What's The Prime Factorization Of 27
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
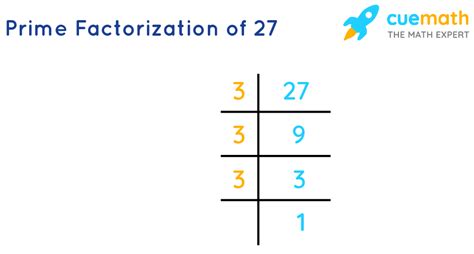
Table of Contents
What's the Prime Factorization of 27? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What's the prime factorization of 27?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, exploring the concept behind it reveals fundamental principles crucial to understanding mathematics and computer science. This article will not only answer the question but delve into the broader context of prime factorization, its applications, and its importance in various fields.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the prime factorization of 27, let's establish a solid understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In simpler terms, a prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite. This seemingly simple definition has profound implications in mathematics.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
A cornerstone of number theory is the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This uniqueness is crucial; it means there's only one way to express a number as a product of primes. This theorem underpins much of our understanding of number systems and provides a framework for various mathematical operations.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 27
Now, let's address the central question: what is the prime factorization of 27? We can approach this using a method called prime factorization, which involves repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factor until we are left with 1.
-
Start with the number 27. We need to find the smallest prime number that divides 27 evenly.
-
Divide by the smallest prime factor. The smallest prime number is 2. However, 27 is not divisible by 2. The next prime number is 3, and 27 is divisible by 3. 27 divided by 3 is 9.
-
Continue the process. Now we have 9. Again, the smallest prime factor of 9 is 3. 9 divided by 3 is 3.
-
Final step. We are left with 3, which is itself a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 27 is 3 x 3 x 3, which can also be written as 3³.
Beyond 27: Exploring Prime Factorization Techniques
The method used for 27 can be applied to any positive integer. Let's explore some additional techniques for finding prime factorizations:
The Factor Tree Method
This visual method is particularly helpful for smaller numbers. You start with the number and branch out, dividing by prime factors until you reach only prime numbers at the end of each branch. For 27, the factor tree would look like this:
27
/ \
3 9
/ \
3 3
The prime factors at the end of the branches (3, 3, 3) represent the prime factorization.
The Division Method
This method involves systematically dividing the number by prime numbers, starting from the smallest. You keep dividing until the result is 1. Let's illustrate with the number 120:
- 120 ÷ 2 = 60
- 60 ÷ 2 = 30
- 30 ÷ 2 = 15
- 15 ÷ 3 = 5
- 5 ÷ 5 = 1
Therefore, the prime factorization of 120 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 5, or 2³ x 3 x 5.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly abstract concept of prime factorization has surprisingly practical applications across diverse fields:
Cryptography
Prime factorization forms the bedrock of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components is what makes these systems secure. RSA encryption, widely used for secure online transactions, relies heavily on this principle. The larger the prime numbers used, the more computationally intensive it becomes to break the encryption.
Computer Science
Prime numbers play a significant role in various computer science algorithms, including hashing functions, random number generation, and data structure optimization. Understanding prime factorization contributes to efficient and secure software development.
Number Theory Research
Prime factorization is a central theme in ongoing research in number theory. Questions about the distribution of prime numbers, the existence of extremely large primes, and the efficiency of factorization algorithms continue to drive mathematical inquiry. The Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics, is directly related to the distribution of prime numbers.
The Significance of Unique Prime Factorization
The uniqueness of prime factorization, guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, has significant consequences. It means that every integer greater than 1 has a unique "fingerprint" represented by its prime factorization. This uniqueness allows for various mathematical operations and comparisons to be performed in a consistent and predictable manner.
Further Exploration: Advanced Concepts
For those interested in delving deeper, the following concepts are related to prime factorization and offer further exploration:
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The largest number that divides two or more integers without leaving a remainder. Prime factorization can be used efficiently to calculate the GCD.
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): The smallest number that is a multiple of two or more integers. Prime factorization also provides an efficient method for calculating the LCM.
- Modular Arithmetic: A system of arithmetic for integers where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus). Prime numbers play a critical role in modular arithmetic, particularly in cryptography.
- Sieve of Eratosthenes: An ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple question of the prime factorization of 27 has led us on a journey through the fascinating world of prime numbers and their applications. From the fundamental theorem of arithmetic to its crucial role in modern cryptography and computer science, the concept of prime factorization remains a cornerstone of mathematics and its practical applications. Understanding this fundamental concept provides a valuable foundation for further exploration in mathematics and related fields. The seemingly simple answer – 3³ – unlocks a universe of mathematical depth and practical significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of A Tissue
Mar 17, 2025
-
Balanced Equation Of Sodium Carbonate And Hydrochloric Acid
Mar 17, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 2 3 And 6
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Sides Of A Parallelogram
Mar 17, 2025
-
Scalene Triangle In Real Life Examples
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Prime Factorization Of 27 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
