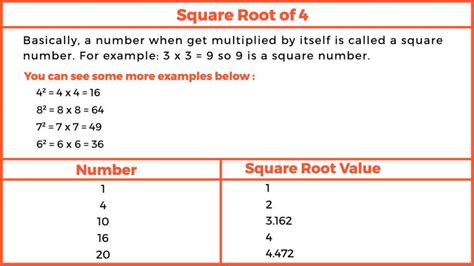
Table of Contents
What's the Square Root of 4? A Deep Dive into the Fundamentals of Mathematics
The seemingly simple question, "What's the square root of 4?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of fundamental mathematical concepts. While the answer itself is straightforward – 2 – the journey to understanding its implications delves into the history of mathematics, its practical applications, and its crucial role in more complex calculations. This article aims to provide a comprehensive explanation, suitable for both beginners and those seeking a deeper understanding of this basic yet essential mathematical operation.
Understanding Square Roots: A Conceptual Overview
Before we tackle the square root of 4 specifically, let's establish a solid understanding of what a square root actually is. In simple terms, the square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself (squared), gives the original number. So, if we have a number 'x', its square root (√x) is a number 'y' such that y * y = x.
This concept is deeply intertwined with the concept of squares. When we square a number, we multiply it by itself. For example:
- 2² = 2 * 2 = 4
- 3² = 3 * 3 = 9
- 4² = 4 * 4 = 16
Therefore, the square root is essentially the reverse operation of squaring a number. It's like asking, "What number, when multiplied by itself, gives me this result?"
The Square Root of 4: The Answer and its Significance
Now, let's address the central question: What is the square root of 4?
The answer is 2. This is because 2 * 2 = 4.
However, the story doesn't end there. While 2 is the principal square root (the positive square root), it's crucial to acknowledge that -2 is also a valid answer. (-2) * (-2) = 4. This highlights an important characteristic of square roots: many positive numbers have two square roots – one positive and one negative. This becomes particularly significant in more advanced mathematical contexts, particularly when dealing with equations and solving for variables.
The simplicity of the square root of 4, however, shouldn't diminish its importance. It serves as a foundational building block for numerous mathematical operations and concepts.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding the square root of 4 lays the groundwork for understanding many related mathematical concepts, including:
1. Perfect Squares:
A perfect square is a number that can be obtained by squaring an integer. 4 is a perfect square because it's the square of 2 (and -2). Other examples include 9 (3²), 16 (4²), 25 (5²), and so on. Recognizing perfect squares is extremely helpful in simplifying calculations involving square roots.
2. Irrational Numbers:
While the square root of 4 is a rational number (it can be expressed as a fraction), many other square roots are irrational numbers. Irrational numbers are numbers that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. For example, the square root of 2 (√2) is an irrational number, approximately equal to 1.414. Understanding the contrast between rational and irrational numbers is vital for a comprehensive grasp of number systems.
3. Complex Numbers:
When dealing with the square roots of negative numbers, we enter the realm of complex numbers. The square root of -1 is represented by the imaginary unit 'i'. This expands the number system beyond real numbers, opening up a whole new branch of mathematics with applications in various fields like electrical engineering and quantum mechanics.
4. Radical Expressions:
Square roots are often written using radical symbols (√). Expressions involving square roots are called radical expressions. Simplifying these expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra, requiring an understanding of perfect squares and factoring. For instance, simplifying √12 involves finding the perfect square factors within 12 (4 x 3), resulting in 2√3.
5. Solving Quadratic Equations:
The square root is a fundamental operation in solving quadratic equations. Quadratic equations are equations of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. The quadratic formula, which involves square roots, provides a method for finding the solutions (roots) of these equations.
Practical Applications of Square Roots: Real-World Examples
Square roots aren't just abstract mathematical concepts; they have practical applications in various fields:
1. Geometry and Measurement:
Calculating the diagonal of a square or rectangle involves using the Pythagorean theorem, which relies heavily on square roots. This is essential in construction, engineering, and surveying. For example, determining the length of a diagonal of a square with sides of length 2 units involves calculating √(2² + 2²) = √8 = 2√2 units.
2. Physics and Engineering:
Many physical formulas utilize square roots, including calculations related to velocity, acceleration, energy, and electricity. For example, the formula for calculating the speed of a wave involves the square root of tension divided by linear density.
3. Finance and Investment:
Understanding square roots is crucial in financial calculations involving compound interest, standard deviation, and other statistical measures used in investment analysis and risk management.
4. Computer Graphics and Programming:
Square roots are frequently used in computer graphics and game development for calculations involving distances, rotations, and transformations in two and three-dimensional spaces.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those interested in delving deeper into the mathematical world surrounding square roots, here are some advanced concepts to consider:
-
Nth Roots: Square roots are a specific type of nth root, where n=2. Nth roots generalize the concept to finding a number that, when multiplied by itself 'n' times, gives the original number.
-
Numerical Methods for Approximating Square Roots: For numbers that aren't perfect squares, numerical methods like the Babylonian method (also known as Heron's method) provide efficient ways to approximate their square roots.
-
Calculus and Derivatives: The derivative of a square root function is an important concept in calculus, providing insights into the rate of change of the function.
-
Series Expansions: Square roots can be expressed as infinite series, providing alternative ways to calculate or approximate their values.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of a Simple Calculation
While the square root of 4 might seem like a trivial calculation, its significance extends far beyond a simple answer of 2. Understanding this basic operation lays a solid foundation for grasping more complex mathematical ideas, unlocking the door to numerous applications across various disciplines. From geometry and physics to finance and computer science, the concept of the square root permeates many aspects of our world. Its seemingly simple nature belies its profound and enduring significance in the vast and intricate landscape of mathematics. By understanding the square root of 4, we gain a stepping stone to appreciate the beauty and power of mathematical concepts that shape our understanding of the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Sign Makes The Statement True
Mar 15, 2025
-
15 Is What Percent Of 50
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Miles Is 25 Km
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Diploid Number For Humans
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 1 25 As A Fraction
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Square Root Of 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
