What's The Prime Factorization Of 30
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
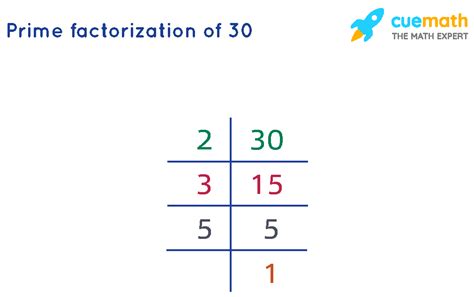
Table of Contents
What's the Prime Factorization of 30? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What's the prime factorization of 30?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of integers. Understanding prime factorization isn't just about finding the answer for 30; it's about grasping fundamental concepts that underpin many areas of mathematics and computer science, including cryptography. This article will explore the prime factorization of 30, explain the concepts behind it, and delve into its broader implications.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 30, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite.
Key Characteristics of Prime Numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This was proven by Euclid over two millennia ago.
- Distribution: While they appear randomly, the distribution of prime numbers follows patterns that have intrigued mathematicians for centuries. The Prime Number Theorem provides an approximation of the density of primes.
- Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: Every whole number greater than 1 can be expressed uniquely as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order of the factors). This is the cornerstone of prime factorization.
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, equal a given number. It's like breaking down a number into its fundamental building blocks. For example, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3). This means that 2 and 3 are the only prime numbers that, when multiplied, result in 12.
Uniqueness of Prime Factorization: The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic guarantees that every number has only one unique prime factorization. This uniqueness is crucial in many mathematical applications.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 30
Now, let's address the question directly: What's the prime factorization of 30? We can use several methods:
Method 1: Factor Tree:
A factor tree is a visual method to break down a number into its prime factors.
30
/ \
2 15
/ \
3 5
Following the branches, we get 2 x 3 x 5. Therefore, the prime factorization of 30 is 2 x 3 x 5.
Method 2: Repeated Division:
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly until you reach 1.
- 30 divided by 2 is 15.
- 15 divided by 3 is 5.
- 5 divided by 5 is 1.
The prime factors are 2, 3, and 5. So, the prime factorization of 30 is 2 x 3 x 5.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple act of finding the prime factorization of a number has profound implications across various fields:
1. Cryptography:
Prime factorization is the cornerstone of many modern encryption techniques, such as RSA cryptography. RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components. The security of these systems hinges on the computational infeasibility of factoring extremely large semiprime numbers (numbers that are the product of two large prime numbers).
2. Number Theory Research:
Prime numbers and their distribution are central to ongoing research in number theory. Unraveling the mysteries of primes leads to deeper understanding of fundamental mathematical structures. Conjectures like the Riemann Hypothesis, which deals with the distribution of prime numbers, remain among the most significant unsolved problems in mathematics.
3. Computer Science:
Prime factorization algorithms are used in various computer science applications, including:
- Hashing: Prime numbers are often used in hashing algorithms to minimize collisions and improve efficiency.
- Data Structures: Certain data structures, such as hash tables, utilize prime numbers for optimal performance.
- Algorithm Design: Prime numbers play a role in designing and analyzing algorithms.
4. Modular Arithmetic:
Prime numbers have special properties within modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus). This has applications in cryptography and computer science.
Beyond 30: Exploring Larger Numbers
While finding the prime factorization of 30 is straightforward, factoring larger numbers becomes significantly more complex. For very large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are needed. These algorithms, often based on probabilistic methods, provide a high probability of finding the prime factors but do not guarantee a solution in polynomial time. The challenge of efficiently factoring large numbers is what secures many modern cryptographic systems.
Practical Applications and Examples
The applications of prime factorization extend beyond theoretical mathematics. Consider these examples:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Prime factorization helps in simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For instance, simplifying 30/42 requires finding the prime factorization of both 30 (2 x 3 x 5) and 42 (2 x 3 x 7). Common factors can then be canceled to obtain the simplified fraction 5/7.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM) and Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): Prime factorization is crucial in efficiently calculating the LCM and GCD of two or more numbers. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers, and the GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a vital role in error-correcting codes, which are essential in data transmission and storage to ensure data integrity.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple task of finding the prime factorization of 30 offers a window into a rich and complex field of mathematics. While the factorization of 30 (2 x 3 x 5) is easily obtained, the broader implications of prime factorization are vast and far-reaching. Its importance in cryptography, number theory, and computer science highlights its enduring significance in our technological world. As we continue to explore the properties of prime numbers, our understanding of mathematics and its applications will undoubtedly continue to evolve. The quest to understand primes is a journey that has captivated mathematicians for centuries and continues to drive innovation in diverse fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is The Sum Of Two Rational Numbers Always Rational
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Are All The Factors Of 75
Mar 18, 2025
-
Is A Colloid Homogeneous Or Heterogeneous
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Cell Stores Food And Water
Mar 18, 2025
-
Function Of The Base On A Microscope
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Prime Factorization Of 30 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
