What Is The Third Root Of 27
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
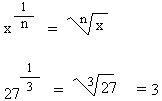
Table of Contents
What is the Third Root of 27? A Deep Dive into Cube Roots and Their Applications
The question, "What is the third root of 27?" seems deceptively simple. The answer, 3, is readily apparent to anyone familiar with basic arithmetic. However, a deeper exploration of this seemingly straightforward mathematical concept reveals a wealth of fascinating connections to algebra, geometry, and various applications across numerous scientific fields. This article will delve into the intricacies of cube roots, exploring their definition, properties, calculation methods, and their significance in various contexts.
Understanding Cube Roots: Beyond the Basics
The third root of a number, denoted as ³√x, is a value that, when multiplied by itself three times, equals x. In simpler terms, it's the inverse operation of cubing a number. For instance, since 3 x 3 x 3 = 27, the third root (or cube root) of 27 is 3. This relationship can be formally expressed as:
³√27 = 3
This seemingly simple equation opens the door to a world of mathematical possibilities. Let's examine some key aspects of cube roots:
Properties of Cube Roots
Cube roots possess several important properties that are essential for understanding their behavior and applications:
-
The cube root of a positive number is always positive. This is unlike square roots, where both positive and negative solutions exist. For example, ³√64 = 4, and there is no negative solution.
-
The cube root of a negative number is always negative. This is a crucial distinction from square roots, which are undefined for negative numbers in the realm of real numbers. For instance, ³√-8 = -2.
-
The cube root of zero is zero. This is intuitive and consistent with the general behavior of roots. ³√0 = 0.
-
The cube root of a product is the product of the cube roots. This property states that ³√(a x b) = ³√a x ³√b. For example, ³√(8 x 27) = ³√8 x ³√27 = 2 x 3 = 6.
-
The cube root of a quotient is the quotient of the cube roots. This property states that ³√(a / b) = ³√a / ³√b. For example, ³√(64 / 8) = ³√64 / ³√8 = 4 / 2 = 2.
These properties form the foundation for various mathematical manipulations involving cube roots, enabling us to simplify complex expressions and solve equations efficiently.
Calculating Cube Roots: Methods and Techniques
While the cube root of 27 is easily determined through basic knowledge of multiplication, calculating cube roots for larger numbers requires more advanced techniques. Here are some common methods:
1. Prime Factorization
This method is particularly useful for numbers that have easily identifiable prime factors. Let's find the cube root of 216:
- Find the prime factorization: 216 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 2³ x 3³
- Group the factors in threes: We have three 2s and three 3s.
- Take the cube root: ³√(2³ x 3³) = 2 x 3 = 6
Therefore, the cube root of 216 is 6.
2. Estimation and Iteration
For numbers without easily identifiable prime factors, estimation and iterative methods become necessary. One such method involves making an initial guess and refining it through successive approximations. For example, let's find the cube root of 125:
- Make an initial guess: Let's guess 5.
- Cube the guess: 5³ = 125. Our guess was correct!
- Refine the guess (if necessary): If our initial guess was incorrect, we would adjust it based on whether the cube of our guess was greater or less than the target number and repeat steps 2 and 3 until we reach an acceptable level of accuracy. Newton-Raphson method is a more sophisticated iterative approach for higher accuracy.
3. Using Calculators and Software
Modern calculators and mathematical software packages readily provide cube root functions. These tools significantly simplify the calculation process, especially for complex numbers.
Applications of Cube Roots in Real-World Scenarios
Cube roots, while seemingly abstract, find practical applications across various disciplines:
1. Geometry and Volume Calculations
Perhaps the most direct application of cube roots is in calculating the side length of a cube given its volume. If a cube has a volume of V, then the length of its side (s) is given by:
s = ³√V
For example, if a cube has a volume of 64 cubic centimeters, its side length is ³√64 = 4 centimeters. This principle extends to other three-dimensional shapes where volume calculations involve cubic relationships.
2. Physics and Engineering
Cube roots appear in various physics and engineering formulas. For example, the relationship between the period of a simple pendulum and its length involves a cube root. In fluid mechanics, the calculation of certain flow rates might utilize cube roots.
3. Statistics and Data Analysis
Cube roots are sometimes used in statistical analysis to stabilize the variance of skewed data or to transform data for better modeling. Specific applications may involve analyzing datasets related to population growth, economic indicators, or environmental data.
4. Chemistry and Material Science
Cube roots can be relevant in calculating the atomic radii or analyzing crystal structures in material science. Chemical kinetics might also involve the application of cube roots in certain rate equations.
5. Finance and Investment
While less direct than in other fields, cube roots might find niche applications in financial modeling or analyzing the growth rate of investments under specific compounding scenarios.
Expanding the Concept: Complex Numbers and Beyond
Our discussion so far has focused on the real cube roots of real numbers. However, the concept of cube roots extends to the realm of complex numbers. Every non-zero complex number has three distinct cube roots. Understanding these complex cube roots requires a deeper understanding of complex number arithmetic and their representation in the complex plane. This involves using De Moivre's Theorem and polar coordinates to solve cubic equations that may not have real solutions.
Conclusion: The Significance of a Simple Question
The seemingly simple question, "What is the third root of 27?" serves as a gateway to a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and their diverse applications. From fundamental algebraic properties to advanced calculations using complex numbers, cube roots demonstrate the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas and their relevance to a wide array of fields. The ability to understand, calculate, and apply cube roots is a valuable skill in mathematics, science, and engineering, underscoring the importance of exploring even the most basic mathematical concepts in depth. Further exploration into the fascinating world of cube roots can lead to a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Difference Between A Purine And A Pyrimidine
May 09, 2025
-
What Are The Basic Units Of Living Matter
May 09, 2025
-
Give The Iupac Names For The Following Compounds
May 09, 2025
-
How Big Is 6 Inches In Cm
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 85 Inches
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Third Root Of 27 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.