What's The Greatest Common Factor Of 8 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
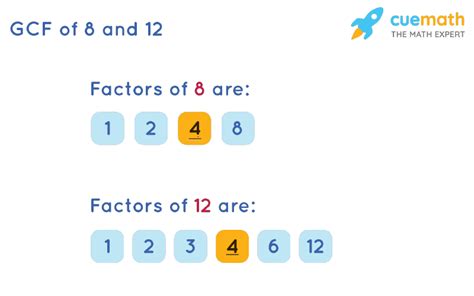
Table of Contents
What's the Greatest Common Factor of 8 and 12? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic problem. However, understanding the concept deeply unlocks a world of mathematical applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex algebraic equations. This article will explore the GCF of 8 and 12, examining various methods to determine it, and then delve into the broader implications of GCFs in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Greatest Common Factors
Before we tackle the specific case of 8 and 12, let's solidify our understanding of GCFs. The GCF of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that goes evenly into both numbers.
Key Concepts:
- Factors: Factors are numbers that divide evenly into a given number. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
- Common Factors: Common factors are numbers that are factors of two or more numbers. For example, the common factors of 8 and 12 are 1, 2, and 4.
- Greatest Common Factor (GCF): The GCF is the largest of the common factors.
Finding the GCF of 8 and 12: Different Approaches
There are several ways to find the GCF of 8 and 12. Let's explore three common methods:
1. Listing Factors
This is a straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list all the factors of each number and then identify the largest common factor.
Factors of 8: 1, 2, 4, 8 Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Comparing the two lists, we see that the common factors are 1, 2, and 4. The greatest of these is 4. Therefore, the GCF of 8 and 12 is 4.
2. Prime Factorization
This method involves breaking down each number into its prime factors. The GCF is then found by multiplying the common prime factors raised to their lowest powers.
Prime factorization of 8: 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³ Prime factorization of 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
The common prime factor is 2. The lowest power of 2 present in both factorizations is 2². Therefore, the GCF is 2² = 4.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCF of two numbers, especially for larger numbers. It involves repeatedly applying the division algorithm until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCF.
- Divide the larger number (12) by the smaller number (8): 12 ÷ 8 = 1 with a remainder of 4.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (8) and the smaller number with the remainder (4): 8 ÷ 4 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
- Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the last non-zero remainder, which is 4.
Applications of GCFs: Beyond Simple Arithmetic
While finding the GCF of 8 and 12 might seem like a basic exercise, the concept of GCFs has far-reaching applications in various areas of mathematics and beyond:
1. Simplifying Fractions
GCFs are crucial for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. To simplify a fraction, we divide both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF. For example, consider the fraction 12/8. Since the GCF of 12 and 8 is 4, we can simplify the fraction as follows:
12/8 = (12 ÷ 4) / (8 ÷ 4) = 3/2
2. Solving Equations
GCFs play a role in solving certain types of equations, particularly those involving modular arithmetic and Diophantine equations. These equations often require finding the GCF to determine the existence and nature of solutions.
3. Geometry and Measurement
GCFs are useful in solving geometric problems involving area, perimeter, and volume. For example, finding the largest square tile that can perfectly cover a rectangular floor involves finding the GCF of the length and width of the floor.
4. Cryptography
The concept of GCF, and more specifically the Euclidean Algorithm used to find it, underpins several cryptographic algorithms. These algorithms are crucial for secure communication and data protection. The efficiency of the Euclidean Algorithm in finding the greatest common divisor is essential for the performance of these cryptographic systems.
5. Computer Science
GCFs and the Euclidean algorithm are fundamental concepts in computer science, used in various algorithms and data structures. Efficient GCF computation is crucial for the optimization of numerous computational tasks.
Extending the Concept: GCFs of More Than Two Numbers
The concept of GCF extends beyond two numbers. We can find the GCF of three or more numbers by applying the same methods. For example, to find the GCF of 8, 12, and 16:
Method 1: Listing Factors:
- Factors of 8: 1, 2, 4, 8
- Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
- Factors of 16: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16
The common factors are 1, 2, and 4. The GCF is 4.
Method 2: Prime Factorization:
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 16: 2⁴
The common prime factor is 2. The lowest power of 2 is 2². Therefore, the GCF is 2² = 4.
Method 3: Iterative Euclidean Algorithm:
While the Euclidean Algorithm is primarily designed for two numbers, it can be extended to multiple numbers by iteratively finding the GCF of pairs of numbers.
- Find the GCF of 8 and 12 (which is 4).
- Find the GCF of 4 and 16 (which is 4). Therefore, the GCF of 8, 12, and 16 is 4.
Conclusion: The Significance of GCFs
The seemingly simple problem of finding the greatest common factor of 8 and 12 opens the door to a deeper understanding of number theory and its wide-ranging applications. From simplifying fractions to advanced cryptographic algorithms, the GCF plays a crucial role in various mathematical and computational processes. Mastering the techniques for finding GCFs is not just about solving basic arithmetic problems; it's about building a foundational understanding of mathematical concepts that underpin many aspects of our technological world. The ability to efficiently calculate GCFs, particularly using methods like the Euclidean Algorithm, is a valuable skill with far-reaching implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Vertical Column In The Periodic Table Called
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Communicable Disease And Non Communicable Disease
May 09, 2025
-
The Energy Required To Start A Chemical Reaction Is Called
May 09, 2025
-
Which Part Of The Clavicle Articulates With The Manubrium
May 09, 2025
-
How To Calculate Rf Value Of Chromatography
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Greatest Common Factor Of 8 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.