What Is The Square Root Of 30
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
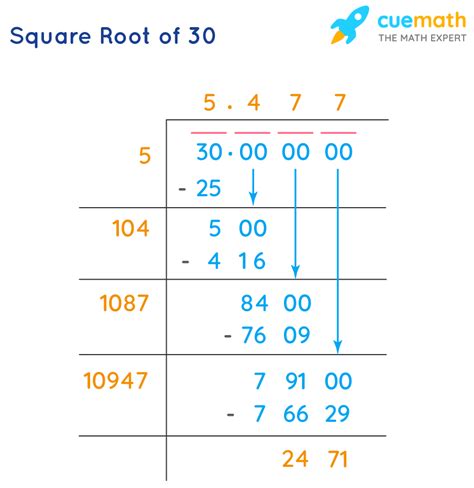
Table of Contents
What is the Square Root of 30? A Deep Dive into Irrational Numbers
The seemingly simple question, "What is the square root of 30?" opens a door to a fascinating world of mathematics, specifically the realm of irrational numbers. While a quick calculator search will give you an approximate decimal value, understanding why it's an irrational number and exploring its properties provides a richer appreciation for the beauty and complexity of mathematics.
Understanding Square Roots
Before delving into the specifics of the square root of 30, let's establish a foundational understanding of square roots. The square root of a number (x) is a value (y) that, when multiplied by itself, equals x. Mathematically, this is represented as:
√x = y where y * y = x
For example:
- √9 = 3 because 3 * 3 = 9
- √16 = 4 because 4 * 4 = 16
- √25 = 5 because 5 * 5 = 25
These are examples of perfect squares – numbers that have whole number square roots. However, not all numbers are perfect squares. This is where the concept of irrational numbers comes into play.
Introducing Irrational Numbers: The Case of √30
The square root of 30 is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction (a ratio of two integers). Its decimal representation is non-terminating (it doesn't end) and non-repeating (it doesn't have a repeating pattern). This is in contrast to rational numbers, which can be expressed as fractions (e.g., 1/2, 3/4, 7/5).
Why is √30 Irrational?
The proof that √30 is irrational is based on a method of proof by contradiction, a common technique in mathematics. We start by assuming the opposite of what we want to prove (that √30 is rational) and then show that this assumption leads to a logical contradiction.
Let's assume: √30 is rational. This means it can be expressed as a fraction a/b, where 'a' and 'b' are integers, 'b' is not zero, and the fraction is in its simplest form (meaning 'a' and 'b' have no common factors other than 1).
If √30 = a/b, then squaring both sides gives:
30 = a²/b²
Rearranging the equation, we get:
30b² = a²
This equation tells us that a² is a multiple of 30. Since 30 = 2 x 3 x 5, this means a² must contain the prime factors 2, 3, and 5. Therefore, 'a' itself must also contain the prime factors 2, 3, and 5. We can express 'a' as:
a = 2m * 3n * 5o * k (where m, n, o are integers ≥1 and k is any other integer)
Substituting this into the equation 30b² = a², we get:
30b² = (2m * 3n * 5o * k)²
This simplifies to show that b² also contains the prime factors 2, 3, and 5. Consequently, 'b' must also contain these factors.
This is our contradiction! We initially assumed that a/b was in its simplest form (no common factors). However, we've shown that both 'a' and 'b' share the common factors 2, 3, and 5. This contradiction proves our initial assumption (that √30 is rational) is false. Therefore, √30 must be irrational.
Approximating √30: Methods and Techniques
While we cannot express √30 as a precise fraction or terminating decimal, we can find increasingly accurate approximations. Several methods exist:
1. Using a Calculator: The Quickest Method
The simplest way to find an approximate value is to use a calculator. Most calculators will provide a decimal approximation, typically to several decimal places. You will find that √30 is approximately 5.477225575.
2. The Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method): An Iterative Approach
The Babylonian method is an iterative algorithm that refines an initial guess to obtain a more accurate approximation of a square root. The formula is:
x_(n+1) = 0.5 * (x_n + S/x_n)
Where:
- x_n is the current approximation
- x_(n+1) is the next approximation
- S is the number whose square root you're seeking (in our case, 30)
Let's demonstrate with an initial guess of 5:
- x_1 = 5
- x_2 = 0.5 * (5 + 30/5) = 5.5
- x_3 = 0.5 * (5.5 + 30/5.5) ≈ 5.477
- x_4 = 0.5 * (5.477 + 30/5.477) ≈ 5.477225
Each iteration brings us closer to the actual value.
3. Linear Approximation: A Simpler Approach
Linear approximation uses the slope of the tangent line to a curve to estimate the value of a function near a known point. While less precise than the Babylonian method, it's simpler to understand.
The Significance of Irrational Numbers
The existence of irrational numbers like √30 highlights the richness and complexity of the number system. While seemingly abstract, irrational numbers have significant practical applications:
-
Geometry: Irrational numbers frequently appear in geometrical calculations, such as the diagonal of a square (involving √2) or the circumference of a circle (involving π). The calculations related to the area of shapes with sides of a particular length often also result in irrational numbers.
-
Physics: Many physical phenomena are described using equations involving irrational numbers. For example, calculations in wave motion and oscillations frequently lead to such values.
-
Engineering: The design and construction of various structures often utilize calculations involving irrational numbers, leading to greater precision and efficiency.
-
Computer Science: The processing of irrational numbers is crucial in various computer algorithms and simulations.
Conclusion: Beyond the Decimal
The question "What is the square root of 30?" leads us beyond a simple numerical answer. It unveils the fascinating world of irrational numbers, their properties, and their importance in mathematics and its applications. While we can approximate its value using various methods, its irrational nature emphasizes the infinite and non-repeating nature of the number system, reminding us of the beauty and complexity inherent in seemingly simple mathematical concepts. Understanding irrational numbers provides a deeper appreciation of the foundations of mathematics and its pervasive influence on our world. The exploration of √30 serves as a microcosm of this broader mathematical journey, a journey that continues to unfold with every new equation, every new discovery, and every new question we ask.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Part Of The Seed That Develops Into The Shoot
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Most Abundant Gas In The Atmosphere
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Litres Are In 5 Gallons
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 72 In
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Are The Lcm Of 8 And 12
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Square Root Of 30 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
