What Kingdom Is A Human In
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
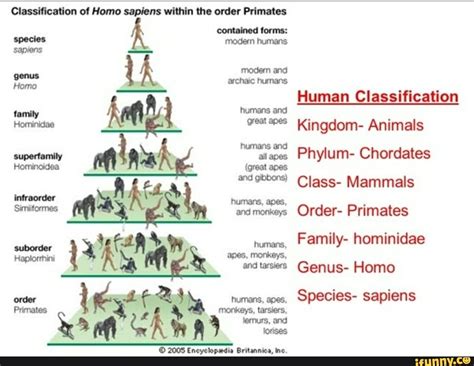
Table of Contents
What Kingdom is a Human In? Exploring the Taxonomic Classification of Homo Sapiens
Humans, with our complex societies, advanced technology, and self-awareness, often consider ourselves separate and superior to the rest of the living world. Yet, scientifically speaking, we are firmly rooted within the grand tapestry of life, occupying a specific and significant place within its hierarchical classification system. So, what kingdom is a human in? The answer, simply put, is Animalia. But understanding this seemingly straightforward answer requires delving into the fascinating world of taxonomy and the characteristics that define each level of biological classification.
Understanding the Linnaean System of Classification
Our understanding of the relationships between different organisms stems largely from the work of Carl Linnaeus, an 18th-century Swedish botanist. He developed a hierarchical system of classification, known as the Linnaean system, which organizes life into a series of nested groups, from broad categories to increasingly specific ones. This system uses a series of ranks, the most inclusive being the Kingdom, followed by Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and finally, Species. Each level represents a shared set of characteristics, tracing the evolutionary relationships between organisms.
The Importance of Kingdoms
Kingdoms represent the highest level of classification, grouping organisms based on fundamental characteristics such as cell structure, mode of nutrition, and evolutionary history. While the precise number and definition of kingdoms have evolved over time with advances in scientific understanding (initially just two, Plant and Animal kingdoms, are now widely expanded to include various others, reflecting the diversity of life), the core principle remains the same: grouping organisms with fundamental similarities.
Why Humans Belong to Kingdom Animalia
Humans are unequivocally classified under the Kingdom Animalia because we possess several key characteristics that define animals:
-
Eukaryotic Cells: Animal cells, including human cells, possess a membrane-bound nucleus containing their genetic material (DNA) and other membrane-bound organelles. This contrasts with prokaryotic cells found in bacteria and archaea, which lack a nucleus.
-
Multicellular Organisms: Humans are complex, multicellular organisms composed of trillions of cells specialized for various functions. These cells work together in a coordinated manner to maintain the organism's life processes.
-
Heterotrophic Nutrition: Humans, unlike plants, are heterotrophs, meaning we cannot produce our own food. We obtain energy and nutrients by consuming other organisms – plants, animals, or fungi. This mode of nutrition is a defining feature of most animals.
-
Motility: While not always evident in all life stages, animals typically exhibit motility at some point in their life cycle. Humans are certainly capable of movement, whether by walking, running, or other forms of locomotion.
-
Specialized Tissues and Organs: Animal bodies are organized into specialized tissues and organs that perform specific functions. From the nervous system coordinating our actions to the digestive system breaking down food, our bodies are marvels of complex organization, a hallmark of Animalia.
-
Sexual Reproduction: While some animals exhibit asexual reproduction, the majority, including humans, reproduce sexually, involving the fusion of gametes (sperm and egg) to produce offspring with a unique genetic combination.
Deeper Dive into Human Classification: Beyond Kingdom Animalia
Classifying humans as members of Animalia is only the beginning. To fully understand our place in the biological world, we need to examine the lower ranks of the Linnaean system:
-
Phylum Chordata: This phylum encompasses animals with a notochord (a flexible rod providing support) at some stage in their development. Humans, along with other vertebrates, possess a vertebral column (backbone) which replaces the notochord during embryonic development.
-
Class Mammalia: Mammals are characterized by several defining features: hair or fur, mammary glands that produce milk to nourish their young, three middle ear bones, and a neocortex (a region of the brain responsible for higher-level cognitive functions). Humans clearly fit within this class.
-
Order Primates: Primates are a diverse group of mammals characterized by features such as five-fingered hands, five-toed feet, relatively large brains, and forward-facing eyes providing excellent depth perception. Our grasping ability, dexterity, and advanced cognitive functions place us firmly within the primate order.
-
Family Hominidae: This family includes great apes, such as chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans, and humans. We share a common ancestor with these great apes, exhibiting similar anatomical characteristics and some behavioral traits.
-
Genus Homo: The genus Homo comprises extinct and extant humans, characterized by bipedalism (walking upright on two legs), large brain size relative to body size, and the capacity for advanced tool use and complex social structures.
-
Species Homo sapiens: This is the species to which modern humans belong, characterized by our unique combination of physical and cognitive abilities, including advanced language skills, abstract thought, and complex culture.
The Evolutionary Context of Human Classification
Understanding our place in the Kingdom Animalia and beyond isn’t just about memorizing a taxonomic hierarchy. It's about appreciating the evolutionary journey that led to the emergence of Homo sapiens. Our classification reflects our evolutionary history, showing our relationships to other organisms. The similarities we share with other animals, particularly primates, underscore our shared ancestry and highlight the interconnectedness of all life. The unique features that define our species, however, showcase the extraordinary evolutionary trajectory that has made us what we are today.
The Ongoing Evolution of Taxonomic Classification
It's important to remember that the Linnaean system, while a cornerstone of biological classification, is not static. As our understanding of evolutionary relationships deepens through advancements in genetic analysis and other fields of study, the taxonomic classification of organisms continues to evolve. New data may lead to adjustments in existing classifications, or even the creation of entirely new taxonomic levels. This dynamic nature of classification reflects the ever-evolving nature of scientific knowledge and our ongoing quest to understand the intricate web of life on Earth.
Beyond Classification: The Significance of Human Place in the Ecosystem
While accurate classification within the animal kingdom is crucial for scientific understanding, it's equally important to recognize the broader ecological context of human existence. We are not just another animal; our actions have profound impacts on the planet and its biodiversity. Understanding our place in the intricate web of life underscores the responsibility we have as stewards of the environment, prompting us to act sustainably and ethically to ensure the health of the planet and the well-being of all living things.
Conclusion: Humans – A Unique Branch in the Tree of Life
The answer to "What kingdom is a human in?" is decisively Animalia. However, this seemingly simple answer opens the door to a wealth of knowledge about our evolutionary history, biological characteristics, and our place within the vast and interconnected tapestry of life on Earth. Our classification highlights both our connections to other organisms and the unique adaptations that distinguish us. By understanding our position within the biological hierarchy, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable diversity of life and our role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems across the globe. Our species' journey – from a humble ancestor within the Animal Kingdom to the complex, culturally rich society we have today – is a testament to the power of evolution and a challenge for us to utilize our advanced abilities responsibly.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
15 5 2b Equivalent Expression Worksheet
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Are Biotic Factors And Abiotic Factors
Mar 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Planets Has No Moon
Mar 04, 2025
-
The Swim Bladder Of Bony Fishes Functions In
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is 3 5 As A Percentage
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Kingdom Is A Human In . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
