What Turns Blue Litmus Paper Red
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
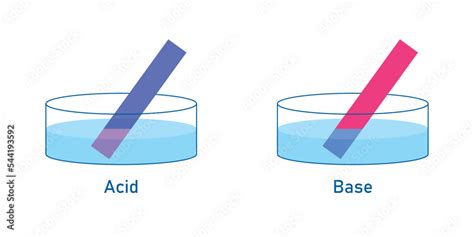
Table of Contents
What Turns Blue Litmus Paper Red? A Deep Dive into Acids and pH
Blue litmus paper is a simple yet powerful tool used to identify the presence of acids. Its color change from blue to red provides a visual indication of acidity, a fundamental concept in chemistry with far-reaching implications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will delve into the science behind this color change, explore different types of acids, and discuss the practical applications of litmus paper.
Understanding pH and the Acid-Base Scale
Before we delve into the specifics of litmus paper, let's establish a solid foundation in understanding pH and the acid-base scale. The pH scale is a logarithmic scale ranging from 0 to 14, measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in a solution. A lower pH value indicates a higher concentration of H⁺ ions, signifying a stronger acid. Conversely, a higher pH value indicates a lower concentration of H⁺ ions, signifying a stronger base (alkaline substance).
- pH 0-6: Acidic solutions. The lower the number, the stronger the acid.
- pH 7: Neutral solution (pure water).
- pH 8-14: Alkaline (basic) solutions. The higher the number, the stronger the base.
The pH scale is crucial in numerous applications, from agriculture and environmental monitoring to medicine and industrial processes. Understanding the pH of a substance is essential for maintaining optimal conditions in various systems.
The Role of Hydrogen Ions (H⁺)
The key to understanding why blue litmus paper turns red lies in the behavior of hydrogen ions. Acids are substances that donate or release hydrogen ions (protons) when dissolved in water. These H⁺ ions are responsible for the acidic properties of a solution. When a substance releases H⁺ ions, it increases the concentration of these ions in the solution, thus lowering the pH.
The Science Behind the Color Change: Litmus Paper and its Composition
Litmus paper is made from a mixture of natural dyes extracted from lichens. These dyes are weak organic acids and bases that change color depending on the pH of the solution they are exposed to. Blue litmus paper contains a dye in its basic (alkaline) form. When it encounters an acidic substance, the H⁺ ions from the acid react with the dye molecules, altering their structure and causing a change in color from blue to red.
This color change is a reversible process. If you were to add a base to the now-red litmus paper, it would revert back to its original blue color, as the base would neutralize the acid and reduce the concentration of H⁺ ions.
Specific Chemical Interactions: A Deeper Look
The exact chemical reactions involved in the color change of litmus are complex and depend on the specific structure of the dye molecules. However, the general principle remains the same: the presence of H⁺ ions leads to a structural change in the dye molecules, resulting in a change in color absorption and thus a visible color shift. This is a classic example of an acid-base indicator, a substance whose color changes depending on the pH of the solution.
Different Types of Acids That Turn Blue Litmus Paper Red
Numerous substances can turn blue litmus paper red, ranging from common household items to strong industrial chemicals. The strength of the acid dictates how quickly and intensely the color change will occur. Here are a few examples:
1. Strong Acids: Rapid and Dramatic Color Change
Strong acids, such as sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), hydrochloric acid (HCl), and nitric acid (HNO₃), readily donate H⁺ ions, causing a swift and intense color change in blue litmus paper. These acids are highly corrosive and should be handled with extreme caution in a properly equipped laboratory setting.
2. Weak Acids: Gradual Color Change
Weak acids, such as acetic acid (CH₃COOH) found in vinegar and citric acid (C₆H₈O₇) found in citrus fruits, also turn blue litmus paper red, but the change is usually less dramatic and occurs more gradually. This is because they only partially dissociate in water, releasing fewer H⁺ ions compared to strong acids.
3. Organic Acids: Naturally Occurring Acids
Many organic acids, such as lactic acid (found in milk and yogurt), formic acid (found in ant stings), and ascorbic acid (vitamin C), are weak acids that will also turn blue litmus paper red. These acids play various roles in biological processes and food preservation.
Practical Applications of Litmus Paper
The simple yet effective nature of litmus paper makes it a valuable tool in various settings:
-
Chemistry Laboratories: Litmus paper is a fundamental tool in chemistry labs for identifying acids and bases, especially in qualitative analysis. It's a quick and easy way to get a preliminary indication of a solution's pH.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Testing the pH of soil and water samples is crucial for environmental monitoring. Litmus paper can be used for a rapid, preliminary assessment of acidity or alkalinity levels, which are vital indicators of environmental health.
-
Food and Beverage Industry: Controlling pH is essential in food processing and preservation. Litmus paper can provide a quick check of the acidity levels in various products during production.
-
Medicine: While not a primary diagnostic tool, litmus paper can be used in some clinical settings to test the pH of body fluids such as urine, providing a preliminary indicator of potential metabolic issues. However, more precise methods are generally used for accurate diagnoses.
Safety Precautions When Using Litmus Paper
While generally safe, handling acids and using litmus paper requires some precautions:
- Always wear appropriate safety glasses: This protects your eyes from potential splashes of chemicals.
- Handle acids with care: Strong acids are corrosive and can cause skin burns. Always wear gloves and avoid direct contact.
- Proper disposal: Dispose of used litmus paper and acid solutions according to local regulations to minimize environmental impact.
- Never taste or ingest chemicals: This is crucial for safety and avoiding serious health consequences.
Beyond Litmus Paper: Other pH Indicators
While litmus paper provides a basic indication of pH, other more precise indicators exist. These include universal indicator solutions, which provide a wider range of color changes across the entire pH scale, and electronic pH meters, which offer highly accurate and quantitative measurements.
Universal Indicator: A Broader pH Spectrum
Universal indicator solutions provide a more nuanced pH assessment than litmus paper. They exhibit a spectrum of colors across the pH scale, providing a more precise estimation of the pH value. This is advantageous when a more specific pH range is required.
Electronic pH Meters: Precision Measurement
Electronic pH meters offer the most accurate and quantitative pH measurements. These devices use a sensitive electrode to measure the hydrogen ion concentration, providing numerical values for the pH. They are commonly used in research, industrial settings, and applications demanding highly precise pH measurements.
Conclusion: The Significance of Acid-Base Chemistry
The seemingly simple color change of blue litmus paper turning red upon contact with an acid underscores the fundamental importance of acid-base chemistry. This chemical reaction, readily observable through a readily available and inexpensive tool, opens a window into a vast world of scientific principles and practical applications. From environmental monitoring and industrial processes to biological systems and everyday household items, the understanding and measurement of pH are critical for countless aspects of modern life. While litmus paper offers a quick and qualitative assessment of acidity, a combination of knowledge, careful experimentation, and appropriate safety measures ensures accurate and safe exploration of this crucial area of chemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Time Of Maximum Daily Temperature Occurs
May 09, 2025
-
Matter Includes All Of The Following Except
May 09, 2025
-
What Is Found In Both Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells
May 09, 2025
-
What Happens To Air As It Is Heated
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Is 8 Millimeters
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Turns Blue Litmus Paper Red . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.